Abstract
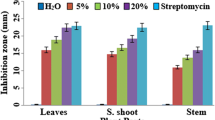
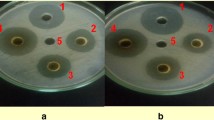
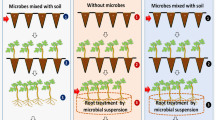
Aqueous extracts and green manures of different parts of Adhatoda vasica, a wild medicinal shrub plant, were tested in vitro and in vivo for the control of bacterial wilt (BW) in tomato. Higher concentration (14%, w/v) of aqueous extracts of leaf, succlent shoot and stem were more effective than the lower concentrations and inhibited the in vitro growth of the pathogen by 94, 89, and 65% respectively, of the growth inhibition produced by streptomycin (200 ppm). Green manure dose of 30 g kg−1 soil strongly suppressed the BW pathogen, reduced disease severity and promoted the yield-contributing plant growth parameters. Green manure of leaves, when applied to soil 4 weeks before the transplantation of tomato seedlings, controlled BW more effectively and significantly increased plant growth parameters as compared to the green manures of other parts of the plant and other application times. It can be clearly concluded from our data that Adhatoda vasica leaves green manure dose of 30 g kg−1 soil (or possibly higher) could be included as an effective and nature-friendly component of the integrated disease management (IDM) against BW and possibly other similar diseases.
Zusammenfassung
Wässrige Extrakte und Gründünger aus verschiedenen Teilen von Adhatoda vasica, einer wilden medizinischen Strauchpflanze, wurden in vitro und in vivo zur Kontrolle der bakteriellen Tomatenwelke getestet. Höhere Konzentrationen (14 %, w/v) von wässrigen Extrakten aus Blättern, Spross und Stiel waren wirksamer als niedrigere Konzentrationen und hemmten das Wachstum des Pathogens in vitro um 94 %, 89 % bzw. 65 % der Wachstumshemmung durch Streptomycin (200 ppm). Die Gründüngerdosis von 30 g/kg Boden unterdrückte den Erreger der Bakterienwelke stark, verringerte den Schweregrad der Erkrankung und förderte die ertragbringenden Pflanzenwachstumsparameter. Die Gründüngung mit Blättern bei Applikation auf den Boden 4 Wochen vor der Verpflanzung der Tomatensämlinge kontrollierte die bakterielle Welke wirksamer und erhöhte die Pflanzenwachstumsparameter signifikant im Vergleich zur Gründüngung mit anderen Pflanzenteilen und zu anderen Anwendungszeiten, Aus unseren Daten lässt sich eindeutig schließen, dass eine Gründüngung mit 30 g Adhatoda-vasica-Blättern/kg Boden (oder möglicherweise höher) als wirksamer und naturverträglicher Bestandteil des integrierten Krankheitsmanagements gegen bakterielle Welke und möglicherweise andere ähnliche Krankheiten aufgenommen werden könnte.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Monaim MF, Abo-Elyousr KAM, Morsy KM (2011) Effectiveness of plant extracts on suppression of damping-off and wilt diseases of lupine (Lupinustermis Forsik). Crop Prot 30:185–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2010.09.016
Arthy JR, Akiew EB, Kirkegaard JA, Trevorrow PR (2005) Using Brassica spp., as bio-fumigants to reduce the population of Ralstonia solanacearum. In: Allen C, Prior P, Haward AC (eds) Bacterial Wilt Disease and Ralstonia solanacearum Species Complex. APS, St. Paul
Aysan Y, Karatas A, Cinar O (2003) Biological control of bacterial stem rot caused by Erwinia chrysanthemi on tomato. Crop Prot 22:807–811. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0261-2194(03)00030-9
Balestra GM, Heydari A, Ceccerelli D, Ovidi E, Quattrucci A (2009) Antibacterial effect of Allium sativum and Ficuscarica extracts on tomato bacterial pathogens. Crop Prot 28:807–811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2009.06.004
Begum N, Haque MI, Mukhtar T, Naqvi SM, Wang JF (2012) Status of bacterial wilt caused by Ralstonia solanacearum in Pakistan. Pak J Phytopathol 24(1):11–20 (http://pakps.com/pjp/files/11-20-irfan-paper.pdf)
Bhatt M, Gahlot M (2011) Phytochemical investigation and antidiabetic activity of Adhatoda zeylanica. Asian J Pharm Clin Res 4(2):27–30 (http://www.ajpcr.com/Vol4Issue2/202.pdf)
Bonanomi G, Antignani V, Pane C, Scala F (2007) Suppression of soilborne fungal disease with organic amendments. J Plant Pathol 89:311–324 (https://www.jstor.org/stable/41998409)
Braddy N, Weil R (1999) Elements of the nature and properties of soil spp. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, p 559 (https://trove.nla.gov.au/version/45005208)
Campbell CL, Madden LV (1990) Introduction to plant disease epidemiology. Wiley, NY (https://www.cabdirect.org/cabdirect/abstract/19912305030)
