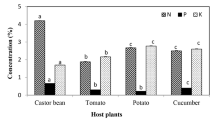Abstract
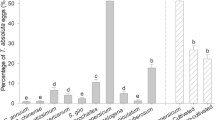
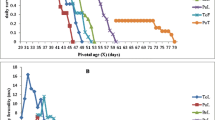
The effect of various host plants; chickpea (varieties Arman, Hashem, Azad and Binivich), bean varieties (Phaseolus vulgaris L.), common bean (Khomein), white kidney bean (Dehghan), red kidney bean (Goli), cowpea (variety Mashhad) and tomato (variety Meshkin) on the life table parameters of the cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) were evaluated under laboratory conditions (25 ± 1 °C, 65 ± 5 % RH and a 16:8 h light:dark photoperiod). Records for larval period, pupal period, and development time of H. armigera were longest on tomato (24.9, 15.1, and 45.4 days, respectively) and shortest on chickpea Arman (17.5, 9.1, and 31.7 days, respectively). Among various host plants fecundity (total number of eggs laid per female) was highest (2,665 eggs) on chickpea Arman and the lowest (700 eggs) on tomato. The net reproductive rate (R 0) was significantly affected by various host plants being highest on chickpea Arman (1,422) and lowest on tomato (111.3 females/female/generation). The highest and lowest intrinsic rates of natural increase (r m) were observed on chickpea Arman (0.244 day−1) and tomato (0.123 day−1) varieties, respectively. Cluster analysis of the life table parameters of H. armigera on various host plants indicated that tomato, in comparison to other plants was an unsuitable host to H. armigera.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrewartha HG, Birch LC (1954) The distribution and abundance of animals. University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Awmack CS, Leather SR (2002) Host plant quality and fecundity in herbivorous insects. Annu Rev Entomol 47:817–844
Birch LC (1948) The intrinsic rate of natural increase of an insect population. J Anim Ecol 17:15–26
Borah SR, Dutta SK (2002) Biology of gram pod borer, Helicoverpa armigera (Hub.) on pigeon pea. J Agric Sci Soc North-East India 15:34–37
Carey JR (2001) Insect biodemography. Annu Rev Entomol 46:79–110
Dhandapani N, Balasubramanian M (1980) Effect of different food plants on the development and reproduction of Heliothis armigera (Huber). Experientia (Basel) 36:930–931
Drake VA (1991) Methods for studying adult movement in Heliothis. In: Zalucki MP (ed) Heliothis: research methods and prospects. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 109–121
Du L, Ge F, Zhu S, Parajulee MN (2004) Effect of cotton cultivar 404 on development and reproduction of Aphis gossypii (Homoptera: Aphididae) and its predator Propylaea japonica (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). J Econ Entomol 97:1278–1283
Fitt GP (1989) The ecology of Heliothis species in relation to agroecosystem. Annu Rev Entomol 34:17–52
Gilbert N, Raworth DA (1996) Insect and temperature, a general theory. Can Entomol 128:1–13
Goyal SP, Rathore VS (1988) Patterns of insect–plant relationship determining susceptibility of different hosts to Heliothis armigera (Hübner). Indian J Entomol 50:193–201
Green PWC, Stevenson PC, Simmonds MSJ, Sharma HC (2002) Can larvae of the pod borer, Helicoverpa armigera (Noctuidae: Lepidoptera), select between wild and cultivated pigeonpea Cajanus sp., Fabaceae? Bull Entomol Res 92:45–51
Greenberg SM, Sappington TW, Legaspi BC, Liu TX, Setamou M (2001) Feeding and life history of Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) on different host plants. Ann Entomol Soc Am 94:566–575
Hemati SA, Naseri B, Ganbalani GN, Dastjerdi HR, Golizadeh A (2012a) Effect of different host plants on nutritional indices of the pod borer, Helicoverpa armigera. J Insect Sci 12: 55. Available online: insectscience.org/12.55
Hemati SA, Naseri B, Ganbalani GN, Dastjerdi HR, Golizadeh A (2012b) Digestive proteolytic and amylolytic activities and feeding responses of Helicoverpa armigera (Noctuidae: Lepidoptera) on different host plants. J Econ Entomol 105(4):1439–1446
Hemati SA, Naseri B, Razmjou J (2013) Reproductive performance and growth indices of cotton bollworm Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) on various host plants. J Crop Prot 2(2):193–208
