Abstract
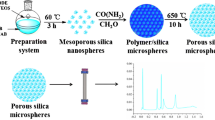
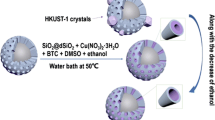
In this study, fibrous core–shell silica particles were successfully synthesized via a one-step oil–water biphase stratification coating strategy. The core–shell silica particles were composed of 3-µm non-pore silica cores and thin shells (50–100 nm), which have radial-like direct channels and a large pore size (19.89 nm). The fibrous core–shell silica particles were further modified by n-octadecyltrichlorosilane and used as stationary-phase media in high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The chromatographic properties of the particles were systematically studied in small-molecule and protein separation processes. The results showed that the back pressure was as low as 8.5 MPa under the 1.0-mL min−1 flow velocity. Furthermore, fibrous core–shell silica particles with an 80-nm shell were used for separating seven small molecules within 10 min and six proteins within 6 min. This work demonstrates that the fibrous core–shell silica particles could be used as an HPLC stationary phase with good performance and low back pressure, and that they have great potential for application to HPLC separation in the future.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hayes R, Ahmed A, Edge T, Zhang HF (2014) Core–shell particles: preparation, fundamentals and applications in high performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1357:36–52
Horvath C, Lipsky SR (1969) Column design in high pressure liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr Sci 7:109–116
Kirkland JJ (1969) Controlled surface porosity supports for high-speed gas and liquid chromatography. Anal Chem 41:218–220
Barhate CL, Breitbach ZS, Pinto EC, Regalado EL, Welch CJ, Armstrong DW (2015) Ultrafast separation of fluorinated and desfluorinated pharmaceuticals using highly efficient and selective chiral selectors bonded to superficially porous particles. J Chromatogr A 1426:241–247
Dolzan MD, Spudeit DA, Breitbach ZS, Barber WE, Micke GA, Armstrong DW (2014) Comparison of superficially porous and fully Porous silica supports used for a cyclofructan 6 hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatographic stationary phase. J Chromatogr A 1365:124–130
Fibigr J, Šatínský D, Havlíková L, Solich P (2016) A new method for rapid determination of indole-3-carbinol and its condensation products in nutraceuticals using core-shell column chromatography method. J Pharm Biomed Anal 120:383–390
Wei TC, Mack A, Chen W, Liu J, Dittmann M, Wang XL, Barber WE (2016) Synthesis characterization, and evaluation of a superficially porous particle with unique, elongated pore channels normal to the surface. J Chromatogr A 1440:55–65
Xia HJ, Wan GP, Chen G, Bai Q (2017) Preparation of superficially porous core-shell silica particle with controllable mesopore by a dual-templating approach for fast HPLC of small molecules. Mater Lett 192:5–8
Deridder S, Catani M, Cavazzini A, Desmet G (2016) A theoretical study on the advantage of core-shell particles with radially-oriented mesopores. J Chromatogr A 1456:137–144
Kirkland JJ, Schuster SA, Johnson WL, Boyes BE (2013) Fused-core particle technology in high-performance liquid chromatography: an overview. J Pharm Anal 3:303–312
Acquaro VRJ, LanÇas FM, Queiroz MEC (2017) Evaluation of superficially porous and fully porous columns for analysis of drugs in plasma samples by UHPLC–MS/MS. J Chromatogr B 1048:1–9
Schure MR, Moran RE (2017) Size exclusion chromatography with superficially porous particles. J Chromatogr A 1480:11–19
Blue LE, Jorgenson JW (2011) 1.1 µm superficially porous particles for liquid chromatography. Part I: Synthesis and particle structure characterization. J Chromatogr A 1218:7989–7995
Dong HJ, Brennan JD (2011) Rapid fabrication of core–shell silica particles using a multilayer-by-multilayer approach. Chem Commun 47:1207–1209
Ahmed A, Myers P, Zhang HF (2014) Synthesis of nanospheres-on-microsphere silica with tunable shell morphology and mesoporosity for improved HPLC. Langmuir 30:12190–12199
Min Y, Jiang B, Wu C, Xia SM, Zhang XD, Liang Z, Zhang LH, Zhang YK (2014) 1.9 m superficially porous packing material with radially oriented pores and tailored pore size for ultra-fast separation of small molecules and biomolecules. J Chromatogr A 1356:148–156
Xia HJ, Wan GP, Zhao JL, Liu JW, Bai Q (2016) Preparation and characterization of monodisperse large-porous silica microspheres as the matrix for protein separation. J Chromatogr A 1471:138–144
Yoon SB, Kim JY, Kim JH, Park YJ, Yoon KR, Park SK, Yu JS (2007) Synthesis of monodisperse spherical silica particles with solid core and mesoporous shell: mesopore channels perpendicular to the surface. J Mater Chem 17:1758–1761
Polshettiwar V, Cha D, Zhang XX, Basset JM (2010) High-surface-area silica nanospheres (KCC-1) with a fibrous morphology. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:9652–9656
Wei J, Zou LK (2016) Synthesis of magnetical microspheres with tunable large pore mesostructures. J Porous Mater 23:577–581
Yu KJ, Zhang XB, Tong HW, Yan XY, Liu SM (2013) Synthesis of fibrous monodisperse core–shell Fe3O4/SiO2/KCC-1. Mater Lett 106:151–154
Qu QS, Mi Y, Zhang LH, Xu Q, Yin YD (2015) Silica microspheres with fibrous shells: synthesis and application in HPLC. Anal Chem 87:9631–9638
Chester TL (2013) Recent developments in high-performance liquid chromatography stationary phases. Anal Chem 85:579–589
Gritti F, Guiochon G (2012) Facts and legends on columns packed with sub-3-µm core–shell particles. LCGC North Am 30(7):586–595
Snyder LR, Kirkland JJ, Dolan JW (2010) Introduction to modern liquid chromatography, 3edn. Wiley, Hoboken
Wahab MF, Patel DC, Wimalasinghe RM, Armstrong DW (2017) Fundamental and practical insights on the packing of modern high efficiency analytical and capillary columns. Anal Chem 89:8177–8191
Patel DC, Breitbach ZS. Wahab MF, Barhate CL, Armstrong DW (2015) Gone in seconds: praxis, performance, and peculiarities of ultrafast chiral liquid chromatography with superficially porous particles. Anal Chem 87:9137–9148
Acknowledgements
We thank Prof. Bai Quan’s group at Northwest University (Xi’an, China) for the non-porous SiO2 microspheres. This work was supported financially by Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province (CN). (Grant No. 2018JM2039).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Li, Sm. & Zhang, J. Preparation and Chromatographic Features of Fibrous Core–Shell HPLC Packing Material. Chromatographia 81, 1249–1256 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-018-3571-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-018-3571-8