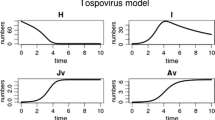
Abstract
Recent outbreaks of viral diseases of rice in east Asia are caused by migratory planthoppers. Epidemic models of these viral diseases are required to predict the annual emergence of the viruses based on established forecasting systems of outbreaks of the planthoppers. Here, we develop an epidemic model for southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus (SRBSDV), which is transmitted by the white-backed planthopper, Sogatella furcifera, as the first epidemic model of viruses borne by migratory planthoppers. The epidemic model, consisting of a Leslie model for the population dynamics of S. furcifera and a transmission model for SRBSDV, predicted a high contribution of the density of viruliferous immigrant S. furcifera to SRBSDV emergence. Early immigration of S. furcifera into paddy fields after transplanting of rice also promoted the virus epidemic primarily because of the emergence of viruliferous old nymphs during the period during which rice plants are susceptible to the virus. The epidemic model developed could be expanded to other planthopper-borne viruses and is effective for understanding the ecological aspects of virus epidemics in the field and for assessing the risk of viral diseases transmitted by migratory vectors.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amodeo MR, Zalba SM (2013) Wild cherries invading natural grasslands: unraveling colonization history from population structure and spatial patterns. Plant Ecol 214:1299–1307. doi:10.1007/s11258-013-0252-4
Bell JR, Aralimarad P, Lim KS, Chapman JW (2013) Predicting insect migration density and speed in the daytime convective boundary layer. PLoS ONE 8:e54202. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0054202
Chapman JW, Reynolds DR, Smith AD, Smith ET, Woiwod IP (2004) An aerial netting study of insects migrating at high altitude over England. Bull Entomol Res 94:123–136. doi:10.1079/BER2004287
Chapman JW, Drake VA, Reynolds DR (2011) Recent insights from radar studies of insect flight. Ann Rev Entomol 56:337–356. doi:10.1146/annurev-ento-120709-144820
Chapman JW, Bell JR, Burgin LE, Reynolds DR, Pettersson LB, Hill JK, Bonsall MB, Thomas JA (2012) Seasonal migration to high latitudes results in major reproductive benefits in an insect. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109:14924–14929. doi:10.1073/pnas.1207255109
Cunniffe NJ, Koskella B, Metcalf CJE, Parnell S, Gottwald TR, Gilligan CA (2015) Thirteen challenges in modelling plant diseases. Epidemics 10:6–10. doi:10.1016/j.epidem.2014.06.002
Cuong HV, Hai NV, Man VT, Matsumoto M (2009) Rice dwarf disease in North Vietnam in 2009 is cause by southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus (SRBSDV). Bull Inst Trop Agric Kyushu Univ 32:85–92. doi:10.11189/bita.32.85
Drake VA, Wang H (2013) Recognition and characterization of migratory movements of Australian plague locusts, Chortoicetes terminifera, with an insect monitoring radar. J Appl Remote Sens 7:075095. doi:10.1117/1.JRS.7.075095
Froissart R, Doumayrou J, Vuillaume F, Alizon S, Michalakis Y (2010) The virulence-transmission trade-off in vector-borne plant viruses: a review of (non-)existing studies. Phil Trans R Soc B. doi:10.1098/rstb.2010.0068
Greenslade P, Farrow RA, Smith JMB (1999) Long distance migration of insects to a subantarctic island. J Biogeogr 26:1161–1167. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2699.1999.00356.x
Hajano JUD, Wang B, Ren Y, Lu C, Wang X (2015) Quantification of southern rice black streaked dwarf virus and rice black streaked dwarf virus in the organs of their vector and nonvector insect over time. Virus Res 208:146–155. doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2015.06.015
Hibino H (1996) Biology and epidemiology of rice viruses. Ann Rev Phytopathol 34:249–274. doi:10.1146/annurev.phyto.34.1.249
