Abstract
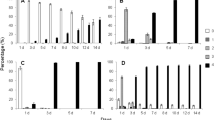
As very little is known about the impact of cold pre-treatments on insecticidal toxicity to the surviving stored-product insects, we examined the effects of cooling (−5 °C) on the toxicity of five contact insecticides to Sitophilus granarius adults from three populations (laboratory, field and selected). We determined: (a) weevil lethal time after exposure to −5 °C, (b) the effects of two cold pre-treatments (LT20 and LT50—lethal time for 20 and 50 % of exposed adults) on 24 and 72 h recovery rates of laboratory adults after exposure to five insecticides and (c) deltamethrin, dichlorvos and malathion toxicity to two weevil populations with altered insecticide susceptibility after exposure to the LT20 and LT50 pre-treatments. The tested S. granarius populations showed no significant differences in their susceptibility to cooling. All insecticides except dichlorvos were more toxic to the laboratory weevils after 24 h than after 72 h recovery from the LT20 pre-treatment. Dichlorvos and deltamethrin were more toxic to the other two populations after 72 h of recovery. Comparing the effects of cold pre-treatment and non-treatment on the laboratory strain, no significant increase in the toxicity of insecticides was detected, while only deltamethrin was significantly more toxic to the field and selected populations recovering for 24 h (12.1 and 11.0 times, respectively) and 72 h (6.9 and 36.6 times) from the LT20 pre-treatment. In conclusion, only the shorter of the two cold pre-treatments was found effective in terms of increasing the insecticidal toxicity, especially against the populations with altered susceptibility to insecticides.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott WS (1925) A method of computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. J Econ Entomol 18:265–267
Arthur FH, Dowdy AK (2003) Impact of high temperatures on efficacy of cyflutrin and hydroprene applied to concrete to control Tribolium castaneum (Herbst). J Stored Prod Res 39:193–204
Burks CS, Johnson JA, Maier DE, Heaps JW (2000) Temperature. In: Subramanyam B, Hagstrum DW (eds) Alternatives to pesticides in stored-product IPM. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston, pp 73–104
Busvine JR (1971) A critical review of the techniques for testing insecticides. Commonwealth Agricultural Bureau, Wallingford
Busvine JR (1980) Recommended methods for measurement of pest resistance to pesticides. FAO Plant Production and Protection Paper 21:77–90
Davis R, Bry RE (1985) Sitophilus granarius, Sitophilus oryzae and Sitophilus zeamais; Tribolium confusum and Tribolium castaneum. In: Singh P, Moore RF (eds) Handbook of Insect Rearing, vol I. Elsevier, Amsterdam-Oxford-NewYork-Tokyo, pp 287–293
Fields PG (1992) The control of stored-product insects and mites with extreme temperatures. J Stored Prod Res 28:89–118
Fields PG (2001) Control of insects in post-harvest: low temperature. In: Vincent C, Panneton B, Fleurat-Lessard F (eds) Physical control methods in plant protection. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 95–110
Fields PG (2006) Alternatives to chemical control of stored product insects in temperate regions. In: Lorini I,Bacaltchuk B, Beckel H, Deckers D, Sunfield E, Dos Santos JP, Biagi JD, Celaro JC, D’A Faroni LR, Bortolini L, de OF, Sartori MR, Elias MC, Guedes RNC, Da Fonseca RG, Scussel VM (eds) Proceedings of the 9th international working conference on stored product protection, 15–18 October 2006, Campinas, Sao Paulo, Brazil, Brazilian Post Harvest Association, Campinas, Brazil, pp 653–662
Fields PG, White NDG (2002) Alternatives to methyl bromide treatments for stored-product and quarantine insects. Annu Rev Entomol 47:331–359
Fields PG, Fleurat-Lessard F, Lavenseau L, Febvay G, Peypelut L, Bonnot G (1998) The effect of cold acclimation and deacclimation on cold tolerance, trehalose and free amino acid levels in Sitophilus granarius and Cryptolestes ferrugineus (Coleoptera). J Insect Physiol 44:955–965
