Abstract
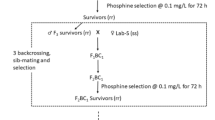
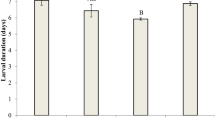
Cryptolestes ferrugineus is a serious cosmopolitan pest of stored products. Frequent and indiscriminate usage of phosphine has caused the development of high levels of resistance to this fumigant. As there are few alternatives, it is imperative that resistance to phosphine is managed. Effective management requires knowledge of key factors driving the rate of selection. One of the most important factors is the response of each resistance genotype to phosphine, especially heterozygotes. Moreover, it is important to understand the expression of resistance in all life stages as all stages are subjected to selection during fumigation. We determined the relative tolerance and resistance levels to phosphine in all life stages of homozygous parental strains (susceptible and resistant) and their F1 progeny (heterozygous) and estimated relative dominance of resistance within life stages over 48 h. In susceptible insects, relative tolerance was highest in eggs followed by pupae, then adults which had about the same tolerance as larvae. In homozygous resistant insects, the order of tolerance was adult = egg > pupae > larvae and in heterozygotes larvae > eggs > pupae > adults. All life stages expressed resistance with resistance ratios highest in adults > pupae > larvae > eggs. At LC50, resistance was incompletely recessive in eggs, pupae and adults and incompletely dominant in larvae. Eggs and adults were also incompletely recessive at LC95, but larvae were completely dominant and pupae were incompletely dominant. Our data showed that a proportion of heterozygotes in all life stages, the major carriers of resistance in the field, will survive at very high concentrations, particularly in the egg stage, forming a nucleus for reinfestation or dispersal of resistance.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott WS (1925) A method of computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. J Econ Entomol 18:265–267
APVMA (2017) ECO2FUME Phosphine fumigant label. Australian pesticides and veterinary medicines authority. http://www.infopest.com.au/extra/asp/infopest/nra/labels.asp?prodcode=50177
Barker PS (1969) Susceptibility of eggs and young adults of Cryptolestes ferrugineus and C. turcicus to hydrogen phosphide. J Econ Entomol 62:363–365
Bell CH (1976) The tolerance of developmental stages of four stored product moths to phosphine. J Stored Prod Res 12:18–21
Bell CH (2000) Fumigation in the twenty-first century. Crop Prot 19:563–569
Bengston M, Collins PJ, Daglish GJ, Hallman VL, Kopittke R, Pavic H (1999) Inheritance of phosphine resistance in Tribolium castaneum. J Econ Entomol 92:17–20
Collins PJ, Lambkin TA, Haddrell RL, Lambkin TM, Bond LA (1996) Does under-dosing select for resistance? In: Donahaye EJ, Navarro S (eds) Proceedings of international conference on controlled atmospheres and fumigation in stored products, 21–26 April 1996. Printco Ltd, Nicosia, Cyprus, pp 493–502
Collins PJ, Daglish GJ, Bengston M, Lambkin TM, Pavic H (2002) Genetics of resistance to phosphine in Rhyzopertha dominica (Coleoptera: Bostrichidae). J Econ Entomol 95:862–869
Daglish GJ (2008) Impact of resistance on efficacy of binary combinations of spinosad, chlorpyrifos-methyl and s-methoprene against five stored-grain beetles. J Stored Prod Res 44:71–76
Daglish GJ, Nayak MK, Pavic H (2014) Phosphine resistance in Sitophilus oryzae (L.) from eastern Australia: inheritance, fitness and prevalence. J Stored Prod Res 59:237–244
Emekci M, Navarro S, Donahaye JE, Rindner M, Azrieli A (2001) Respiration of stored-product pests in hermetic conditions. Phytoparasitica 29:8S–9S
FAO (1975) Recommended methods for detection and measurement of resistance of agricultural pests to pesticides. Tentative method for adults of some major pest species of stored cereals, with methyl bromide and phosphine. FAO Method No. 16. FAO Plant Prot Bull 23:12–26
Finney DJ (1979) Probit analysis, 3rd edn. Cambridge University Press, London
GenStat for Windows Release. 14.1. (2013) V. S. N. International, Hemel Hempstead/Oxford
Hagstrum DW, Klejdysz T, Subramanyam B, Nawrot J (2013) Atlas of stored-product insects and mites. AACC International, Minnesota
Ho SH, Winks RG (1995) The response of Liposcelis bostrychophila Badonnel and L. entomophila (Enderlein) (Psocoptera) to phosphine. J Stored Prod Res 31:191–197
Hole BD, Bell CH, Mills KA, Goodship G (1976) The toxicity of phosphine to all developmental stages of thirteen species of stored product beetles. J Stored Prod Res 12:235–244
Howe RW (1973) The susceptibility of immature and adult stages of Sitophilus granarius to phosphine. J Stored Prod Res 8:241–262
Jagadeesan R, Collins PJ, Daglish GJ, Ebert PR, Schlipalius DI (2012) Phosphine resistance in the rust red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum (Herbst) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae): Inheritance, gene interactions and fitness costs. PLoS ONE 7(2):e31582. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0031582
Jagadeesan R, Nayak MK, Dawson K, Byrne V, Collins PJ (2013) Dietary media for mass rearing of rusty grain beetle, Cryptolestes ferrugineus (Stephens) and flat grain beetle, Cryptolestes pusillus (Schonherr) (Coleoptera). J Stored Prod Res 55:68–72
Jagadeesan R, Nayak MK, Pavic H, Collins PJ (2015) Susceptibility to sulfuryl fluoride and lack of cross-resistance to phosphine in developmental stages of the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). Pest Manag Sci 71:1379–1386
