Abstract
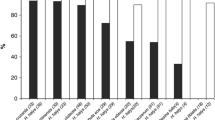
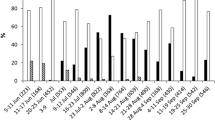
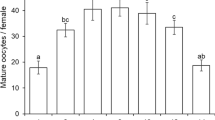
Halyomorpha halys, the brown marmorated stink bug, is a serious agricultural and horticultural pest native to East Asia, which became an invasive pest in northern temperate parts of other regions in the mid-1990s. Trissolcus japonicus is a dominant egg parasitoid of H. halys in its native range. In this paper, we investigated mating, oviposition and fecundity of both virgin and mated females of H. halys. Virgin H. halys females produced unfertilized eggs, while mated females produced fertilized eggs, but mating states of adult females did not affect the number of eggs produced. We further compared the development and fecundity of T. japonicus on fertilized or unfertilized eggs of various ages. Fertilized eggs were tested continuously for up to 5 days (time to hatch), while unfertilized eggs were tested for up to 11 days (time to egg collapse). The fertilization status of the host egg had a significant effect on the development, emergence success, and sex ratio of T. japonicus progeny. A small increase in development time was observed for T. japonicus in fertilized eggs, fewer T. japonicus emerged from fertilized eggs than unfertilized eggs, and the proportion of female progeny was lower on fertilized eggs. The age of host eggs also significantly affected the development rate and fecundity of T. japonicus, with unfertilized eggs becoming more favorable than fertilized eggs as egg age increased. In summary, unfertilized H. halys eggs were better suited for T. japonicus development and fecundity, indicating their potential use in T. japonicus mass rearing.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abram PK, Hoelmer KA, Acebes-Doria A et al (2017) Indigenous arthropod natural enemies of the invasive brown marmorated stink bug in North America and Europe. J Pest Sci 90:1009–1020
Bariselli M, Bugiani R, Maistrello L (2016) Distribution and damage caused by Halyomorpha halys in Italy. EPPO Bull 46:332–334
Barrett M, Schmidt JM (1991) A comparison between the amino acid composition of an egg parasitoid wasp and some of its hosts. Entomol Exp Appl 59:29–41
Chu FJ, Zhou ZF, Li SP, Liu XC (1997) Studies on biological characteristic observation and control methods of Halyomorpha picus Fabricius. J Agric Univ Hebei 20(2):12–17
Cira TM, Venette RC, Aigner J, Kuhar T, Mullins DE, Gabbert SE, Hutchison WD (2016) Cold tolerance of Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) across geographic and temporal scales. Environ Entomol 45(2):484–491
Consoli FL, Parra JRP, Zucchi RA (2010) Egg parasitoids in agroecosystems with emphasis on Trichogramma. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 25–55
Costi E, Haye T, Maistrello L (2017) Biological parameters of the invasive brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys, in southern Europe. J Pest Sci 90:1059–1067
Faúndez EI, Rider DA (2017) The brown marmorated stink bug Halyomorpha halys (Stål 1885) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) in Chile. Arquivos Entomol 17:305–330
Godin C, Boivin G (2000) Effects of host age on parasitism and progeny allocation in Trichogrammatidae. Entomol Exp Appl 97:149–160
Harris C, Abubeker S, Yu M, Leskey T, Zhang A (2015) Semiochemical production and laboratory behavior response of the brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys. PLoS ONE 10:e0140876
Haye T, Abdallah S, Gariepy T, Wyniger D (2014) Phenology, life table analysis and temperature requirements of the invasive brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys, in Europe. J Pest Sci 87:407–418
Haye T, Fischer S, Zhang J, Gariepy T (2015) Can native egg parasitoids adopt the invasive brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae), in Europe? J Pest Sci 88:693–705
Hedstrom C, Lowenstein D, Andrews H, Bai B, Wiman N (2017) Pentatomid host suitability and the discovery of introduced populations of Trissolcus japonicus in Oregon. J Pest Sci 90:1169–1179
Herlihy MV, Talamas EJ, Weber DC (2016) Attack and success of native and exotic parasitoids on eggs of Halyomorpha halys in three Maryland habitats. PLoS ONE 11(3):e0150275
Hoebeke ER, Carter ME (2003) Halyomorpha halys (Stål) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae): a polyphagous plant pest from Asia newly detected in North America. P Entomol Soc Wash 105:225–237
Kawada H, Kitamura C (1983) The reproductive behavior of the brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha mista Uhler (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). I. Observation of mating behavior and multiple copulation. Appl Entomol Zool 18:234–242
