Abstract
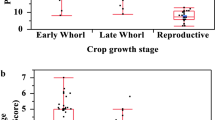
Although there has been intensive use of insecticides for the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) management, their effects on population reduction and natural enemies’ performance have not been adequately studied. Therefore, this study investigated the diversity and activity of natural enemies under insecticide and insecticide-free applications. Natural enemies were collected annually from 2016 to 2022 from 348 maize farms throughout the West African nation of Togo. The collections included an entomopathogenic nematode, unidentified bacteria from Enterobacteriaceae and Enterococcus, unidentified viruses from Ascoviruses and Baculoviruses, and several fungal species. Parasitoids collected included hymenopteran and dipteran species that attacked eggs and larvae. The collected predators included species in the following families: Anthocoridae, Carabidae, Chrysopidae, Coccinellidae, Forficulidae, Formicidae, Mantidae, and Reduviidae. The parasitism rates were from 14.72% in 2018 to 45.38% in 2022 for egg masses and from 1.32% in 2016 to 41.85% in 2021 for larvae. The parasitism rates were three to four times higher in unsprayed farms than sprayed farms.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abang AF, Nanga SN, Kuate AF, Kouebou C, Suh C, Masso C, Saethre MG, Fiaboe KKM (2021) Natural enemies of fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in different agro-ecologies. InSects 12:509. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12060509
Agboyi LK, Goergen G, Beseh P, Mensah SA, Clottey VA, Glikpo R, Buddie A, Cafá G, Offord L, Day R, Rwomushana I, Kenis M (2020) Parasitoid complex of fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda, in Ghana and Benin. InSects 11(2):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11020068
Anderson CJ, Oakeshott JG, Tay WT, Gordon KHJ, Zwick A, Walsh TK (2018) Hybridization and gene flow in the mega-pest lineage of moth, Helicoverpa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115:5034–5039. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1718831115
Baker GL, Capinera JL (1997) Nematodes and nematomorphs as control agents of grasshoppers and locusts. Mem Entomol Soc Can 129:157–211. https://doi.org/10.4039/entm129171157-1
Berny P, Velardo P, Pulce C, D’iamico A, Kammerer M, Lasseur R (2010) Prevalence of anticoagulant rodenticide poisoning in humans and animals in France and substances involved. J Clin Toxol 48(9):935–941. https://doi.org/10.3109/15563650.2010.533678
Bourke M, Sar S (2020) Fall armyworm in Papua New Guinea: how big is the risk? Australian National University. pp 5. https://devpolicy.org/potential-impact-of-fall-armyworm-in-papua-new-guinea-20200526-1/
Braet Y, Rousse P, Sharkey MJ (2012) New data on African Cheloninae (Hymenoptera, Braconidae) show a strong biogeographic signal for taxa with spined propodea. Zootaxa 3385(1):1–32. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3385.1.1
Brindle A (1967) A key to the Ethiopian genus Diaperasticus Burr (Dermaptera: Forficulidae). Proc r Entomol Soc Ser B 36(9–10):147–152. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3113.1967.tb00552.x
Crosskey RW (1968) The identity of Palexorista quadrizonula (Thomson) (Diptera), a tachinid parasite of Lepidopterous pests in Africa. Bull Entomol Res 59(4):579–583. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007485300003564
Dassou AG, Idohou R, Azandémè-Hounmalon GY, Sabi-Sabi A, Houndété J, Silvie P, Dansi A (2021) Fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (J.E. Smith) in maize cropping systems in Benin: abundance, damage, predatory ants and potential control. Int J Trop Insect Sci 41:2627–2636. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-021-00443-5
De Barro PJ, Liu SS, Boykin LM, Dinsdale AB (2015) Bemisia tabaci: a statement of species status. Ann Rev Entomol 56:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ento-112408-085504
Durocher-Granger L, Mfune T, Musesha M, Lowry A, Reynolds K, Buddie A, Cafà G, Offord L, Chipabika G, Dicke M, Kenis M (2021) Factors influencing the occurrence of fall armyworm parasitoids in Zambia. J Pest Sci 94:1133–1146. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-020-01320-9
Eilenberg J, Vlak JM, Nielsen-LeRoux C, Cappellozza S, Jensen AB (2015) Diseases in insects produced for food and feed. J Insect Food Feed 1(2):87–102. https://doi.org/10.3920/JIFF2014.0022
Federici BA, Bigot Y (2008) Ascoviruses. In Encyclopedia of virology, Elsevier, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, pp 186–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-012374410-4.00347-2
Firake DM, Behere GT (2020) Natural mortality of invasive fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (J. E. Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in maize agroecosystems of northeast India. Biol Control 148:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2020.104303
Girod C, Lassalle B (2017) Liste annotée des Perce-oreilles du Tchad (Dermaptera). Bull La Société Entomol Fr 122(2):161–168. https://doi.org/10.3406/bsef.2017.3192
Goergen G, Kumar PL, Sankung SB, Togola A, Tamo M (2016) First report of outbreaks of the fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda (J E Smith) (Lepidoptera, Noctuidae), a new alien invasive pest in west and central Africa. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0165632
