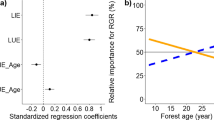
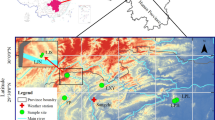
Abstract
Crown width (CW) is an important individual tree variable commonly used to assess tree vigor and the production efficiency of stands. However, our understanding of the effects of climate and the combined effects of climate with competition on the variation of CW remains unknown. Therefore, this study developed CW models by nonlinear mixed-effects (NLME) to explore these effects. Data were obtained from Korean pine (Pinus koraiensis Siebold and Zucc.) plantations in five forestry agencies in northeastern China. The results showed that stand basal area (BA), height to crown base (HCB), isothermality (BIO3), and annual precipitation (BIO12) were significantly related to the variations of CW. CW increased with increasing BIO12, while decreased with increasing BA, HCB, and BIO3. The hierarchical partitioning (HP) analysis showed that the relative importance of BIO3 was larger than BA, HCB, and BIO12. In addition, we found that competition altered the variations of CW responses to climate. Competition, tree size, and climate CW model (CC-CWM) performed the best performance in model fitting and prediction accuracy. Therefore, CC-CWM was selected to predict CW under future climate change. By comparing the eleven sampling methods with eighteen sample sizes, it was reasonable to select six medium-trees to estimate the random effect parameters. Our study provides evidence of the effects of climate and the combined effects of competition and climate on the variations of CW, potentially useful for the development of rational and scientific forest management decisions under future climate changes.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The processed data used during the study are available from the corresponding author by request.
Code availability
The R code generated or used during the study are available from the corresponding author by request.
Change history
24 February 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10342-023-01533-4
References
Bronisz K, Mehtätalo L (2020) Mixed-effects generalized height–diameter model for young silver birch stands on post-agricultural lands. For Ecol Manage 460:117901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2020.117901
Buchacher R, Ledermann T (2020) Interregional crown width models for individual trees growing in pure and mixed stands in Austria. Forests 11:114. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11010114
Buckley TN, Cescatti A, Farquhar GD (2013) What does optimization theory actually predict about crown profiles of photosynthetic capacity when models incorporate greater realism? Plant, Cell Environ 36:1547–1563. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12091
Calama R, Montero G (2004) Interregional nonlinear height diameter model with random coefficients for stone pine in Spain. Can J for Res 34:150–163. https://doi.org/10.1139/X03-199
Calama R, Conde M, de-Dios-García, J., Madrigal, G., Vázquez-Piqué, J., Gordo, F.J., et al (2019) Linking climate, annual growth and competition in a Mediterranean forest: Pinus pinea in the Spanish Northern Plateau. Agric for Meteorol 264:309–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2018.10.017
Canavan SJ, Ramm CW (2000) Accuracy and precision of 10 year predictions for forest vegetation simulator–Lake States. North J Appl for 17:62–70
Carvalho JP, Parresol BR (2003) Additivity in tree biomass components of Pyrenean oak (Quercus pyrenaica Willd.). For Ecol Manage 179:269–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-1127(02)00549-2
Chen HH, Luo Y, Reich PB, Searle EB, Biswas SR (2016) Climate change-associated trends in net biomass change are age dependent in western boreal forests of Canada. Ecol Lett 19:1150–1158. https://doi.org/10.1111/ele.12653
Chen Q, Duan G, Liu Q, Ye Q, Sharma RP, Chen Y et al (2021) Estimating crown width in degraded forest: A two-level nonlinear mixed-effects crown width model for Dacrydium pierrei and Podocarpus imbricatus in tropical China. For Ecol Manage 497:119486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2021.119486
Chevan A, Sutherland M (1991) Hierarchical partitioning. Am Stat 45:90–96. https://doi.org/10.1080/00031305.1991.10475776
Ciceu A, Garcia-Duro J, Seceleanu I, Badea O (2020) A generalized nonlinear mixed-effects height–diameter model for Norway spruce in mixed-uneven aged stands. For Ecol Manage 477:118507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2020.118507
Cortini F, Comeau PG (2020) Pests, climate and competition effects on survival and growth of trembling aspen in western Canada. New for 51:175–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11056-019-09726-9
Cortini F, Comeau PG, Bokalo M (2012) Trembling aspen competition and climate effects on white spruce growth in boreal mixtures of Western Canada. For Ecol Manage 277:67–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2012.04.022
Crecente-Campo F, Tomé M, Soares P, Diéguez-Aranda U (2010) A generalized nonlinear mixed-effects height–diameter model for Eucalyptus globulus L. in northwestern Spain. For Ecol Manage 259:943–952. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2009.11.036
Crecente-Campo F, Corral-Rivas JJ, Vargas-Larreta B, Wehenkel C (2014) Can random components explain differences in the height–diameter relationship in mixed uneven-aged stands? Ann for Sci 71:51–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13595-013-0332-6