Hochberg ME (1987) The within-plant distribution and feeding behaviour of Heliothis armigera Hübner (Lep., Noctuidae) on greenhouse tomatoes. J Appl Entomol 104:256–261
Hwang SY, Liu CH, Shen TC (2008) Effects of plant nutrient availability and host plant species on the performance of two Pieris butterflies (Lepidoptera: Pieridae). Biochem Syst Ecol 36:505–513
Jallow MFA, Zalucki MP (1996) Within and between population variation in host plant preference and specificity in Australian Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Aust J Zool 44(5):503–519
Jallow MFA, Zalucki MP (2003) Relationship between oviposition preference and offspring performance in Australian Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Aust J Entomol 42:343–348
Jallow MFA, Cunningham JP, Zalucki MP (2004) Intra-specific variation for host plant use in Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae): implications for management. Crop Prot 23:955–964
Jones D, Jones G, Hammock BD (1981) Growth parameters associated with endocrine events in larval Tricoplusia ni (Hübner) and timing of these events with developmental markers. J Insect Physiol 27:779–788
Kulkarni US, Gawande RB, Kulkarni SS, Yadgirwar PV (2004) Comparative studies on the biology of Helicoverpa armigera on different food substrates. J Soils Crops 14:207–208
Kyi A, Zalucki MP, Titmarsh IJ (1991) An experimental study of early stage survival of Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) on cotton. Bull Entomol Res 81:263–271
Liu ZD, Li DM, Gong PY, Wu KJ (2004) Life table studies of the cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), on different host plants. Environ Entomol 33:1570–1576
Lokar MK, Rahoo GM, Rind AW (1993) Effect of food plants on the development of cutworm species, Heliothis armigera (Hübner) and Spodoptera litura F. In: Ahmed M, Sakoori AR (eds) Proceedings of Pakistan Congress of Zoology, Publications of Zoological Society of Pakistan, Pakistan 13: 225–233
Maelzer DA, Zalucki MP (1999) Analysis and interpretation of long-term light trap data for Helicoverpa spp. (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in Australia: the effect of climate and crop host plants. Bull Entomol Res 89:455–464
Maia AHN, Luiz AJB, Campanhola C (2000) Statistical inference on associated fertility life table parameters using jackknife technique: computational aspects. J Econ Entomol 93:511–518
Minitab Inc (1994) Philadelphia
Moral Garcia FJ (2006) Analysis of the spatio-temporal distribution of Helicoverpa armigera (Huber) in a tomato fields using a stochastic approach. Biosyst Eng 93:253–259
Naseri B, Fathipour Y, Moharramipour S, Hosseininaveh V (2009a) Comparative life history and fecundity of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) on different soybean varieties. Entomol Sci 12:147–154
Naseri B, Fathipour Y, Moharramipour S, Hosseininaveh V (2009b) Life table parameters of the cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera (Lep.: Noctuidae) on different soybean cultivars. J Entomol Soc Iran 29(1):25–40
Naseri B, Fathipour Y, Moharramipour S, Hosseininaveh V (2011) Comparative reproductive performance of Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) reared on thirteen soybean varieties. J Agric Sci Technol 13:17–26
Patal CC, Koshyia DJ (1997) Life table and innate capacity of Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) on pearl millet. Indian J Entomol 59(4):389–395
Perkins LE, Cribb BW, Hanan J, Golan E, Beveridge C, Zalucki MP (2008) Where to from here? The mechanisms enabling movement of Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) first instar larvae on pea plants. Arthropod–Plant Interact 2:197–207
Perkins LE, Cribb BW, Hanan J, Zalucki MP (2009) The role of two plant-derived volatiles in the foraging movement of 1st instar Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner): time to stop and smell the flowers. Arthropod–Plant Interact 3:173–179
Rajapakse CNK, Walter GH, Moore CJ, Hull CD, Cribb BW (2006) Host recognition by a polyphagous lepidopteran (Helicoverpa armigera): primary host plants, host produced volatiles and neurosensory stimulation. Physiol Entomol 31:270–277