Kriticos DJ, KeanJM Phillips CB, Senay SD, Acosta H, Haye T (2017) The potential global distribution of the brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys, a critical threat to plant biosecurity. J Pest Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-017-0869-5
Krugner R (2014) Suitability of non-fertilized eggs of Homalodisca vitripennis for the egg parasitoid Gonatocerus morrilli. Biol Control 59:167–174
Lee DH, Short BD, Joseph SV, Bergh JC, Leskey TC (2013) Review of the biology, ecology, and management of Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) in China, Japan, and the Republic of Korea. Environ Entomol 42(4):627–641
Leskey TC, Nielsen AL (2018) Impact of the invasive brown marmorated stink bug in North America and Europe: history, biology, ecology, and management. Ann Rev Entomol 63:599–618
Leskey TC, Lee DH, Short BD, Wright SE (2012a) Impact of insecticides on the invasive Halyomorpha halys (Stål) (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae): analysis on the insecticide lethality. J Econ Entomol 105:1726–1735
Leskey TC, Short BD, Butler BR, Wright SE (2012b) Impact of the invasive brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys (Stål), in mid-Atlantic tree fruit orchards in the United States: case studies of commercial management. Psyche 2012:1–14
Leskey TC, Wright SE, Short BD, Khrimian A (2012c) Development of behaviorally based monitoring tools for the brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys (Stål) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) in commercial tree fruit orchards. J Entomol Sci 47:76–85
Leskey TC, Short BD, Lee DH (2013) Efficacy of insecticide residues on adult Halyomorpha halys (Stål) (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) mortality and injury in apple and peach orchards. Pest Manag Sci 70:1097–1104
Medal J, Smith T, Cruz AS (2013) Biology of the brown marmorated stink bug Halyomorpha halys (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) in the laboratory. Fla Entomol Soc 96:1209–1212
Milnes JM, Wiman NG, Talamas EJ et al (2016) Discovery of an exotic egg parasitoid of the brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys (Stål) in the Pacific Northwest. Proc Entomol Soc Wash 118:466–470
Nielsen AL, Hamilton GC, Matadha D (2008) Developmental rate estimation and life table analysis for Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). Environ Entomol 37:348–355
Ogburn EC, Bessin R, Dieckhoff C et al (2016) Natural enemy impact on eggs of the invasive brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys (Stål) (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae), in organic agroecosystems: a regional assessment. Biol Control 101:39–51
Pennacchio F, Strand MR (2006) Evolution of developmental strategies in parasitic Hymenoptera. Annu Rev Entomol 51(51):233–258
Pimentel D (2009) Environmental and economic costs of the application of pesticides primarily in the United States. In: Peshin R, Dhawan AK (eds) Integrated pest management: innovation-development process. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 89–111
Pimentel D, Andow D, Dyson-Hudson R, Gallahan D, Jacobson S, Irish M, Kroop S, Moss A, Schreiner I, Shephard M, Thompson T, Vinzant B (1980) Environmental and social costs of pesticides: a preliminary assessment. Oikos 34:126–140
Qin WL (1990) The regularity outbreak and control technique of Halyomorpha picus Fabricius. Plant Prot 16(6):22–23
Qiu LF (2008) Studies on biology of the brown marmorated stink bug Halyomorpha halys (Stål) (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae), an important pest for pome trees in China and its biological control. Dissertation, Chinese Academy of Forestry
Qiu LF, Yang ZQ, Tao WQ (2007) Biology and population dynamics of Trissolcus halyomorphae. Sci Silvae Sin 43(11):62–65
Reed DA, Luhring KA, Stafford CA, Hansen AK, Millar JG, Hanks LM, Paine TD (2007) Host defensive response against an egg parasitoid involves cellular encapsulation and melanisation. Biol Control 41:214–222
Rice KB, Bergh CJ, Bergmann EJ, Biddinger DJ et al (2014) Biology, ecology, and management of brown marmorated stink bug (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). J Integr Pest Manag 5(3):A1–A13
Roversi PF, Binazzi F, Marianelli L, Costi E, Maistrello L, Sabbatini Peverieri G (2016) Searching for native egg-parasitoids of the invasive alien species Halyomorpha halys Stål (Heteroptera, Pentatomidae) in Southern Europe. Redia 99:63–70