Holt J, Mushobozi W, Day RK, Knight JD, Kimani M, Njuki J, Musebe R (2006) A simple Bayesian network to interpret the accuracy of armyworm outbreak forecasts. Ann Rev Appl Biol 148:141–146. doi:10.1111/j.1744-7348.2006.00050.x
Hunter D, Deveson T (2002) Forecasting and management of migratory pests in Australia. Insect Sci 9:13–25. doi:10.1111/j.1744-7917.2002.tb00168.x
Jabłońska-Sabuka M, Kalaria R, Kauranne T (2015) A dynamical model for epidemic outbursts by begomovirus population clusters. Ecol Model 297:60–68. doi:10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2014.11.008
Jeger MJ, Holt J, Van Den Bosch F, Madden LV (2004) Epidemiology of insect-transmitted plant viruses: modelling disease dynamics and control interventions. Physiol Entomol 29:291–304. doi:10.1111/j.0307-6962.2004.00394.x
Jeger M, Chen Z, Cunningham E, Martin G, Powell G (2012) Population biology and epidemiology of plant virus epidemics: from tripartite to tritrophic interactions. Eur J Plant Pathol 133:3–23. doi:10.1007/s10658-011-9913-0
Jia D, Chen H, Mao Q, Liu Q, Wei T (2012) Restriction of viral dissemination from the midgut determines incompetence of small brown planthopper as a vector of Southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus. Virus Res 167:404–408. doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2012.05.023
Jones R (2006) Control of plant virus diseases. Adv Virus Res 67:205–244. doi:10.1016/S0065-3527(06)67006-1
Kisimoto R (1967) Genetic variation in the ability of a planthopper vector; Laodelphax striatellus (Fallén) to acquire the rice stripe virus. Virology 32:144–152. doi:10.1016/0042-6822(67)90262-0
Lee BC, Yoon YN, Hong SJ, Hong YK, Kwak DY, Lee JH, Yae US, Kang HW, Hwang HG (2008) Analysis of the occurrence of Rice stripe virus. Res Plant Dis 14:210–213. doi:10.5423/RPD.2008.14.3.210
Leskinen M, Markkula I, Kostnen J, Pylkkö P, Ooperi S, Siljamo P, Ojanen H, Raiskio S, Tiilikkala K (2011) Pest insect immigration warning by an atmospheric dispersion model, weather radars and traps. J Appl Entomol 135:55–67. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0418.2009.01480.x
Lopes C, Péry ARR, Chaumot A, Charles S (2005) Ecotoxicology and population dynamics: using DEBtox models in a Leslie modeling approach. Ecol Model 188:30–40. doi:10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2005.05.004
Madden LV, Jeger MJ, van den Bosch F (2000) A theoretical assessment of the effects of vector-virus transmission mechanism on plant virus disease epidemics. Phytopathology 90:576–594. doi:10.1094/PHYTO.2000.90.6.576
Matsuhira K (2015) Risk of Southern rice black-streaked dwarf disease and its management. Green Rep 548:10–11 (in Japanese)
Matsukura K, Towata T, Sakai J, Onuki M, Okuda M, Matsumura M (2013) Dynamics of Southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus in rice and implication for virus acquisition. Phytopathology 103:509–512. doi:10.1094/PHYTO-10-12-0261-R
Matsukura K, Towata T, Yoshida K, Sakai J, Okuda M, Onuki M, Matsumura M (2015) Quantitative analysis of Southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus in Sogatella furcifera and virus threshold for transmission. Phytopathology 105:550–554. doi:10.1094/PHYTO-05-14-0142-R
Matsumura M, Sakai J (2011) Occurrence of new disease caused by Southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus transmitted by the whitebacked planthopper. Plant Prot 65:46–48 (in Japanese)
Matsumura M, Sanada-Morimura S (2010) Recent status of insecticide resistance in Asia rice planthoppers. Jpn Agric Res Q 44:225–230. doi:10.6090/jarq.44.225
Matsumura M, Sanada-Morimura S (2014) Factors affecting outbreaks of the brown planthopper in 2013 in Japan. Plant Prot 68:336–340 (in Japanese)
Matsumura M, Sanada-Morimura S, Otuka A, Ohtsu R, Sakumoto S, Takeuchi H, Satoh M (2014) Insecticide susceptibilities in populations of two rice planthoppers, Nilaparvata lugens and Sogatella furcifera, immigrating into Japan in the period 2005–2012. Pest Manag Sci 70:615–622. doi:10.1002/ps.3590
