Abstract
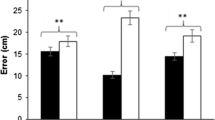
Gaze patterns and verbal reports of golfers at three skill levels (professional, elite amateur and club) were recorded as they read the slope of a virtual golf green from six different positions. The results showed that the professional golfers used a more economical gaze pattern consisting of fewer fixations of longer duration than the amateur and club players. Gaze pattern was accompanied by verbal reports that were not significantly more accurate in terms of aiming accuracy, although the professionals were accurate on 76.5 % of putts compared to 57.1 % for the elite and club groups. Two read positions lead to more accurate predictions by the professional golfers only, suggesting distinctive periods of visual perceptual–cognitive attention may underly higher levels of putting skill. Theoretical implications of these results are discussed in relation to the application of visual attention theory to practise, as well as suggestions provided for further research.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abernethy B (1990) Expertise, visual search, and information pick-up in squash. Perception 19:63–77
Autodesk (2006) 3D Studio Max. http://www.autodesk.com/products/autodesk-3ds-max/overview
Beilock SL, Afremow JA, Rabe AL, Carr TH (2001) “Don’t miss!” The debilitating effects of suppressive imagery on golf putting performance. J Sport Exerc Psychol 23:200–221
Beilock SL, Carr TH, MacMahon C, Starkes JL (2002a) When paying attention becomes counterproductive: impact of divided versus skill-focused attention on novice and experienced performance of sensorimotor skills. J Exp Psychol Appl 8:6–16
Beilock SL, Wierenga SA, Carr TH (2002b) Expertise, attention and memory in sensorimotor skill execution: impact of novel task constraints on dual-task performance and episodic memory. Q J Exp Psychol Hum Exp Psychol Sect A 55:1211–1240
Beilock SL, Wierenga SA, Carr TH (2003) Memory and expertise: What do experienced athletes remember? In: Starkes JL, Ericsson KA (eds) Recent advances in research on sport expertise. Human Kinetics, Champaign, pp 295–320
Bertrand C, Thullier F (2009) Effects of player position task complexity in visual exploration behavior in soccer. Int J Sport Psychol 40:306–323
Bilalic M, McLeod P, Gobet F (2009) Specialization effect and its influence on memory and problem solving in expert chess players. Cogn Sci 33:1117–1143
Campbell M (2006) An empirical investigation of expertise in golf putting and green-reading. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, University College, Dublin, Ireland
Causer J, Holmes PS, Smith NC, Williams AM (2011) Anxiety, movement kinematics and visual attention in elite level performers. Emotion 11(3):595–602
Correia V, Araujo D, Cummins A, Craig CM (2012) Perceiving and acting upon spaces in a virtual reality rugby task: expertise effects in affordance detection and task achievement. J Sport Exerc Psychol 34:252–259
Craig CM, Delay D, Grealy MA, Lee DN (2000) Guiding the swing in golf putting. Nature 405(6784):295–296
Crews DJ, Landers DM (1993) Electroencephalographic measures of attentional patterns prior to the golf putt. Med Sci Sports Exerc 25(1):116–126
Dicks M, Button C, Davids K (2010) Examination of gaze behaviours under in situ and visuo simulation task constraints reveals differences in information pickup for perception and action. Atten Percept Psychophys 72(3):706–720
Gegenfurtner A, Lehtinen E, Säljö R (2011) Expertise differences in the comprehension of visualizations: a meta-analysis of eye-tracking research in professional domains. Educ Psychol Rev 23:523–552. doi:10.1007/s10648-011-9174-7
Greene HH (2006) The control of fixation duration in visual search. Perception 35:303–315
Harle S, Vickers JN (2001) Training quiet eye (QE) to improve shooting accuracy in the basketball free throw. Sport Psychol 15:289–305
Helsen WE, Starkes JL (1999) A multidimensional approach to skilled perception and performance in sport. Appl Cogn Psychol 13:1–27
Hodges NJ, Starkes JL, MacMahon C (2006) Expert performance in sport: a cognitive perspective. In: Ericsson KA, Charness N, Feltovich PJ, Hoffman RR (eds) The Cambridge handbook of expertise and expert performance. Cambridge University Press, New York, pp 471–488
Hung GK (2003) Effect of putting grip on eye and head movements during the golf putting stroke. Sci World J 24:122–137
Interactive Minds Dresden (2005) NYAN eye-tracking analysis software, version 1. www.eyegaze.com
Kahneman D, Klein, G (2009) Conditions for intuitive expertise: a failure to disagree. Am Psychol 64(6):515-526. doi:10.1037/a0016755
Konstantopoulos P (2009) Investigating drivers visual search strategies: towards an efficient training intervention. Unpublished doctoral thesis, University of Nottingham, Nottingham, England
Kornspan AS, Overby LY, Lerner BS (2004) Analysis and performance imagery and other strategies on a golf putting task. J Ment Imag 28:59–74
LC Technologies (2005) http://www.eyegaze.com/eye-gaze-tracker/
Libet B (2004) Mind time: the temporal factor in consciousness. Perspect Cogn Neurosci. Harvard University Press
