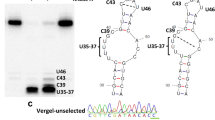
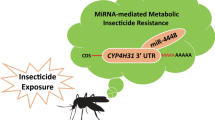
Abstract
Pyrethroid resistance has become one of the largest obstacles to mosquito control, and Anopheles sinensis is the main malaria vector in China and southeast countries. miRNAs play important roles in many biological processes in insects; however, the diversity and regulation of miRNAs associated with pyrethroid resistance are still little understood at the whole-genome level. This study performed the sequencing and analysis of miRNAs relative to pyrethroid resistance in An. sinensis for the first time, and identified 328 miRNAs, of which 247 are new. A total of 39 miRNAs are identified to be significantly downregulated commonly in all three pyrethroid-resistant populations investigated in comparison to the susceptible strain. There are 7475 genes to be predicted to be targeted by the 39 significantly down-regulated miRNAs, and they were enriched to seven pathways. The regulation of Transferrin by asi-miR-87 was verified using dual-luciferase, and the asi-miR-87 might be involved in P450 pyrethroid detoxification with the affection of iron ion transportation and synthesis through Transferrin. In addition, nine miRNAs were identified to be positively relative to eight genes. This is the first systematic study on the diversity and regulation of miRNAs associated with insecticide resistance at the whole-genome level, and provides an information frame for the understanding of miRNAs and their function in insecticide resistance.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW et al (2015) Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. Elife 4:e05005. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.05005
Ahn KC, Watanabe T, Gee SJ et al (2004) hapten and antibody production for a sensitive immunoassay determining a human urinary metabolite of the pyrethroid insecticide permethrin. J Agric Food Chem 52(15):4583–4594. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf049646r
Alout H, Roche B, Dabiré RK et al (2017) Consequences of insecticide resistance on malaria transmission. PLoS Pathog 13(9):e1006499. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1006499
Asgari S (2013) MicroRNA functions in insects. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 43(4):388–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2012.10.005
Ashburner MCA, Ball JA, Blake D et al (2000) Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nat Genet 25(1):25–29. https://doi.org/10.1038/75556
Avila-Bonilla RG, Yocupicio-Monroy M, Marchat LA et al (2017) Analysis of the miRNA profile in C6/36 cells persistently infected with dengue virus type 2. Virus Res 232:139–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virusres.2017.03.005
Campbell CL, Rodriguez KS, Kubik TD et al (2019) Vgsc-interacting proteins are genetically associated with pyrethroid resistance in Aedes aegypti. PLoS ONE 14(1):e0211497. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0211497
Chang ZX, Tang N, Wang L et al (2016) Identification and characterization of microRNAs in the white-backed planthopper, Sogatella Furcifera. Insect Sci 23(3):452–468. https://doi.org/10.1111/1744-7917.12343
Chen B, Zhang YJ, He ZB et al (2014) De novo transcriptome sequencing and sequence analysis of the malaria vector Anopheles sinensis (diptera: Culicidae). Parasit Vectors 7(7):314. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-3305-7-314
Chris B, Schroder I, Turberg A et al (2004) Identification of mutations associated with pyrethroid resistance in the para-type sodium channel of the cat flea, Ctenocephalides felis. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 34(12):1305–1313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2004.09.002
Dennison NJ, Hidalgo OJB, Dimopoulos G (2015) MicroRNA-regulation of Anopheles gambiae immunity to plasmodium falciparum infection and midgut microbiota. Dev Comp Immunol 49(1):170–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dci.2014.10.016
Enright AJ, John B, Gaul U et al (2004) MicroRNA targets in Drosophila. Genome Biol. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2003-4-11-p8
Feng X, Zhang S, Huang F et al (2017) Biology, bionomics and molecular biology of Anopheles sinensis wiedemann 1828 (diptera: Culicidae), main malaria vector in China. Front Microbiol 8:1473. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.01473
Feng X, Wu J, Zhou S et al (2018a) Characterization and potential role of microRNA in the chinese dominant malaria mosquito Anopheles sinensis (diptera: Culicidae) throughout four different life stages. Cell Biosci 8:29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-018-0227-1