Meng X, Li Z (2010) The dynamics of plant disease models with continuous and impulsive cultural control strategies. J Thelor Biol 266:29–40. doi:10.1016/j.jtbi.2010.05.033
Miller DH, Jenesen AL, Hammill JH (2002) Density dependent matrix model for gray wolf population projection. Ecol Model 151:271–278. doi:10.1016/S0304-3800(01)00493-8
Miyai S, Hokyo N (1992) Modelling approach to simulate the progress of insect-borne rice virus disease in paddy fields. In: Shiyomi M, Yano E, Koizumi H, Andow DA, Hokyo N (eds) Ecological processes in agro-ecosystems. National Institute of Agro-Environmental Science, Tukuba, pp 139–154
Mollet HF, Cailliet M (2002) Comparative population demography of elasmobranchs using life history tables, Leslie matrices and stage-based matrix models. Mar Freshw Res 53:503–515. doi:10.1071/MF01083
Noda H (1989) Developmental zero and total effective temperature of three rice planthoppers (Homoptera: Delphacidae). Jpn J Appl Entomol 33:263–266. doi:10.1303/jjaez.33.263
Otuka A, Dudhia J, Watanabe T, Furuno A (2005a) A new trajectory analysis method for migratory planthoppers, Sogatella furcifera (Horváth) (Homoptera: Delphacidae) and Nilaparvata lugens (Stål), using an advanced weather forecast model. Agric For Entomol 7:1–9. doi:10.1111/j.1461-9555.2005.00236.x
Otuka A, Watanabe T, Suzuki Y, Matsumura M, Furuno A, Chino M (2005b) Real-time prediction system for migration of rice planthoppers Sogatella furcifera (Horváth) and Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) (Homoptera: Delphacidae). Appl Entomol Zool 40:221–229. doi:10.1303/aez.2005.221
Otuka A, Matsumura M, Sanada-Morimura S, Takeuchi H, Watanabe T, Ohtsu R, Inoue H (2010) The 2008 overseas mass migration of the small brown planthopper, Laodelphax striatellus, and subsequent outbreak of rice stripe disease in western Japan. Appl Entomol Zool 45:259–266. doi:10.1303/aez.2005.221
Otuka A, Zhou Y, Lee G, Matsumura M, Zhu Y, Park H, Liu Z, Sanada-Morimura S (2012) Prediction of overseas migration of the small brown planthopper, Laodelphax striatellus (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) in East Asia. Appl Entomol Zool 47:379–388. doi:10.1007/s13355-012-0130-x
Pedgley DE (1993) Managing migratory insect pests—a review. Int J Pest Manag 39:3–12. doi:10.1080/09670879309371751
Pu L, Xie G, Ji C, Ling B, Zhang M, Xu D, Zhou G (2012) Transmission characteristics of Southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus by rice planthoppers. Crop Prot 41:71–76. doi:10.1016/j.cropro.2012.04.026
Reynolds DR, Chapman JW, Harrington R (2006) The migration of insect vectors of plant and animal viruses. Adv Virus Res 67:453–517. doi:10.1016/S0065-3527(06)67012-7
Sanada-Morimura S, Sakumoto S, Ohtsu R, Otuka A, Huang S, Thanh DV, Matsumura M (2011) Current status of insecticide resistance in the small brown planthopper, Laodelphax striatellus, in Japan, Taiwan, and Vietnam. Appl Entomol Zool 46:65–73. doi:10.1007/s13355-010-0009-7
Sanada-Morimura S, Otuka A, Matsumura M, Etoh T, Zhu Y, Zhou Y, Zhang G (2015) Take-off time of the first generation of the overwintering small brown planthopper, Laodelphax striatellus in the temperate zone in east Asia. PLoS ONE 10:e0120271. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0120271
Sogawa K, Liu G, Teng K, Lin H, Shun L (1990) Mechanisms of varietal resistance to the whitebacked planthopper in a Chinese japonica rice “Chenjiang 06”. Kyushu Pl Prot Res 45:45–53. doi:10.4241/kyubyochu.45.45
Stinner RE (1983) Dispersal and movement of insect pests. Ann Rev Entomol 28:319–335. doi:10.1146/annurev.en.28.010183.001535
Tojo S, Ryuda M, Fukuda T, Matsunaga T, Choi DR, Otuka A (2013) Overseas migration of the common cutworm, Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), from May to mid-July in east Asia. Appl Entomol Zool 48:131–140. doi:10.1007/s13355-013-0162-x
