Abstract
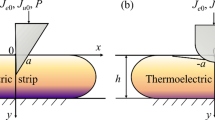
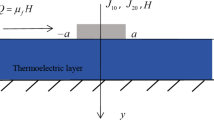
In this paper, the thermo-electro-mechanical coupling contact problem of thermoelectric material with double punches is analyzed accurately. Using the Fourier cosine transform technique, the thermo-electro-elastic problem is transformed into three sets of singular integral equations, which are numerically solved by the Gauss–Chebyshev integral formula according to the unknown normal electric current density, normal energy flux and normal contact stress. For a rigid flat indenter, the results can be covered by the degradation results of two rigid flat indenters. The numerical results reveal the interaction between two punches and the effect of thermoelectric load on the indentation behaviors. The interaction between the two punches reduces the contact pressure at the inner edge of the indenter as the thermoelectric load increases while increasing the stress singularity at the outer edge. The change of punches’ spacing makes the singularity of normal stress at the inner and outer edges asymmetric. The results provide an in-depth understanding of the multi-region contact damage mechanism of thermoelectric material.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hertz H. On the contact of elastic solids. Reine Angew Math. 1882;92:156–71.
Muskhelishvili NT. Singular integral equations. Moscow: Nauka; 1946.
Galin LA. Contact problems in the theory of elasticity, translated from Rassian, ed. I. N. Sneddon. North Carolina State University. 1961.
Gladwell GML. Contact problems in the classical theory of elasticity. The Netherlands: Sijthoff and Noordhoff, Aalphen aan den Rijn. 1980.
Sneddon IN. Fourier transforms. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1954.
Ratwani M, Erdogan F. On the plane contact problem for frictionless elastic layer. Int J Solids Struct. 1973;9(8):921–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/0020-7683(73)90021-8.
Civelek MB, Erdogan F. The axisymmetric double contact problem for a frictionless elastic layer. Int J Solids Struct. 1974;10(6):639–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/0020-7683(74)90048-1.
Barber JR. Contact mechanics. In Solid mechanics and its applications. 2018.
Cai BW, Hu HH, Zhuang HL, Li JF. Promising materials for thermoelectric applications. J Alloy Compd. 2019;806:471–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.07.147.
Sanjeev KB, Anil K, Suresh KG. Bismuth telluride (Bi2Te3) thermoelectric material as a transducer for solar energy application. Mater Today Proc. 2020;26:3131–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.02.646.
Sajid M, Hassan I, Rahman A. An overview of cooling of thermoelectric devices. Renew Sust Energ Rev. 2017;78:15–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.04.098.
Mao J, Chen G, Ren ZF. Thermoelectric cooling materials. Nat Mater. 2020;20(4):454–61. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-020-00852-w.
Barako MT, Park W, Marconnet AM, Asheghi M, Goodson KE. Thermal cycling, mechanical degradation, and the effective figure of merit of a thermoelectric module. J Electron Mater. 2013;42(3):372–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-012-2366-1.
Tian XJ, Zhou YT, Guan XF, Wang LH, Ding SH. The frictional contact problem of a rigid punch sliding over thermoelectric materials. Int J Solids Struct. 2020;200:145–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2020.04.034.
Ozsahin TS, Taskiner O. Contact problem for an elastic layer on an elastic half plane loaded by means of three rigid flat punches. Math Probl Eng. 2013;2013:137427. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/137427.
Danouni S, Zamree AR, Abdellah E, Mat SN. Thermo elasto-plastic contact analysis for high temperature applications. Therm Sci. 2021. https://doi.org/10.2298/TSCI201026276D.
Li JE, Wang BL, Zhang C. Thermal and electrical electrode/punch problem of thermoelectric materials. Inter J Heat Mass Tran. 2019;143:118504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2019.118504.
Zhou YT, Tian XJ, Li FJ. On coupling contact analysis of thermoelectric materials. Appl Math Model. 2021;89:1459–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2020.08.024.
Li X, Tian XJ, Zhou YT. Thickness size effect on contact behavior of a thermoelectric strip. Acta Mech. 2021;232(8):3305–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-021-03001-9.
Tian XJ, Zhou YT, Wang LH, Ding SH. Surface contact behavior of functionally graded thermoelectric materials indented by a conducting punch. Appl Math Mech. 2021;42(5):649–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-021-2732-8.
Zhang CX, Ding SH. Continuous contact problem of thermoelectric layer pressed by rigid punch. Appl Math Model. 2021;100:536–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2021.07.029.
Wang BL, Han JC, Du SY, Zhang HY, Sun YG. Electromechanical behavior of a finite piezoelectric layer under a flat punch. Int J Solids Struct. 2008;45(25–26):6384–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2008.08.001.
Artan R, Omurtag M. Two plane punches on a nonlocal elastic half plane. Int J Eng Sci. 2000;38(4):395–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7225(99)00053-1.
Ozsahin TS. Frictionless contact problem for a layer on an elastic half plane loaded by means of two dissimilar rigid punches. Struct Eng Mech. 2007;25(4):383–403. https://doi.org/10.12989/sem.2007.25.4.383.
Zhou YT, Kim TW. Closed-form solutions for the contact problem of anisotropic materials indented by two collinear punches. Int J Mech Sci. 2014;89:332–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2014.09.017.
Polat A, Kaya Y, Ozsahin TS. Analytical solution to continuous contact problem for a functionally graded layer loaded through two dissimilar rigid punches. Meccanica. 2018;53(14):3565–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-018-0902-7.
Zhou YT, Zheng Z. The interaction of two rigid semi-cylinders over anisotropic piezoelectric materials by the generalized Almansi theorem. Smart Mater Struct. 2015;24(8):085011. https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/24/8/085011.
Bedoidze MV, Pozharskii DA. The interaction of punches on a transversely isotropic half-space. J Appl Math Mech. 2014;78(4):409–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappmathmech.2014.12.012.
Pozharskii DA. Periodic contact problem for an elastic wedge. J Appl Math Mech. 2015;79(6):604–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappmathmech.2016.04.007.
Roman KZ, Stanisław JM, Adam SB. Semi-analytical solution of three-dimensional thermoelastic problem for half-space with gradient coating. J Therm Stresses. 2018;41(9):1169–81. https://doi.org/10.1080/01495739.2018.1460227.
Zhou YT, Lee KY. Contact problem for magneto-electro-elastic half-plane materials indented by a moving punch. Part I: closed-form solutions. Int J Solids Struct. 2012;49(26):3853–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2012.08.017.
Erdogan F. Mixed boundary value problems in mechanics. Mech Today. 1981. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-021792-5.50009-4.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 11762016, 12062021, and 12062022), Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region Science and Technology Innovation Leading Talent Training Project (KJT2020001), and the Natural Science Foundation of Ningxia (2022AAC03068, 2022AAC03001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YZ: Formal analysis, investigation, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. HM: Conceptualization, formal analysis, software. JY: Conceptualization, formal analysis, software. SD: Conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, funding acquisition, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Ma, H., Yang, J. et al. Frictionless Multi-field Coupling Contact Problem for a Thermoelectric Layer Loaded by Two Rigid Punches. Acta Mech. Solida Sin. 36, 282–292 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10338-022-00355-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10338-022-00355-y