Finney DJ (1971) Probit analysis, 3rd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Fontenot EA, Arthur FH, Nechols JR, Throne JE (2012) Using a population growth model to simulate response of Plodia interpunctella Hubner populations to timing and frequency of insecticide treatments. J Pest Sci 85:469–476
Haliscak JP, Beeman RW (1983) Status of malathion resistance in five genera of beetles infesting farm-stored corn, wheat and oats in the United States. J Econ Entomol 76:717–722
Harein CR, Soderstrom EL (1966) Coleoptera infesting stored products. In: Smith CN (ed) Insect colonization and mass production. Academic Press, New York and London, pp 241–257
Jankov D, Inđić D, Kljajić P, Almaši R, Andrić G, Vuković S, Grahovac M (2013) Initial and residual efficacy of insecticides on different surfaces against rice weevil Sitophilus oryzae (L.). J Pest Sci 86:211–216
Kljajić P, Perić I (2006) Susceptibility to contact insecticides of granary weevil Sitophilus granarius (L.) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) originating from different locations in the former Yugoslavia. J Stored Prod Res 42:149–161
Kljajić P, Perić I (2007) Altered susceptibility of granary weevil Sitophilus granarius (L.) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) populations to insecticides after selection with pirimiphos-methyl and deltamethrin. J Stored Prod Res 43:134–141
Kljajić P, Perić Ž, Perić I (1994) Interaction between extreme temperatures and insecticide effects on granary weevil (Sitophilus granarius L.) adults. Pesticides 9:57–63 (in Serbian with abstract in English)
Kljajić P, Perić Ž, Perić I (1996) Lethal effects of extreme temperatures on granary weevil adults Sitophilus granarius (L.) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Pesticides 11:195–202 (in Serbian with abstract in English)
Kljajić P, Andrić G, Perić I (2009) Impact of short-term heat pre-treatment at 50°C on the toxicity of contact insecticides to adults of three Sitophilus granarius (L.) populations. J Stored Prod Res 45:272–278
Phillips TW, Throne JE (2010) Biorational approaches to managing stored-product insects. Annu Rev Entomol 55:375–397
Pozidi-Metaxa E, Athanassiou CG (2013) Comparison of spinosad with three traditional grain protectants against Prostephanus truncatus (Horn) and Ephestia kuehniella (Zeller) at different temperatures. J Pest Sci 86:203–210
Raymond M (1985) Presentation d′un programme 2Basic2 d′analyse log-probit pour micro-ordinnateur. Cahier ORSTOM, série. Entomologie, Médecine et Parasitologie 22:117–121
Subramanyam B, Hagstrum DW (1996) Resistance measurement and management. In: Subramanyam B, Hagstrum DW (eds) Integrated management of insects in stored products. Marcel Dekker Inc, New York, pp 331–397
Tyler PS, Binns TJ (1982) The influence of temperature on the susceptibility to eight organophosphorus insecticides of susceptible and resistant strains of Tribolium castaneum, Oryzaephilus surinamensis and Sitophilus granarius. J Stored Prod Res 18:13–19
Vincent C, Hallman G, Panneton B, Fleurat-Lessard F (2003) Management of agricultural insects with physical control methods. Annu Rev Entomol 48:261–281
Wijayaratne LKW, Fields PG (2010) Effect of methoprene on the heat tolerance and cold tolerance of Tribolium castaneum (Herbst) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). J Stored Prod Res 46:166–173
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the Serbian Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development, Grant No.: III 46008.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by C. G. Athanassiou.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kljajić, P., Andrić, G., Pražić-Golić, M. et al. The effects of cold pre-treatment on the toxicity of several contact insecticides on adults of three Sitophilus granarius (L.) populations. J Pest Sci 87, 301–308 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-014-0552-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-014-0552-z