Razmjou J, Moharramipour S, Fathipour Y, Mirhoseini SZ (2006) Effect of cotton cultivar on performance of Aphis gossypii (Homoptera: Aphididae) in Iran. J Econ Entomol 99:1820–1825
Reddy KS, Rao GR, Rao PA, Rajasekhar P (2004) Life table studies of the capitulum borer, Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) infesting sunflower. J Entomol Res 28:13–18
Ruan YM, Wu KJ (2001) Performances of the cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera on different food plants. Acta Entomol Bohemoslov 44:205–212
Sachan JN (1990) Progress in host–plant resistance work in chickpea and pigeonpea against Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner). In: Summary proceedings of the first consultative group meeting on the host selection behavior of Helicoverpa armigera, ICRISAT, p 19–22
Saeed S, Sayyed AH, Ahmad I (2009) Effect of host plants on life-history traits of Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J Pest Sci 83:165–172
Saour G, Causse R (1996) Feeding behavior of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) on tomatoes. J Appl Entomol 120:87–92
Sarfraz M, Dosdall LM, Keddie BA (2006) Diamondback moth-host plant interactions: implications for pest management. Crop Prot 25:625–636
Schellhorn NA, Pierce S, Bianchi FJJA, Williams D, Zalucki MP (2008) Designing landscapes for multiple outcomes in broad-acre environments. Aust J Exp Agric 48:1549–1559
Shorey HH, Hale RL (1965) Mass-rearing of the larvae of nine noctuid species on a simple artificial medium. J Econ Entomol 58:522–524
Singh AK, Mullick S (1997) Effect of leguminous plants on the growth and development of gram pod borer, Helicoverpa armigera. Indian J Entomol 59:209–214
Singh OP, Parihar SBB (1988) Effect of different hosts on the development of Heliothis armigera Hub. Bull Entomol 29:168–172
Sison MLJ, Shanower TG (1994) Development and survival of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) on short duration pigeon pea. J Econ Entomol 32:1749–1753
Soleimannejad S, Fathipour Y, Moharrampour S, Zalucki MP (2010) Evaluation of potential resistance in seeds of different soybean cultivars to Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) using demographic parameters and nutritional indices. J Econ Entomol 103:1420–1430
Southwood TRE, Henderson PA (2000) Ecological methods, 3rd edn. Blackwell Science, Oxford, p 592
Syed TS, Abro GH (2003) Effect of Brassica vegetable hosts on biology and life table parameters of Plutella xylostella under laboratory conditions. Pak J Biol Sci 6:1891–1896
Talekar NS, Opena RT, Hanson P (2006) Helicoverpa armigera management: a review of AVRDC’s research on host plant resistance in tomato. Crop Prot 25:461–467
Umbanhowar J, Hastings A (2002) The impact of resource limitation and phenology of parasitoid attack on the duration of insect herbivore outbreaks. Theor Popul Biol 62:259–269
Zalucki MP, Furlong MJ (2005) Forecasting Helicoverpa populations in Australia: a comparison of regression based models and a bio-climatic based modelling approach. Insect Sci 12(1):45–56
Zalucki MP, Daglish G, Firempong S, Twine P (1986) The biology and ecology of Heliothis armigera (Hübner) and Heliothis punctigera Wallengren (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in Australia: what do we know? Aust J Zool 34:779–814
Zalucki MP, Clarke AR, Malcolm SB (2002) Ecology and behavior of first instar larval Lepidoptera. Annu Rev Entomol 47:361–393
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge S. Keyani and N. Esmaeili (from University of Mohaghegh Ardabili) for their valuable help in this study. Special thanks to L. Mottaghinia from University of Mohaghegh Ardabili for the reviewing and improving of the manuscript. This work is financially supported by the University of Mohaghegh Ardabili, (Ardabil, Iran), which is appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by T. Haye.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Razmjou, J., Naseri, B. & Hemati, S.A. Comparative performance of the cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) on various host plants. J Pest Sci 87, 29–37 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-013-0515-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-013-0515-9