Crookston NL, Rehfeldt GE, Dixon GE, Weiskittel AR (2010) Addressing climate change in the forest vegetation simulator to assess impacts on landscape forest dynamics. For Ecol Manage 260:1198–1211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2010.07.013
Davidian M, David MG (2003) Nonlinear models for repeated measurement data: an overview and update. Forestry 8:387–419
Dong L, Widagdo FRA, Xie L, Li F (2020) Biomass and volume modeling along with carbon concentration variations of short-rotation Poplar plantations. Forests 11:780. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11070780
Elmugheira MI, Elmamoun HO (2014) Diameter at breast height-crown width prediction models for Anogeissus Leiocarpus (DC.) Guill & Perr and Combretum Hartmannianum Schweinf. J Forest Product Industries 3:191–197
Ford KR, Breckheimer IK, Franklin JF, Freund JA, Kroiss SJ, Larson AJ et al (2017) Competition alters tree growth responses to climate at individual and stand scales. Can J for Res 47:53–62. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjfr-2016-0188
Fu L, Sun H, Sharma RP, Lei Y, Zhang H, Tang S (2013) Nonlinear mixed-effects crown width models for individual trees of Chinese fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata) in south-central China. For Ecol Manage 302:210–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FORECO.2013.03.036
Fu L, Sharma RP, Hao K, Tang S (2017) A generalized interregional nonlinear mixed-effects crown width model for Prince Rupprecht larch in northern China. For Ecol Manage 389:364–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2016.12.034
Gonzalez-Benecke CA, Gezan SA, Samuelson LJ, Cropper WP, Leduc DJ, Martin TA (2014) Estimating Pinus palustris tree diameter and stem volume from tree height, crown area and stand-level parameters. J for Res 25:43–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-014-0427-4
Gregory JJ, Mark JD (2007) Predicting crown radius in eastern white pine (pinusstrobus l.) stands in new hampshire. North Am J Fish Manage 24:61–64
He X, Lei X, Dong L (2021) How large is the difference in large-scale forest biomass estimations based on new climate-modified stand biomass models? Ecol Indic 126:107569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107569
Hernandez-Moreno JM, Bayeur NM, Coley HD, Hughes NM (2017) Clouds homogenize shoot temperatures, transpiration, and photosynthesis within crowns of Abies fraseri (Pursh.) Poiret. Oecologia 183:667–676. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-016-3799-7
Hijmans RJ, Cameron SE, Parra JL, Jones PG, Jarvis A (2005) Very high resolution interpolated climate surfaces for global land areas. Int J Climatol 25:1965–1978. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.1276
Hou R, Chai Z (2022) Predicting crown width using nonlinear mixed-effects models accounting for competition in multi-species secondary forests. PeerJ 10:e13105. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.13105
Hu X, Duan G, Zhang H (2021) Modelling individual tree diameter growth of Quercus mongolica secondary forest in the northeast of China. Sustainability 13:4533. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13084533
Hussain A, Shahzad MK, Jiang L (2021) The effect of crown dimensions on stem profile for Dahurian Larch, Korean Spruce, and Manchurian Fir in northeast China. Forests 12:398. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12040398
Jiang L, Liu R (2011) Segmented taper equations with crown ratio and stand density for Dahurian Larch (Larix gmelinii) in Northeastern China. J for Res 22:347–352. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-011-0178-4
Jin X, Pukkala T, Li F (2016) A management planning system for even-aged and uneven-aged forests in northeast China. J for Res 27:837–852. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-016-0216-3
Korhonen L, Korhonen K, Rautiainen M, Stenberg P (2006) Estimation of forest canopy cover: a comparison of field measurement techniques. Silva Fennica. https://doi.org/10.14214/sf.315
Lei X, Yu L, Hong L (2016) Climate-sensitive integrated stand growth model (CS-ISGM) of Changbai larch (Larix olgensis) plantations. For Ecol Manage 376:265–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2016.06.024
Leiterer R, Furrer R, Schaepman ME, Morsdorf F (2015) Forest canopy-structure characterization: A data-driven approach. For Ecol Manage 358:48–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2015.09.003
Leites LP, Robinson AP, Crookston NL (2009) Accuracy and equivalence testing of crown ratio models and assessment of their impact on diameter growth and basal area increment predictions of two variants of the Forest Vegetation Simulator. Can J for Res 39:655–665. https://doi.org/10.1139/X08-205
Lu L, Chhin S, Zhang X, Zhang J (2021) Modelling tree height-diameter allometry of Chinese fir in relation to stand and climate variables through Bayesian model averaging approach. Silva Fenn. 55. https://doi.org/10.14214/sf.10415
Li Y, Wang W, Zeng W, Wang J, Meng J (2020) Development of Crown Ratio and Height to Crown Base Models for Masson Pine in Southern China. Forests 11:1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11111216