Cardoso SC, Soares ACF, Brito ADS, Laranjeira FF, Ledo CAS, dos Santos AP (2006) Control of tomato wilt through the incorporation of aerial parts of pigeon pea and crotalaria to soil. Summa Phytopathol 32:27–33. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-54052006000100004
Cavoski I, Chami ZAl, Bouzebboudja F, Sasanelli N, Simeone V, Mondelli D, Miano T, Sarais G, Ntalli NG, Caboni P (2012) Meliaazedarach controls Meloidogyne incognita and triggers plant defense mechanisms on cucumber. Crop Prot 35:85–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2012.01.011
Chanu WS, Sarangthem K (2014) Phytochemical constituents of Justica adhatoda Linn found in Manipur. Indian J Plant Sci 3(2):19–21
Claeson UP, Malmfros T, Wikman G, Bruhn JG (2000) Adhatoda vasica: a critical review of ethnopharmacological and toxicological data. J Ethnopharmacol 72:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-8741(00)00225-7
Din N, Ahmad M, Siddique M, Ali A, Naz I, Ullah N, Ahmad F (2016) Phytobiocidal management of bacterial wilt of tomato caused by Ralstonia solanacearum (Smith) Yabuuchi. Span J Agri Res 14(3):e1006. https://doi.org/10.5424/sjar/2016143-9012
Flores-Moctezuma HE, Montes-Belmont RA, Jimenez-Perez, Nava-Juarez R (2006) Pathogenic diversity of Sclerotium rolfsii isolates from Mexico, and potential control of southern blight through solarization and organic amendments. Crop Prot 25(3):195–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2005.04.007
Frey MF, Meyers R (2010) Antibacterial activity of traditional medicinal plants used by Haudenosaunee peoples of New York State. BMC Complement Altern Med 10:64. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6882-10-64
Gao H, Huang Y, Gao BL, Inagaki C, Kawabata J (2008) Inhibitory effect on alpha glucosidase by Adhatoda vasica Nees. Food Chem 108(3):965–972. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.12.002
Gomez KA, Gomez AA (1984) Statistical procedures for agricultural research. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Govindappa M, Umesha S, Lokesh S (2011) Adhatoda vasica leaf extract induces resistance in rice against bacterial leaf blight disease (Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae). Int J Plant Physiol Biochem 3(1):6–14 (https://academicjournals.org/journal/IJPPB/article-abstract/218B96B9946)
Ji P, Momol MT, Rich JR, Olson SM, Jones JB (2007) Development of an integrated approach for managing bacterial wilt and root-knot on tomato under field conditions. Plant Dis 91:1321–1326. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-91-10-1321
Kagale S, Marimuthu T, Thayumanavan B, Nandakumar R, Sammiyappan R (2004) Antibacterial activity and induction of systemic resistance in rice by leaf extracts of Daturametel against Rhizoctonia solani and Xanthomonas oryzae pv oryzae. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 65:91–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmpp.2004.11.008
Kang MJ, Lee MH, Shim JK, Seo ST, Sherestha R, Cho MS, Hahn JH, Park DS (2007) PCR-based specific detection of Ralstonia solanacearum by amplification of Cytochrome C1 signal peptide sequences. J Microbiol Biotec 17(11):1765–1771 (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18092459)
Kaur I, Chauhan PK, Jaryal M, Saxen S, Kanishak K (2012) Antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of leaf extract of Adhatoda vasica against the bacteria isolated from the sputum samples of asthmatic patients. Int J Drug Res Technol 2(3):273–278
Klein E, Katan J, Austerweil M, Gamleil A (2007) Controlled laboratory system to study soil solarization and organic amendments effect on plant pathogens. Phytopathology 97(11):1476–1483. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-97-11-1476
Klein E, Katan J, Gamleil A (2011) Combining residues of herb crops with soil heating for control of soil borne pathogens in a controlled laboratory system. Crop Prot 30(3):368–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2010.12.005
Kumar S, Choudhary HS, Seniya C (2011) in vitro antibacterial study of aqueous and methanolic extracts of some selected medicinal plants. J Chem Pharm Rese 3:854–860 (http://www.jocpr.com/articles/in vitro-antibacterial-study-of-aqueous-and-methanolic-extracts-of-some-selected-medicinal-plants.pdf)
Latifa A, Idriss T, Hassan B, Amine M, El Hassane SB, Abdellah AB (2011) Effects of organic acids and salts on the development of Penicillium italicum: the causal agent of citrus blue mold. Plant Pathol J 10(3):99–107 (https://scialert.net/abstract/?doi=ppj.2011.99.107)