Guo J, Wu S, Zhang F, Huang C, He K, Babendreier D, Wang Z (2020) Prospects for microbial control of the fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda: a review. Biocontrol 65:647–662. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526020-10031-0
Haase S, Sciocco-Cap A, Romanowski V (2015) Baculovirus insecticides in Latin America: historical overview, current status and future perspectives. Viruses 7:2230–2267. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7052230
Haile F, Nowatzki T, Storer N (2021) Overview of pest status, potential risk, and management considerations of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) for US soybean production. J Integr Pest Manag 12(1):3. https://doi.org/10.1093/jjpm/pmaa030
Hussain AG, Wennmann JT, Goergen G, Bryon A, Ros VID (2021) Viruses of the fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda: a review with prospects for biological control. Viruses 13:2220. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13112220
Kenis M, Benelli G, Biondi A, Calatayud P-A, Day R, Desneux N, Harrison RD, Kriticos D et al (2022) Invasiveness, biology, ecology, and management of the fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda. Entomol Gen. https://doi.org/10.1127/entomologia/2022/1659
Kim J, Nam HY, Kwon M, Kim HJ, Yi HJ, Haenniger S, Unbehend M, Heckel DG (2021) Development of a simple and accurate molecular tool for Spodoptera frugiperda species identification using LAMP. Pest Manag Sci 77(7):3145–3153. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.6350
Koffi D, Agboka K, Adenka KD, Osae M, Tounou AK, Adjevi MKA, Fening KO, Meagher RL Jr (2020a) Maize infestation of fall armyworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) within agro-ecological zones of Togo and Ghana in West Africa 3 Yr after its invasion. Environ Entomol 49:645–650. https://doi.org/10.1093/ee/nvaa048
Koffi D, Kyerematen R, Eziah VY, Osei-Mensah YO, Afreh-Nuamah K, Aboagye E, Osae M, Meagher RL (2020b) Assessment of impacts of fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) on maize production in Ghana. J Integ Pest Manag 11:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1093/jipm/pmaa015
Koffi D, Kyrematen R, Eziah YV, Agboka K, Adom M, Goergen G, Meagher RL (2020c) Natural enemies of fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (J.E. Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in Ghana. Fla Entomol 103:85–90. https://doi.org/10.1653/024.103.0414
Koffi D, Kyerematen R, Osae M, Amouzou K, Ezeah VY (2021) Assessment of Bacillus thuringiensis and emamectin benzoate on the fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda (J. E. Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) severity on maize under farmers’ fields in Ghana. Int J Trop Insect Sci 42:1619–1626. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-021-00683-5
Koffi D, Agboka K, Fening KO, Adjevi MKA, Badziklou JEA, Tchegueni M, Tchao M, Meagher RL (2022) Spodoptera frugiperda in Togo 5 years on: early impact of the invasion and future developments. Bull Entomol Res. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007485322000207
Kwadjo KE, Doumbia M, Haubruge E (2012) Description et distinction des larves et des exuvies de Rhynocoris albopilosus Signoret (Heteroptera: Reduviidae). Entomol Faun Faun Entomol 65:15–23
Li C, Deng H, Wang G, Li T, Xu Y, Gao Y (2003) Appetite of Spodoptera litura larvae infected by Ovomermis sinensis. Chinese J Biol Control 19:205–215
Meagher RL, Nuessly G, Nagoshi RN, Hay-Roe MM (2016) Parasitoids attacking fall armyworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in sweet corn habitats. Biol Control 95:66–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2016.01.006
Molina-Ochoa J, Carpenter JE, Heinrichs EA, Foster JE (2003a) Parasitoids and parasites of Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in the Americas and Caribbean basin: an inventory. Fla Entomol 86:254–289. https://doi.org/10.1653/0015-4040(2003)086[0254:PAPOSF]2.0.CO;2
Molina-Ochoa J, Lezama-Gutiérrez R, González-Ramírez M, López-Edwards M, Rodriguez-Vega MA, Arceo-Palacios F (2003b) Pathogens and parasitic nematodes associated with populations of fall armyworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) larvae in Mexico. Fla Entomol 86:244–253. https://doi.org/10.1653/0015-4040(2003)086[0244:PAPNAW]2.0.CO;2
Montezano DG, Specht A, Sosa-Gómez DR, Roque-Specht VF, Sousa-Silva JC, Paula-Moraes SV, Peterson JA, Hunt TE (2018) Host plants of Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in the Americas. African Entomol 26(2):286–300. https://doi.org/10.4001/003.026.0286
Murúa MG, Molina-Ochoa J, Fidalgo P (2009) Natural distribution of parasitoids of larvae of the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda, in Argentina. J Insect Sci 9:20. https://doi.org/10.1673/031.009.2001
Nagoshi RN, Koffi D, Agboka K, Tounou KA, Banerjee R, Jurat-Fuentes JL, Meagher RL (2017) Comparative molecular analyses of invasive fall armyworm in Togo reveal strong similarities to populations from the eastern United States and the Greater Antilles. PLoS ONE 12:e0181982. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0181982