Liang H, Jiang S, Muhammad A, Kang J, Zhu H, Li X et al (2021) Radial growth response of Picea crassifolia to climatic conditions in a dryland forest ecosystem in northwest China. Forests 12:1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12101382
Luo Y, McIntire EJB (2020) Climatic change only stimulated growth for trees under weak competition in central boreal forests. J Ecol 108:36–46. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2745.13228
Meng SX, Huang S (2009) Improved calibration of nonlinear mixed-effects models demonstrated on a height growth function. For Sci 55:239–248
Meng SX, Huang S, Lieffers VJ, Nunifu T, Yang Y (2008) Wind speed and crown class influence the height–diameter relationship of lodgepole pine: Nonlinear mixed effects modeling. For Ecol Manage 256:570–577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2008.05.002
Meng J, Li S, Wang W, Liu Q, Xie S, Ma W (2016) Estimation of forest structural diversity using the spectral and textural information derived from spot-5 satellite images. Remote Sens 8:125. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8020125
Monserud RA, Sterba H (1996) A basal area increment model for individual trees growing in even-and uneven-aged forest stands in Austria. For Ecol Manage 80:57–80
Nally RM, Walsh CJ (2004) Hierarchical partitioning public-domain software. Biodivers Conserv 13:659–660
Nigh G, Smith W (2012) Effect of climate on lodgepole pine stem taper in British Columbia. Canada Forestry 85:579–587. https://doi.org/10.1093/forestry/cps063
Nord-Larsen T, Meilby H, Skovsgaard JP (2009) Site-specific height growth models for six common tree species in Denmark. Scand J for Res 24:194–204. https://doi.org/10.1080/02827580902795036
Oboite FO, Comeau PG (2019) Competition and climate influence growth of black spruce in western boreal forests. For Ecol Manage 443:84–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2019.04.017
Okano K, Bret-Harte MS (2015) Warming and neighbor removal affect white spruce seedling growth differently above and below treeline. Springerplus 4:79. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-015-0833-x
Paula S, Margarida T (2001) A tree crown ratio prediction equation for eucalypt plantations. Ann for Sci 58:193–202
Paulo JA, Faias SP, Ventura-Giroux C, Tomé M (2016) Estimation of stand crown cover using a generalized crown diameter model: application for the analysis of Portuguese cork oak stands stocking evolution. iForest - Biogeosc. For 9:437–444. https://doi.org/10.3832/ifor1624-008
Pinheiro JC, Bates DM (2000) Mixed-effects models in S and S-PLUS. Springer-Verlag, New York
Pinheiro, J., Bates, D., DebRoy, S., Sarkar, D., R Core Team, 2020. nlme: Linear and Nonlinear Mixed Effects Models, Version.
Power H, LeMay V, Berninger F, Sattler D, Kneeshaw D (2012) Differences in crown characteristics between black (Picea mariana ) and white spruce (Picea glauca ). Can J for Res 42:1733–1743. https://doi.org/10.1139/x2012-106
Pukkala T, Becker P, Kuuluvainen T, Oker-Blom P (1991) Predicting spatial distribution of direct radiation below forest canopies. Agric for Meteorol 55:295–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-1923(91)90067-Z
Qin Y, He X, Lei X, Feng L, Zhou Z, Lu J (2022) Tree size inequality and competition effects on nonlinear mixed effects crown width model for natural spruce-fir-broadleaf mixed forest in northeast China. For Ecol Manage 518:120291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2022.120291
Qiu H, Liu S, Zhang Y, Li J (2021) Variation in height-diameter allometry of ponderosa pine along competition, climate, and species diversity gradients in the western United States. For Ecol Manage 497:119477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2021.119477
R Core Team, 2020. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria.
Raptis D, Kazana V, Kazaklis A, Stamatiou C (2018) A crown width-diameter model for natural even-aged black pine forest management. Forests 9:610. https://doi.org/10.3390/f9100610
Raptis DI, Kazana V, Kazaklis A, Stamatiou C (2021) Mixed-effects height–diameter models for black pine (Pinus nigra Arn.) forest management. Trees 35(4):1167–1183. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-021-02106-x
Ritchie MW, Hamann JD (2008) Individual-tree height-, diameter- and crown-width increment equations for young Douglas-fir plantations. New for 35:173–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11056-007-9070-7
Rollinson CR, Kaye MW, Canham CD (2016) Interspecific variation in growth responses to climate and competition of five eastern tree species. Ecology 97:1003–1011. https://doi.org/10.1890/15-1549.1
RStudio team, (2015) RStudio: Integrated development for R. RStudio Inc., Boston
Samantha JG, Gregory SB, Edward CM (2000) Modeling conifer tree crown radius and estimating canopy cover. For Ecol Manage 126:405–416
Sánchez-González M, Cañellas I, Montero G (2007) Generalized height-diameter and crown diameter prediction models for cork oak forests in Spain. Investigación Agraria: Sistemas y Recursos Forestales 16(1):76. https://doi.org/10.5424/srf/2007161-00999
Sharma RP, Vacek Z, Vacek S (2016) Individual tree crown width models for Norway spruce and European beech in Czech Republic. For Ecol Manage 366:208–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2016.01.040
Shaw, J.D., 2003. Models for estimation and simulation of crown and canopy cover. Proceedings of the Fifth Annual Forest Inventory and Analysis Symposium, 183–191.