Litchfield D, Ball LJ, Donovan T, Manning DJ, Crawford T (2008) Learning from others: effects of viewing another person’s eye movements while searching for chest nodules. In: Sahiner B, Manning DJ (eds) Medical imaging 2008: image perception, observer performance, and technology assessment, vol 6917. SPIE, Bellingham, pp 691715–691719
Mackenzie SJ, Sprigings EJ (2005) Evaluation of the plumb bob method for reading greens in putting. J Sports Sci 23:81–87
Martell SG, Vickers JN (2004) Gaze characteristics of elite and near-elite athletes in ice hockey defensive tactics. Hum Mov Sci 21:689–712
Moran A, Byrne A, McGlade N (2002) The effects of anxiety and strategic planning on visual search behaviour. J Sports Sci 20:1–12
Müller S, Abernethy B, Farrow D (2006) How do world-class cricket batsmen anticipate a bowler’s intention? Q J Exp Psychol 59:2162–2186
Parry D, Chinnasamy C, Micklewright D (2012) Optic flow influences perceived exertion during cycling. J Sport Exerc Psychol 34:444–456
Pelz D (1994) A study of golfers abilities to read greens. In: Cochran AJ, Farrelly MR (eds) Science and golf II. Proceedings of the 1994 world scientific congress of golf. E & F.N. Spon, London, pp 180–185
Pelz D (2000) Dave Pelz’s putting bible. Aurum, London
Perkins-Ceccato N, Passmore SR, Lee TD (2003) Effects of focus of attention depend on golfers’ skill. J Sports Sci 21:593–600
PGA (2011) Putting statistics. http://www.pgatour.com/r/stats/info/wm3.html?104. Retrieved 2 Dec 2012
Rey G, Buchwald F (2011) The expertise reversal effect: cognitive load and motivational explanations. J Exp Psychol Appl 17(1):33–48
Ripoll H, Kerlirzin Y, Stein JF (1993) Cognition and decision making in externally-paced sport situation: French boxing. In: Serpa S, Alves J, Ferreira V, Paula-Britto A (eds) Sport psychology: an integrated approach. Proceedings of the 8th world congress on sport psychology (pp. 383–386). University of Lisboa Press, Lisboa
Roberts JR, Jones R, Rothberg SJ, Mansfield NJ, Meyer C (2005) The feel of a golf shot: a major factor in golf equipment selection. The Impact of Technology on Sport. In: Subic A, Ujhashi S (eds) ASTA, proceedings of the Asia-Pacific congress on sports technology, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Sept, pp 20–26
Ross PE (2006) The expert mind. Sci Am 295:64–71
Ross JS, Thach J, Ruggieri PM, Lieber M, Lapresto E (2003) The mind’s eye: functional MR imaging evaluation of golf motor imagery. Am J Neuroradiol 24(6):1036–1044
Short SE, Bruggeman JM, Engel SC, Marback TL, Wang LJ, Willadsen A, Short MW (2002) The effect of imagery function and imagery direction on self-efficacy and performance on a golf-putting task. Sport Psychol 16:48–67
Singer RN, Cauragh JH, Chen D, Steinberg GM, Frehlich SG (1996) Visual search, anticipation, and reactive comparisons between highly-skilled and beginning tennis players. J Appl Sport Psychol 8:9–26
Utley S, Rudy M (2006) The art of putting. Penguin, London
Van Lier WH, van der Kamp J, Savelsbergh G (2011) Perception and action in golf putting: skill differences reflect calibration. J Sport Exerc Psychol 33:349–369
Vickers JN (1992) Gaze control in putting. Perception 21:117–132
Vickers JN (1996) Visual control when aiming at a far target. J Exp Psychol Hum Percept Perform 22:342–354
Vickers JN (2006) Gaze of Olympic speed skaters while skating at full speed on a regulation oval. Perception–action coupling in a dynamic performance environment. Cogn Process 7:102–105
Vickers JN (2007) Perception, cognition and decision training: the quiet eye in action. Human Kinetics, Champaign
Vickers JN, Adolphe RM (1997) Gaze behaviour during a ball tracking and aiming skill. Int J Sports Vis 4:18–27
Vickers JN, Rodrigues ST, Brown LN (2002) Gaze pursuit and arm control of adolescent males diagnosed with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and normal controls: evidence of a disassociation in processing visual information of short and long duration. J Sport Sci 20:1–16
Vine SJ, Moore LJ, Wilson MR (2011) Quiet eye training facilitates competitive putting performance in elite golfers. Front Psychol 2. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2011.00008
Vogt S, Magnussen S (2007) Expertise in pictorial perception: eye movement patterns and visual memory in artists and laymen. Perception 36:91–100
Ward P, Williams AM, Hancock PA (2006) Simulation for performance and training. In: Ericsson KA, Charness N, Feltovich PJ, Hoffman RR (eds) The Cambridge handbook of expertise and expert performance. Cambridge University Press, New York, pp 243–262
Williams AM, Davids K, Williams JG (1999) Visual perception and action in sport. E. & F. N. Spon, London
Williams AM, Singer RN, Frehlich S (2002) Quiet eye duration, expertise, and task complexity in near and far aiming tasks. J Mot Behav 34:197–207
Wilson MR, Pearcy RC (2009) Visuomotor control of straight and breaking golf putts. Percept Mot Skills 109:1–8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Campbell, M.J., Moran, A.P. There is more to green reading than meets the eye! Exploring the gaze behaviours of expert golfers on a virtual golf putting task. Cogn Process 15, 363–372 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10339-014-0608-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10339-014-0608-2