Lin CH, Tsai KC, Prior P, Wang JF (2014) Phylogenetic relationships and population structure of Ralstonia solanacearum isolated from diverse origins in Taiwan. Plant Pathol 63:1395–1403. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppa.12209
Madden LV, Hughes G, van den Bosch F (2007) The study of plant disease epidemics. APS press, Minnesota
Mahlo SM, Mcgaw LJ, Eloff JN (2010) Antifungal activity of leaf extracts from South African trees against plant pathogens. Crop Prot 29(12):1529–1533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2010.08.015
Naz I, Saifullah, Palomeres-Rius JE, Khan SM, Ali S, Ahmad M, Ali A, Khan A (2015a) Control of southern Root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne incognita (Kofoid and white) Chitwood on tomato using green manure of Fumaria parviflora Lam (Fumariaceae). Crop Prot 67:121–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2014.10.005
Naz I, Saifullah, Palomeres-Rius JE, Block V, Khan SM, Ali S, Baig A (2015b) Sustainable management of the southern Root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne incognita (Kofoid and white) Chitwood, by means of amendments of Fumaria parviflora. Int J Agri Biol 17:289–296 (http://www.fspublishers.org/published_papers/72259_..pdf)
Nico AI, Rafael RM, Jimenez-Diaz M, Castillo P (2004) Control of root-knot nematodes by composted agro-industrial wastes in potting mixtures. Crop Prot 23(7):581–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2003.11.005
Paul PK, Sharma PD (2002) Azadirachna indica leaf extract induces resistance in barley against leaf stripe disease. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 61(1):3–13. https://doi.org/10.1006/pmpp.2002.0412
Porras M, Barrau C, Arroyo FT, Santos B, Blanco C, Romero F (2007) Reduction of Phytopthora cactorum in strawberry fields by Trichoderma spp. and soil solarization. Plant Dis 91(2):142–146. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-91-2-0142
Pradhanang PM, Momol MT, Rich JR, Olson SM, Jones JB (2003) Effect of plant essential oils on Ralstonia solanacearum population density and bacterial wilts incidence in tomato. Plant Dis 87(4):423–427. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS.2003.87.4.423
Qasem JR, Abu-Blan HA (1996) Fungicidal activity of some common weed extracts against different plant pathogenic fungi. J Phytopathol 144(3):157–161. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0434.1996.tb01507.x
Ramesh R, Joshi A, Ghanekar M (2009) Pseudomonands: major antagonistic endophytic bacteria to suppress bacterial wilt pathogen, Ralstonia solanacearum in egg plant (Solanummelongena L.). World J Micrbiol Biotechnol 25:47–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-008-9859-3
Sarada KC, Rao GP (2008) Antimicrobial activity of essential oils of Adhatoda vasica (Basaka) fresh and shade dried leaves and roots from Anantapur District, Andhra Pradesh. Indian J Microb World 10:86-90
Sayeed A, Madhukar G, Maksood A, Mhaveer S, Tanwir MA, Shahid HA (2009) A phytopharmacological overview on Adhatoda zelanica Medic. Syn. A. vasica (Linn.) Nees. Nat Prod Rad 8(5):549–554 (https://www.cabdirect.org/cabdirect/abstract/20103010255)
Sharma JR, Cheema GS, Saini SS, Gill BS (2010) Soft rot disease of Aloe barbadensis and its management. J Res Punjab Agri Uni 47:18–19 (https://www.cabdirect.org/cabdirect/abstract/20113213221)
Singh R, Kumar U, Singh A (2015) Nematicidal efficacy of botanicals extracted from Adhatoda vasica and Andrographi saffinis against Meloidogyne incognita. Int J Sci Nat 6(2):155–160 (http://www.scienceandnature.org/IJSN_Vol6(2)J2015/IJSN-VOL6(2)15‑6.pdf)
Stapleton JJ (2000) Soil solarization in various agricultural production systems. Crop Prot 19:837–841. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0261-2194(00)00111-3
Wai KPP, Lee J, Mo H, Kim B (2013) Sources of resistance to bacterial wilt and restorer-of-fertility genotype for Cytoplasmic male sterility in Capsicum pepper. Horticult Envirn Biotechnol 54(3):266–271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-013-0006-1
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
R.A.A. Khan, N. Ullah, S.S. Alam, A. Ali, I. Naz, B. Ahmad, M. Ahmad and I. Ullah declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, R.A.A., Ullah, N., Alam, S.S. et al. Management of Ralstonia solanacearum (Smith) Wilt in Tomato Using Green Manure of the Medicinal Plant Adhatoda vasica (L.) Nees. Gesunde Pflanzen 72, 129–138 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-019-00492-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-019-00492-4