Santacruz EN, Venette R, Dieckhoff C, Hoelmer K, Koch RL (2017) Cold tolerance of Trissolcus japonicus and T. cultratus, potential biological control agents of Halyomorpha halys, the brown marmorated stink bug. Biol Control 107:11–20
Skillman VP, Lee JC (2017) Nutrient content of brown marmorated stink bug eggs and comparisons between experimental uses. J Insect Sci 17(6):120; 1–8
Talamas EJ, Buffington M, Hoelmer K (2013) New synonymy of Trissolcus halyomorphae Yang. J Hymenopt Res 33:113–117
Talamas EJ, Herlihy MV, Dieckhoff C, Hoelmer KA, Buffington ML, Bon MC, Weber DC (2015) Trissolcus japonicus (Ashmead) emerges in North America. J Hymenopt Res 43:119–128
United States Apple Association (2010) Asian pest inflicting substantial losses, raising alarm in eastern apple orchards. Apple News 41:488
van Lenteren JC, Bolckmans K, Köhl J et al (2018) Biological control using invertebrates and microorganisms: plenty of new opportunities. Biocontrol 63(1):39–59
Wang YM, Wang YN (1988) Studies on the pear bug, Halyomorpha picus Fabricius (Hemiptera:Pentatomidae). Acta Agri Boreali-Sinica 3(4):96–101
Wermelinger B, Wyniger D, Forster B (2008) First records of an invasive bug in Europe: Halyomorpha halys Stål (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae), a new pest on woody ornamentals and fruit trees? Mitt Schweiz Entomol Ges 81:1–8
Yang ZQ, Yao YX, Qiu LF, Li ZX (2009) A new species of Trissolcus (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae) parasitizing eggs of Halyomorpha halys (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) in China with comments on its biology. Ann Entomol Soc Am 102:39–47
Yang YL, Zhong YZ, Zhang F, Zhou CQ, Yang SY, Zhang JP (2015) Parasitic capacity of Trissolcus halyomorphae and T. flavipes (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae) on eggs of Halyomorpha halys. Chin J Environ Entomol 37:1257–1262
Yu CL, Jin XF, Liu XQ, Zhao HY, Jin CC, Sun LH (2002) Study on injury by Halyomorpha halys and Dolycoris baccarum in pear tree and their control. China Fruits 2:7–9
Zhang CT, Li DL, Sui HF, Xu GL (1993) Study on the biological characteristics of Halyomorpha picus Fabricius and Erthesina fullo Thunberg. For Res 6(3):271–275
Zhang JP, Zhang F, Gariepy T, Mason P, Gillespie D, Talamas E, Haye T (2017) Seasonal parasitism and host specificity of Trissolcus japonicus in northern China. J Pest Sci 90:1127–1141
Zhou Y, Abram PK, Boivin G, Brodeur J (2014) Increasing host age does not have the expected negative effects on the fitness parameters of an egg parasitoid. Entomol Exp Appl 151(2):106–111
Zhu G, Gariepy TD, Haye T, Bu W (2017) Patterns of niche filling and expansion across the invaded ranges of Halyomorpha halys in North America and Europe. J Pest Sci 90(4):1045–1057
Acknowledgements
We thank two anonymous reviewers for their very constructive comments on the manuscript. We also thank Dr Qing-Hai Fan of Plant Health and Environment Laboratory, Ministry for Primary Industries, New Zealand, for improving the English throughout the manuscript. This research was supported by China’s donation to the CABI Development Fund, Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province for Talent Youth (gxbjZD2016016) and Natural Science Foundation of China (31070338). CABI is an international intergovernmental organization and we gratefully acknowledge the core financial support from our member countries (and lead agencies) including the United Kingdom (Department for International Development), China (Chinese Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs), Australia (Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research), Canada (Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada), Netherlands (Directorate-General for International Cooperation), and Switzerland (Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation). See https://www.cabi.org/about-cabi/who-we-work-with/key-donors/for full details.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Author notes
Shi-Yong Yang and Hai-Xia Zhan have contributed equally to this work and should be considered co-first authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or vertebrate performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by D.C. Weber.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, SY., Zhan, HX., Zhang, F. et al. Development and fecundity of Trissolcus japonicus on fertilized and unfertilized eggs of the brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys. J Pest Sci 91, 1335–1343 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-018-0998-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-018-0998-5