Jagadeesan R, Collins PJ, Nayak MK, Schlipalius DI, Ebert PR (2016) Genetic characterisation of field-evolved resistance to phosphine in the rusty grain beetle, Cryptolestes ferrugineus (Laemophloeidae: Coleoptera). Pest Biochem Physiol 127:67–75
Kaur R, Nayak MK (2014) Developing effective fumigation protocols to manage strongly phosphine-resistant Cryptolestes ferrugineus (Stephens) (Coleoptera: Laemophloeidae). Pest Manag Sci 71:1297–1302
Kaur R, Schlipalius DI, Collins PJ, Swain AJ, Ebert PR (2012) Inheritance and relative dominance, expressed as toxicity response and delayed development, of phosphine resistance in immature stages of Rhyzopertha dominica (F.) (Coleoptera: Bostrichidae). J Stored Prod Res 51:74–80
Lindgren DL, Vincent LE (1966) Relative toxicity of hydrogen phosphide to various stored-product insects. J Stored Prod Res 2:141–146
Manivannan S (2015) Toxicity of phosphine on the developmental stages of rust-red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum Herbst over a range of concentrations and exposures. J Food Sci Technol 52:6810–6815
McCullagh P, Nelder JA (1989) Generalized linear models. Chapman and Hall, London
McKenzie JA (1996) Ecological and evolutionary aspects of insecticide resistance. RG Landes Company and Academic Press, Austin
Nayak MK, Holloway JC, Emery RN, Pavic H, Bartlet J, Collins PJ (2012) Strong resistance to phosphine in the rusty grain beetle, Cryptolestes ferrugineus (Stephens) (Coleoptera, Laemophloeidae): its characterisation, a rapid assay for diagnosis and its distribution in Australia. Pest Manag Sci 69:48–53
Nguyen TT, Collins PJ, Ebert PR (2015) Inheritance and characterization of strong resistance to phosphine in Sitophilus oryzae (L.). PLoS ONE 10:0124335. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0124335
Onstad DW (2008) Chapter 1 major issues in insect resistance management. In: Onstad DW (ed) Insect resistance management: biology, economics and prediction. Academic Press, London, pp 1–16
Onstad DW, Guse CA (2008) Chapter 4 concepts and complexities of population genetics. In: Onstad DW (ed) Insect resistance management: biology, economics and prediction. Academic Press, London, pp 69–88
Opit G, Collins PJ, Daglish GJ (2012) Ch 13 resistance management. In: Hagstrum D, Phillips TW, Cuperus G (eds) Stored product protection. Kansas State University, Manhattan KS, pp 143–155
Price NR, Bell CH (1981) Structure and development of embryos of Ephestia cautella (Walker) during anoxia and phosphine treatment. Int J Invert Rep 3:17–25
Rajendran S, Parveen H, Begumand K, Chethana R (2004) Influence of phosphine on hatching of Cryptolestes ferrugineus (Coleoptera: Cucujidae), Lasioderma serricorne (Coleoptera: Anobiidae) and Oryzaephilus surinamensis (Coleoptera: Silvanidae). Pest Manag Sci 60:1114–1118
Reed C (1997) Influence of grain temperature on efficacy of fumigation on leaky bins. In: Donahaye EJ, Navarro S, Varnava A (eds) Proceedings international conference on controlled atmosphere and fumigation in stored products, 21–26 April 1996. Nicosia, Cyprus, Printco Ltd, pp 235–242
Rilett RO (1949) The biology of Laemophloeus ferrugineus (Steph.). Can J Res Sec D Zool Sci 27:112–148
Robertson JL, Russell RM, Preisler HK, Savin NE (2007) Bioassays with arthropods. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Roush RT, Daley JC (1990) The role of population genetics in resistance research and management. In: Roush RT, Tabashnik BE (eds) Pesticide resistance in arthropods. Chapman and Hall, New York, pp 97–152
Stone BF (1968) A formula for determining degree of dominance in cases of monofactorial inheritance of resistance to chemicals. Bull World Health Organ 38:325–326
Tsai WT (2010) Environmental and health risks of sulfuryl fluoride, a fumigant replacement for methyl bromide. J Environ Sci Health Part C Environ Carcinog Ecotox Rev 28:125–145
Wang DX, Collins PJ, Gao XW (2006) Optimising indoor phosphine fumigation of paddy rice bag-stacks under sheeting for control of resistant insects. J Stored Prod Res 42:207–217
Winks RG, Waterford CJ (1986) The relationship between concentration and time in the toxicity of phosphine to adults of a resistant strain of Tribolium castaneum (Herbst). J Stored Prod Res 22:85–92
Acknowledgements
The senior author wishes to thank Prof Gimme Walter for supporting his training fellowship at the University of Queensland and Queensland Department of Agriculture and Fisheries. We acknowledge the support of the Australian Government’s Australia-India Strategic Research Funds (GCF010006 and AISRF48516), under which the research, training and analysis were completed. We thank Virgine T Singarayan, Hervoika Pavic and Linda Bond for excellent technical assistance. We thank Dr Greg Daglish for his constructive comments on the manuscript.
Funding
This study was in part funded by the Australian Government’s Australia-India Strategic Research Funds (Grant Numbers GCF010006 and AISRF48516).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by C.G. Athanassiou.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Venkidusamy, M., Jagadeesan, R., Nayak, M.K. et al. Relative tolerance and expression of resistance to phosphine in life stages of the rusty grain beetle, Cryptolestes ferrugineus . J Pest Sci 91, 277–286 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-017-0875-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-017-0875-7