Nagoshi RN, Goergen G, Tounou KA, Agboka K, Koffi D, Meagher RL (2018) Analysis of strain distribution, migratory potential, and invasion history of fall armyworm populations in northern sub-Saharan Africa. Sci Rep 8(1):3710. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-21954-1
Nagoshi RN, Htain NN, Boughton D, Zhang L, Xiao Y, Nagoshi BY, Mota-Sanchez D (2020) Southeastern Asia fall armyworms are closely related to populations in Africa and India, consistent with common origin and recent migration. Sci Rep 10:1421. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-58249-3
Nagoshi RN, Goergen G, Koffi D, Agboka K, Adjevi MKA, du Plessis A, Van den Berg J, Tepa-Yotto GT, Winsou JK, Meagher RL, Brévault T (2022) Genetic studies of fall armyworm indicate a new introduction into Africa and identify limits to its migratory behavior. Sci Rep 12:1941. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-05781-z
Nicolas V, Coutanceau JP, Poussereau J, Gomy Y (2015) Les Coccinelles de l’île de La Réunion. In: Actes Des «Premières Rencontres Nationales Des Coccinellistes » - Angers, 2014. 157–186. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/327273560
O’Dowd DJ, Green PT, Lake PS (2003) Invasional “meltdown” on an oceanic island. Ecol Lett 6:812–817. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1461-0248.2003.00512.x
Otim MH, Aropet SA, Opio M, Kanyesigye D, Opolot HN, Tay WT (2021) Parasitism of fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in different maize producing regions of Uganda. InSects 12:121. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12020121
Ramírez-Cabral N, Medina-García G, Kumar L (2020) Increase of the number of broods of fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) as an indicator of global warming. Rev Chapingo Ser Zonas Áridas 19:1–16. https://doi.org/10.5154/r.rchsza.2020.11.01
Roger B, Quinn N, David D, Richard E (2014) Effectiveness of rodenticides for managing invasive roof rats and native mice in orchards. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:5795–5802. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2525-4
Ruppert JLW, Vigliola L, Kulbicki M, Labrosse P, Fortin MJ, Meekan MG (2018) Human activities as a driver of spatial variation in the trophic structure of fish communities on Pacific coral reefs. Global Change Biol 24:e67–e79. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13882
Sala S, Farioli F, Zamagni A (2013) Life cycle sustainability assessment in the context of sustainability science progress (part 2). Int J Life Cycle Assess 18:1686–1697. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11367-012-0509-5
Sisay B, Simiyu J, Malusi P, Likhayo P, Mendesil E, Elibariki N, Wakgari M, Ayalew G (2018) First report of the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), natural enemies from Africa. J Appl Entomol 142:800–804. https://doi.org/10.1111/jen.12534
Sun B, Li F, He X, Cao F, Bandason E, Shapiro-Ilan D, Ruan W, Wu S (2020) First report of Ovomermis sinensis (Nematoda: Mermithidae) parasitizing fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in China. J Nematol 52:e2020–e2050. https://doi.org/10.21307/jofnem-2020-050
Szwabiński J, Pekalski A, Bena I, Droz M (2010) Food web model with detritus path. Phys A 389:2545–2556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2010.02.050
Tay WT, Gordon KHJ (2019) Going global - genomic insights into insect invasions. Curr Opin Insect Sci 31:123–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cois.2018.12.002
Valicente FH (2019) Entomopathogenic Viruses. In: Souza B, Vázquez LL, Marucci RC (eds) Natural enemies of insect pests in neotropical agroecosystems. Springer International Publishing, Germany, pp 137–150. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-24733-1_12
Voirol LRP, Frago E, Kaltenpoth M, Hilker M, Fatouros NE (2018) Bacterial symbionts in Lepidoptera: their diversity, transmission, and impact on the host. Front Microbiol 9:556. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00556
Waller A, Caussanel C, Jamet C, Albouy V (1999) Etude comparée des pièces thoraciques et de leurs appendices chez quelques Dermaptères. Bull La Société Entomol Fr 104(5):427–440. https://doi.org/10.3406/bsef.1999.16609
Zamagni A (2012) Life cycle sustainability assessment. Int J Life Cycle Assess 17:373–376. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11367-012-0389-8
Acknowledgements
The data collection and laboratory works were sponsored by the International Foundation of Sciences (IFS/C/6255-1). We thank Dr. Louela Castrillo, Acting Curator; USDA-ARS Collection of Entomopathogenic Fungal Cultures at the Robert W. Holley Center for Agriculture & Health, Ithaca, NY, USA for identification of fungal samples.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Hannalene Du Plessis.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Koffi, D., Agboka, K., Adjevi, M.K.A. et al. The natural control agents of the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda in Togo: moderating insecticide applications for natural control of the pest?. J Pest Sci 96, 1405–1416 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-023-01662-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-023-01662-0