Feng X, Zhou X, Zhang S et al (2018b) Analysis of microRNA profile of Anopheles sinensis by deep sequencing and bioinformatic approaches. Parasit Vectors 11(1):172. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-018-2734-7
Freitas FC, Pires CV, Claudianos C et al (2017) MicroRNA-34 directly targets pair-rule genes and cytoskeleton component in the Honey Bee. Sci Rep 7:40884. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep40884
Friedlander MR, Mackowiak SD, Li N et al (2012) Mirdeep2 accurately identifies known and hundreds of novel microRNA genes in seven animal clades. Nucleic Acids Res 40(1):37–52. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr688
Fu X, Dimopoulos G, Zhu J (2017) Association of microRNAs with argonaute proteins in the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae after blood ingestion. Sci Rep 7(1):6493. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-07013-1
Gendron CM, Pletcher SD (2017) MicroRNAs miR-184 and let-7 alter Drosophila metabolism and longevity. Aging Cell 16(6):1434–1438. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12673
Green AJ, Rivers SL, Cheesman M et al (2001) Expression, purification and characterization of cytochrome p450 biol: a novel p450 involved in biotin synthesis in Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Inorg Chem 6(5–6):523–533. https://doi.org/10.1007/s007750100229
Guo Q, Huang Y, Zou F et al (2017) The role of miR-2 approximately 13 approximately 71 cluster in resistance to deltamethrin in Culex pipiens pallens. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 84:15–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2017.03.006
He X, He ZB, Zhang YJ (2016) Genome-wide identification and characterization of odorant-binding protein (obp) genes in the malaria vector Anopheles sinensis (diptera: Culicidae). Insect Sci 23(3):366–376. https://doi.org/10.1111/1744-7917.12333
He Q, Yan Z, Si F et al (2019) Atp-binding cassette (abc) transporter genes involved in pyrethroid resistance in the malaria vector Anopheles sinensis: genome-wide identification, characteristics, phylogenetics, and expression profile. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061409
Hong S, Guo Q, Wang W et al (2014) Identification of differentially expressed microRNAs in Culex pipiens and their potential roles in pyrethroid resistance. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 55:39–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2014.10.007
Hu D, Li MQ, Su J et al (2019) Dual-targeting of mir-124-3p and abcc4 promotes sensitivity to adriamycin in breast cancer cells. Genet Test Mol Biomark 23(3):156–165. https://doi.org/10.1089/gtmb.2018.0259
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA (2009) Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using david bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc 4(1):44–57. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.211
Hung JH, Li CH, Yeh CH et al (2018) MicroRNA-224 down-regulates Glycine N-methyltransferase gene expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Sci Rep 8(1):12284. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-30682-5
Hussain M, Walker T, O’Neill SL (2013) Blood meal induced microRNA regulates development and immune associated genes in the dengue mosquito vector, Aedes aegypti. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 43(2):146–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2012.11.005
Kanehisa M, Goto S (2000) Kegg: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 28(1):27–30. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.1.27
Kozomara A, Griffiths-Jones S (2014) Mirbase: annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res 42(D1):D68–D73. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1181
Kruger J, Rehmsmeier M (2006) RNAhybrid: MicroRNA target prediction easy, fast and flexible. Nucleic Acids Res 34:W451–W454. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkl243
Lei Z, Lv Y, Wang W et al (2015) MiR-278-3p regulates pyrethroid resistance in Culex pipiens pallens. Parasitol Res 114(2):699–706. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-014-4236-7
Li T, Cao C, Yang T et al (2015) A g-protein-coupled receptor regulation pathway in cytochrome p450-mediated permethrin-resistance in mosquitoes, Culex Quinquefasciatus. Sci Rep 5:17772. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep17772
