Abstract
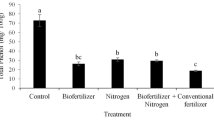
Strawberry is one of the important fruits whose importance is increasing day by day due to some of its properties such as phytochemicals. This study investigated the effect of inhibitor fertilizer applications on yield and quality criteria in strawberry cultivation. It was carried out in the field prepared in three replications according to the “arbitrary blocks, parcels trial design” in the cultivation period of June–September 2021. According to the post-harvest data averages obtained from the sowing norms created to compare the doses of fertilizer with and without inhibitor (0-40-80–120 kg ha−1), the highest fruit yield (50100 kg ha−1) and fruit length were obtained from the 120 kg ha−1 inhibitory fertilizer application. The highest fruit width and dry matter ratios were obtained with the application of 120 kg ha−1 without inhibitor fertilizer, while the highest amount of water-soluble dry matter was obtained with 80 kg ha−1 without inhibitor fertilizer application. According to this study, the highest values in terms of total fruit yield and fruit length were obtained with dimethylpyrazol glyceborate (DMPB) at an application dose of 80 kg ha−1, and when the general averages in other parameters were examined, it was observed that higher results were obtained compared to without inhibitor fertilizer applications. When compared with the ammonium sulfate fertilizer with inhibitor to the control plots in terms of yield parameter, it was determined that it provided a yield increase of a minimum of 8.9% and maximum of 40.7%. However, it would be appropriate to calibrate the results by testing these studies on different plants and in different climatic regions.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ağgün Z, Geçer MK, Aslantaş R (2018) The effects of root bacteria applications on fruit yield and yield characteristics in some strawberry varieties. Int J Agric Wildl Sci 4(1):20–25
Akçay V (2014) The effect of different nitrogen doses on yield and fruit quality criteria of rubygem and fortuna strawberry cultivars. Adnan Menderes University (Master Thesis)
Atasay A, Türemiş N (2007) Research on organic strawberry cultivation. Directorate of Aegean Agricultural Research Institute TAYEK
Atasay A, Türemiş N (2008) A study on the applicability of organic strawberry cultivation in Eğirdir (Isparta) conditions. Cukurova Univ J Sci Technol Inst 18(3):72–81
Bouyoucos GH (1951) A recalibration of the hydrometer for making mechanical analysis of soils. Agronomy J 43:434–438
Cantlıffe DJ, Castellanos JZ, Paranjpe AV (2007) Yield and quality of greenhouse-grown strawberries as affected by nitrogen level in coco coir and pine bark media. Proc Fla State Hort Soc 120:157–161
Çekiç Ç, Güneş M, Gerçekçioğlu M (2003) Determination of adaptation characteristics of some strawberry varieties to tokat ecology. National Kiwi and Berries Symposium, Ordu, pp 221–225
Chien-Ying K, Al-Abdulkarim, AM, Al-Jowid SM, Al-Baiz A (2009) An effective disinfection protocol for plant regeneration from shoot tip cultures of strawberry. Afric J Biotechnol 8(11):2611–2615
Ercisli S, Esitken A, Turkkal C, Orhan E (2005) The allelopathic effects of juglone and walnut leaf extracts on yield, growth, chemical and PNE composition of strawberry cv. Fern. Plant Soil Environ 51(6):283–387
Erturk Y, Ercisli S, Cakmakci R (2012) Yield and growth response of strawberry to plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria inoculation. J Plant Nutr 35(6):817–826
Geçer MK, Yılmaz H (2011) Determination of fruit yield characteristics of strawberry seedlings produced in Van ecological conditions. Igdir Univ J Grad School Nat Appl Sci 1(2):15–22
Hummer KE, Hancock J (2009) Strawberry genomics: botanical history, cultivation, traditional breeding, and new technologies. In: Genetics and genomics of Rosaceae. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 413–435
İpek M, Pırlak L, Eşitken A, Dönmez M, Şahin F (2009) The effects of plant growth-increasing bacteria (BBAB) on yield and development in strawberry cultivated in lime soils. III. National Symposium on Berries, Kahramanmaraş, pp 73–77