Sönmez T (2009) Diameter at breast height-crown diameter prediction models for Picea orientalis. AFR J AGR RES 4:215–219
State Forestry Administration, 2014. The seventh forest resource survey report, Beijing.
Subedi N, Sharma M (2013) Climate-diameter growth relationships of black spruce and jack pine trees in boreal Ontario. Canada Globle Change Biol 19:505–516. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.12033
Timilsina N, Staudhammer CL (2013) Individual tree-based diameter growth model of slash pine in florida using nonlinear mixed modeling. For Sci 59:27–37. https://doi.org/10.5849/forsci.10-028
Uzoh FCC, Oliver WW (2008) Individual tree diameter increment model for managed even-aged stands of ponderosa pine throughout the western United States using a multilevel linear mixed effects model. For Ecol Manage 256:438–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2008.04.046
Vacek Z, Prokůpková A, Vacek S, Bulušek D, Šimůnek V, Hájek V, Králíček I (2021) Mixed vs. monospecific mountain forests in response to climate change: structural and growth perspectives of Norway spruce and European beech. For Ecol Manage 488:119019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2021.119019
Vonesh EF, Chinchili VM (1997) Linear and nonlinear models for the analysis of repeated measurements. Marcel Dekker, New York
Wang W, Ge F, Hou Z, Meng J (2021a) Predicting crown width and length using nonlinear mixed-effects models: a test of competition measures using Chinese fir Cunninghamia lanceolata Lamb. Hook. Ann. for. Sci. 78:1099. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13595-021-01092-x
Wang Z, Zhang X, Chhin S, Zhang J, Duan A (2021b) Disentangling the effects of stand and climatic variables on forest productivity of Chinese fir plantations in subtropical China using a random forest algorithm. Agric for Meteorol 304–305:108412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2021.108412
Wickham H (2016) ggplot2: Elegrant graphics for data analysis. Springer, New York
Xu H, Sun YJ, Wang XJ, Wang J, Fu Y (2015) Linear mixed-effects models to describe individual tree crown width for China-fir in Fujian Province, southeast China. PLoS ONE 10:e0122257. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0122257
Yang Y, Huang S (2011) Comparison of different methods for fitting nonlinear mixed forest models and for making predictions. Can J for Res 41:1671–1686. https://doi.org/10.1139/x11-071
Yang Y, Huang S (2017) Allometric modelling of crown width for white spruce by fixed- and mixed-effects models. For Chron 92:138–147
Yang Y, Huang S (2018) Effects of competition and climate variables on modelling height to live crown for three boreal tree species in Alberta. Canada Eur J Forest Res 137:153–167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10342-017-1095-7
Yang Y, Huang S, Meng SX, Trincado G, VanderSchaaf CL (2009) A multilevel individual tree basal area increment model for aspen in boreal mixedwood stands. Can J for Res 39:2203–2214. https://doi.org/10.1139/X09-123
Zhang L, Peng C, Huang S, Zhou X (2002) Development and evaluation of ecoregion-based jack pine. For Chron 78:530–538
Zhang X, Chhin S, Fu L, Lu L, Duan A, Zhang J (2019) Climate-sensitive tree height–diameter allometry for Chinese fir in southern China. Forestry 92:167–176. https://doi.org/10.1093/forestry/cpy043
Acknowledgements
The authors are deeply grateful to the researchers who contributed to this article. We appreciate the valuable comments and constructive suggestions from anonymous reviewers and the Editor.
Funding
This research was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31570624, 32271866); Heilongjiang Touyan Innovation Team Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YY contributed to formal analysis, software, validation, investigation, writing—original draft, writing—review & editing. JW contributed to investigation and visualization. SBM contributed to writing—review & editing. LJ contributed to conceptualization, methodology, validation, writing—review & editing, and funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Communicated by Peter Annighöfer.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised due to the author's corrections were inadvertently missed and the article has been corrected.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, Y., Wang, J., Mahardika, S.B. et al. Effects of climate and competition on crown width: a case of Korean pine plantations. Eur J Forest Res 142, 231–244 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10342-022-01515-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10342-022-01515-y