Li Y, Li SJ, Li RM et al (2017) Genome-wide miRNA screening reveals miR-310 family members negatively regulate the immune response in Drosophila melanogaster via co-targeting drosomycin. Dev Comp Immunol 68:34–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dci.2016.11.014
Li S, Xu X, Zheng Z, Zheng J, Shakeel M, Jin F (2019) MicroRNA expression profiling of Plutella xylostella after challenge with B. thuringiensis. Dev Comp Immunol 93:115–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dci.2018.12.008
Li M, Lv M, Liu T et al (2022) Lipid metabolic disorder induced by pyrethroids in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease of xenopus laevis. Environ Sci Technol 56(12):8463–8474. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.2c00516
Liu Y, Zhou Y, Wu J et al (2015) The expression profile of Aedes albopictus miRNAs is altered by dengue virus serotype-2 infection. Cell Biosci 5:16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-015-0009-y
Liu B, Tian M, Guo Q et al (2016) MiR-932 regulates pyrethroid resistance in Culex pipiens pallens (diptera: Culicidae). J Med Entomol 53(5):1205–1210. https://doi.org/10.1093/jme/tjw083
Liu BQ, Qiao L, He QY et al (2018) Genome-wide identification, characterization and evolution of cuticular protein genes in the malaria vector Anopheles sinensis (diptera: Culicidae). Insect Science 25(5):739–750. https://doi.org/10.1111/1744-7917.12483
Ma K, Li X, Hu H et al (2017) Pyrethroid-resistance is modulated by miR-92a by targeting cpcpr4 in Culex pipiens pallens. Comp Biochem Physiol Part B Biochem Mol Biol 203:20–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpb.2016.09.002
Manyi-Loh C, Mamphweli S, Meyer E, Okoh A (2018) Antibiotic use in agriculture and its consequential resistance in environmental sources: potential public health implications. Molecules 23:795. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23040795
Menzel P, McCorkindale AL, Stefanov SR et al (2019) Transcriptional dynamics of microRNAs and their targets during Drosophila neurogenesis. RNA Biol 16(1):69–81. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2018.1558907
Nolan T, Hands RE, Bustin SA (2006) Quantification of mRNA using real-time rt-PCR. Nat Protoc 1(3):1559–1582. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.236
Organization WH (2016) Test procedures for insecticide resistance monitoring in malaria vector mosquitoes
Perrie S, Moreau E, Deshayes C et al (2021) Compensatory mechanisms in resistant anopheles gambiae Acerkis and Kdrkis neurons modulate insecticide-based mosquito control. Communications Biology 4(1):665. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-021-02192-0
Pfaffl WM (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time rt-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29(9):e45. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/29.9.e45
Pignatelli P, Ingham VA, Balabanidou V et al (2018) The Anopheles gambiae atp-binding cassette transporter family: Phylogenetic analysis and tissue localization provide clues on function and role in insecticide resistance. Insect Mol Biol 27(1):110–122. https://doi.org/10.1111/imb.12351
Qiu X, Zhou D, Liu X, Sun Y et al (2015) Genomic analysis of detoxification supergene families in the mosquito Anopheles sinensis. PLoS ONE 10:e0143387. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0143387
Qiu L, Zhang B, Liu L et al (2017) Proteomic analysis of Cry2Aa-binding proteins and their receptor function in Spodoptera exigua. Sci Rep 7:40222. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep40222
Shakeel M, Xu X, Xu J et al (2018) Genome-wide identification of destruxin a-responsive immunity-related microRNAs in diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella. Front Immunol 9:185. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.00185
Shi TF, Wang YF, Liu F et al (2017) Influence of the neonicotinoid insecticide thiamethoxam on miRNA expression in the Honey Bee (Hymenoptera: Apidae). J Insect Sci 17(5):96. https://doi.org/10.1093/jisesa/iex074
Si FL, Qiao L, He QY et al (2019) HSP superfamily of genes in the malaria vector Anopheles sinensis: diversity, phylogenetics and association with pyrethroid resistance. Malar J 18(1):132. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12936-019-2770-6
Smoot ME, Ono K, Ruscheinski J et al (2011) Cytoscape 2.8: new features for data integration and network visualization. Bioinformatics 27(3):431–432. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq675
Takeda Y, Itaya-Hironaka A, Yamauchi A et al (2021) Intermittent hypoxia upregulates the renin and Cd38 mRNAs in renin-producing cells via the downregulation of miR-203. Int J Mol Sci 22(18):10127. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221810127