Tu X, Li Z, Wang J, Huang X, Yang J, Fan C, Wu H, Wang Q, Zhang Z (2014) Improving the degree-day model for forecasting Locusta migratoria manilensis (Meyen) (Orthoptera: Acridoidea). PLoS ONE 9:e89523. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0089523
Wang HD, Chen JP, Zhang HM, Sun XL, Zhu JL, Wang AG, Sheng WX, Adams MJ (2008) Recent rice stripe virus epidemics in Zhejiang Province, China, and experiments on sowing date, disease—yield loss relationships, and seedling susceptibility. Plant Dis 92:1190–1196. doi:10.1094/PDIS-92-8-1190
Wang HD, Chen JP, Wang AG, Jiang XH, Adams MJ (2009) Studies on the epidemiology and yield loss from rice black-streaked dwarf disease in a recent epidemic in Zhejiang province, China. Plant Pathol 58:815–825. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3059.2009.02091.x
Wang ZC, Yu DD, Li XY, Zeng MJ, Chen Z, Bi L, Liu JJ, Jin LH, Hu DY, Yang S, Song BA (2012) The development and application of a dot-ELISA assay for diagnosis of southern rice black-streaked dwarf disease in the field. Viruses 4:167–183. doi:10.3390/v4010167
Watanabe T (1994) Population dynamics of long distance migratory planthoppers, Nilaparvata lugens Stål and Sogatella furcifera Horvath, and growth and yield analysis of rice plant infested with these planthoppers. Dissertation, Kyoto University
Watanabe T, Matsumura M, Otuka A (2009) Recent occurrence of long-distance migratory planthoppers and factors causing outbreaks in Japan. In: Heong HK, Hardy B (eds) Planthoppers: new threats to sustainability of intensive rice production systems in Asia. International Rice Research Institute, Los Baños, pp 179–190
Yoshida K, Matsukura K, Sakai J, Onuki M, Sanada-Morimura S, Towata T, Matsumura M (2014) Seasonal occurrence of Laodelphax striatellus (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) in a rice-forage crops mixed cropping area in central Kyushu, Japan. Appl Entomol Zool 49:475–481. doi:10.1007/s13355-014-0275-x
Zhang XS, Holt J, Colvin J (2000) A general model of plant-virus disease infection incorporating vector aggregation. Plant Pathol 49:435–444. doi:10.1046/j.1365-3059.2000.00469.x
Zhou G, Wen J, Cai D, Li P, Xu D, Zhang S (2008) Southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus: a new proposed Fijivirus species in the family Reoviridae. Chin Sci Bull 53:3677–3685. doi:10.1007/s11434-008-0467-2
Zhou T, Du L, Lan Y, Sun F, Fan Y, Zhou Y (2014) Development of SYBR Green I-based one-step real time RT-PCR assay for quantifying Southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus in rice. J Phytopathol 162:26–32. doi:10.1111/jph.12152
Acknowledgements
We thank Robert Cowie of the University of Hawaii for editorial help with the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the program of research and development projects for application in promoting new policy on agriculture, forestry and fisheries (ID: 23034) from the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All three authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Data accessibility
(1) The Leslie matrix projection: uploaded as online supporting figures. (2) Equations to determine parameter values related to the population growth of S. furcifera and a result of a comparison between simulated and actual emergence peaks of S. furcifera at the first and second generations: uploaded as online supporting tables.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by M. Traugott.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsukura, K., Watanabe, T. & Matsumura, M. An epidemic model of a rice virus transmitted by a migratory planthopper. J Pest Sci 90, 669–682 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-016-0811-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-016-0811-2