Juric S, Vlahovicek-Kahlina K, Duralija B, Maslov Bandic L, Nekic P, Vincekovic M (2021) Stimulation of plant secondary metabolites synthesis in soilless cultivated strawberries (Fragaria × ananassa Duchesne) using zinc-alginate microparticles. Turk J Agric For 45:324–334
Kacar B, Katkat V (2007) Plant nutrition. Nobel Publications, Ankara, pp 145–147
Larrigaudiere C, Lentheric I, Puy J, Pinto E (2004) Biochemical characterisation of core browning and brown heart disorders in pear by multivariate analysis. Postharv Biol Technol 31(1):29–39
Lindsay W, Norwell WA (1978) Development of a DTPA soil test for Zn Fe Mn and Cu. Soil Sci Sco Am J 42:421–428
Martinelli A (1992) Micropropagation of Strawberry (Fragaria spp.). In: High-Tech and Micropropagation II. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 354–370
Nelson DW, Sommer LE (1996) Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. In Spark, D.L. (ed) Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 3. American Society of Agronomy. 34. p 961–1010
Olsen SR, Cole CV, Watanabe FS (1954) Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate. USDA Circular No. 939, US Government Printing Office, Washington DC
Özbay H, Gündüz K (2020) Distributions of total fruit yield, harvest period and monthly yield cultivated in different production places of some strawberry genotypes. Mustafa Kemal Univ J Agricult Sci 25(3):499–508. https://doi.org/10.37908/mkutbd.779170
Özgüven AI, Yılmaz C (2003) Adaptation of some California strawberry cultivars in Adana ecological conditions. National Kiwi and Berries Symposium, p 208–212
Santos MB, Chandler CR (2009) Influence of nitrogen fertilization rates on the performance of strawberry cultivars. Int J Fruit Sci 9:126–135. https://doi.org/10.1080/15538360902991337
Summer ME, Miller WP (1996) Cation exchange capacity and exchange coefficients. In Sparks DL et al (eds) Methods of Soil Analaysis, Part 3 Chemical Methods. Soil Science Society of America Inc., Madison. p 1201–1029
Tabatabaei SJ, Fatemi LS, Fallahi E (2006) Effect of ammonium: nitrateratio on yield, calcium concentration, and photosynthesis ratein strawberry. J Plant Nutr 29:1273–1285
Taiz L, Zeiger E (2006) Plant physiology
TOB (2021) General directorate of meteorology. https://www.mgm.gov.tr/tahmin/il-ve-ilceler.aspx?il=Kayseri&ilce=Talas. Accessed 11.2021
Topcu H (2022) Reference gene selection for RT-qPCR normalization of strawberry at various organs, different growing stages of fruits and salt-stress treatment. Turk J Agric For 46:509–524
Trenkel ME (2010) Slow- and controlled-release and stabilized fertilizers: An option for enhancing nutrient use efficiency in agriculture, 2nd edn. IFA, Paris
Yaman M, Yilmaz KU (2016) Yield and quality-enhancer chemical treatments in strawberry seedling production of Cappadocia region (İnitial results). Bahce J 45:401–404
Yaman M, Yilmaz KU (2022) The effects of different chemicals on runner yield and quality of ‘Kabarla’strawberry young plants grown in Cappadocia region. Erwerbs-Obstbau 64(1):85–90
Yılmaz KU, Yaman M (2016) The effects of different chemicals on yield and quality of ‘Sweet Ann’strawberry nursery plants grown in Cappadocia Region–preliminary results. III Balkan Symposium on Fruit Growing. vol 1139, pp 559–564
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the Kayseri Erciyes University Agricultural Research and Application Center (ERUTAM) and Erciyes University Faculty of Agriculture for conducting the study, setting up the experiment and conducting the analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
E. Pak and A. Güneş declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature oder sein Lizenzgeber (z.B. eine Gesellschaft oder ein*e andere*r Vertragspartner*in) hält die ausschließlichen Nutzungsrechte an diesem Artikel kraft eines Verlagsvertrags mit dem/den Autor*in(nen) oder anderen Rechteinhaber*in(nen); die Selbstarchivierung der akzeptierten Manuskriptversion dieses Artikels durch Autor*in(nen) unterliegt ausschließlich den Bedingungen dieses Verlagsvertrags und dem geltenden Recht.
About this article
Cite this article
Pak, E., Güneş, A. Determination of the Effect of Inhibitor Fertilizers on the Production and Quality Parameters of Strawberry (Fragaria x ananassa). Erwerbs-Obstbau 65, 1421–1427 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10341-023-00923-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10341-023-00923-7