Terhzaz S, Cabrero P, Brinzer RA et al (2015) A novel role of Drosophila cytochrome p450–4e3 in permethrin insecticide tolerance. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 67:38–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2015.06.002
Tian M, Liu B, Hu H et al (2016) MiR-285 targets p450 (cyp6n23) to regulate pyrethroid resistance in Culex pipiens pallens. Parasitol Res 115(12):4511–4517. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-016-5238-4
Vijay S, Rawal R, Kadian K et al (2015) Annotated differentially expressed salivary proteins of susceptible and insecticide-resistant mosquitoes of Anopheles stephensi. PLoS ONE 10(3):e0119666. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0119666
Wang L, Feng Z, Wang X, Wang X et al (2010) DEGseq: an R package for identifying differentially expressed genes from RNA-seq data. Bioinformatics 26(1):136–138. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp612
Wang TT, Si FL, He ZB et al (2018) Genome-wide identification, characterization and classification of ionotropic glutamate receptor genes (iglurs) in the malaria vector Anopheles sinensis (diptera: Culicidae). Parasit Vectors 11(1):34. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-017-2610-x
Wu XM, Xu BY, Si FL et al (2018) Identification of carboxylesterase genes associated with pyrethroid resistance in the malaria vector Anopheles sinensis (diptera: Culicidae). Pest Manag Sci 74(1):159–169. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.4672
Xie MY, Hou LJ, Sun JJ et al (2019) Porcine milk exosome miRNAs attenuate lps-induced apoptosis through inhibiting TLR4/NF-KB and p53 pathways in intestinal epithelial cells. J Agric Food Chem 67(34):9477–9491. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b02925
Yan ZW, He ZB, Yan ZT (2018) Genome-wide and expression-profiling analyses suggest the main cytochrome p450 genes related to pyrethroid resistance in the malaria vector, Anopheles sinensis (diptera culicidae). Pest Manag Sci 74(8):1810–1820. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.4879
Yang B, Liu B, Bi PD et al (2015) An integrated analysis of differential miRNA and mRNA expressions in human gallstones. Mol BioSyst 11(4):1004–1011. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4MB00741G
Yuan J, Zheng Y, Gu Z (2021) Effects of cypermethrin on the hepatic transcriptome and proteome of the red claw crayfish Cherax quadricarinatus. Chemosphere 263:128060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128060
Zhang GM, Hussain M, O’Neill SL (2013) Wolbachia uses a host microRNA to regulate transcripts of a methyltransferase, contributing to dengue virus inhibition in Aedes aegypti. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(25):10276–10281. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1303603110
Zhang HW, Liu Y, Hu T et al (2015) Knockdown resistance of Anopheles sinensis in henan province, china. Malar J 14:137. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12936-015-0662-y
Zhang YJ, Lan Y, Chen B (2021) Asdb: a comprehensive omics database for Anopheles sinensis. Genomics 113(3):976–982. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2021.02.005
Zhu G, Zhong D, Cao J et al (2014) Transcriptome profiling of pyrethroid resistant and susceptible mosquitoes in the malaria vector. Anopheles Sinensis BMC Genomics 15:448. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-15-448
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the following, The National Natural Science Foundation of China (31872262, 31672363).
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31872262, 31672363).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed while conducting this research.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Communicated by Wannes Dermauw.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10340_2024_1776_MOESM1_ESM.tiff
Identification of miRNAs related to pyrethroid resistance in Anopheles sinensis. Expression profile of significantly downregulated 39 miRNAs in three pyrethroid-resistant populations compared with pyrethroid-susceptible strain of Anopheles sinensis. The colors (on the right panel) indicate the fold change between pyrethroid-resistant and susceptible samples (TIFF 1758 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, X., Asghar, S., Hu, C. et al. miRNAs and their regulation in pyrethroid resistance at whole-genome level in the malaria vector Anopheles sinensis. J Pest Sci (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-024-01776-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-024-01776-z