Abstract
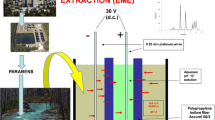
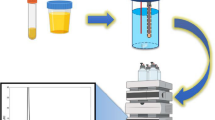
Electromembrane extraction (EME) was carried out using a round-headed platinum wire as the inner electrode. The round-headed platinum electrode was prepared by a simple electrothermal process based on discharging of the electrical energy stored in a capacitor bank. The effect of the experimental parameters on the recovery of the extraction was investigated for amlodipine (AMP), verapamil (VPL) and clomipramine (CLP) as the model analytes and 2-ethyl hexanol as the supported liquid membrane solvent. It was found that the application of round-headed electrode (RHE) significantly improves the performance and stability of EME in comparison to a classical electrode. It was found that the improvement factor greatly depends on the sample properties such as the ionic strength and matrix complexity. The improvement factors for the extraction of AMP, VPL and CLP from standard solutions were 39.7, 54.4 and 43.2%, respectively. Higher improvement factors were recorded during extraction from real samples or saline solutions. Also, the application of RHE changed the extractability of AMP and VPL from complex matrices such as human plasma. The model analytes were successfully extracted from wastewater, human plasma and human urine samples with recoveries ranging from 36.3 to 88.7%. The relative standard deviations of the determinations were in the range of 8.2–14.8%.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AMP:
-
Amlodipine
- CE:
-
Classical electrode
- CLP:
-
Clomipramine
- EME:
-
Electromembrane extraction
- RHE:
-
Round-headed electrode
- SLM:
-
Supported liquid membrane
- VPL:
-
Verapamil
References
Pedersen-Bjergaard S, Rasmussen KE (2006) Electrokinetic migration across artificial liquid membranes: new concept for rapid sample preparation of biological fluids. J Chromatogr A 1109:183–190
Gjelstad A, Rasmussen KE, Pedersen-Bjergaard S (2006) Electrokinetic migration across artificial liquid membranes: tuning the membrane chemistry to different types of drug substances. J Chromatogr A 1124:29–34
Ocaña-González JA, Fernández-Torres R, Bello-López M, Ramos-Payán M (2016) New developments in microextraction techniques in bioanalysis: a review. Anal Chim Acta 905:8–23
Fotouhi L, Yamini Y, Molaei S, Seidi S (2011) Comparison of conventional hollow fiber based liquid phase microextraction and electromembrane extraction efficiencies for the extraction of ephedrine from biological fluids. J Chromatogr A 1218:8581–8586
Kjelsen IJØ, Gjelstad A, Rasmussen KE, Pedersen-Bjergaard S (2008) Low-voltage electromembrane extraction of basic drugs from biological samples. J Chromatogr A 1180:1–9
Gjelstad A, Rasmussen KE, Pedersen-Bjergaard S (2009) Electromembrane extraction of basic drugs from untreated human plasma and whole blood under physiological pH conditions. Anal Bioanal Chem 393:921–928
Eibak LEE, Gjelstad A, Rasmussen KE, Pedersen-Bjergaard S (2010) Kinetic electro membrane extraction under stagnant conditions—fast isolation of drugs from untreated human plasma. J Chromatogr A 1217:5050–5056
Basheer C, Lee J, Pedersen-Bjergaard S, Rasmussen KE, Lee HK (2010) Simultaneous extraction of acidic and basic drugs at neutral sample pH: a novel electro-mediated microextraction approach. J Chromatogr A 1217:6661–6667
Seidi S, Yamini Y, Heydari A, Moradi M, Esrafili A, Rezazadeh M (2011) Determination of thebaine in water samples, biological fluids, poppy capsule, and narcotic drugs, using electromembrane extraction followed by high-performance liquid chromatography analysis. Anal Chim Acta 701:181–188
Balchen M, Reubsaet L, Pedersen-Bjergaard S (2008) Electromembrane extraction of peptides. J Chromatogr A 1194:143–149
Balchen M, Halvorsen TG, Reubsaet L, Pedersen-Bjergaard S (2009) Rapid isolation of angiotensin peptides from plasma by electromembrane extraction. J Chromatogr A 1216:6900–6905
Basheer C, Tan SH, Lee HK (2008) Extraction of lead ions by electromembrane isolation. J Chromatogr A 1213:14–18
Kubáň P, Strieglerová L, Gebauer P, Boček P (2011) Electromembrane extraction of heavy metal cations followed by capillary electrophoresis with capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detection. Electrophoresis 32:1025–1032
Davarani SSH, Moazami HR, Keshtkar AR, Banitaba MH, Nojavan S (2013) A selective electromembrane extraction of uranium(VI) prior to its fluorometric determination in water. Anal Chim Acta 783:74–79
Hu Z, Chen H, Yao C, Zhu Y (2011) Determination of inorganic anions in ethyl acetate by ion chromatography with an electromembrane extraction method. J Chromatogr Sci 49:617–621
Kiplagat IK, Doan TK, Kubáň P, Boček P (2011) Trace determination of perchlorate using electromembrane extraction and capillary electrophoresis with capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detection. Electrophoresis 32:3008–3015
Middelthon-Bruer TM, Gjelstad A, Rasmussen KE, Pedersen-Bjergaard S (2008) Parameters affecting electro membrane extraction of basic drugs. J Sep Sci 31:753–759
Balchen M, Hatterud AG, Reubsaet L, Pedersen-Bjergaard S (2011) Fundamental studies on the electrokinetic transfer of net cationic peptides across supported liquid membranes. J Sep Sci 34:186–195
Gjelstad A, Rasmussen KE, Pedersen-Bjergaard S (2007) Simulation of flux during electro-membrane extraction based on the Nernst–Planck equation. J Chromatogr A 1174:104–111
Šlampová A, Kubáň P, Boček P (2012) Electromembrane extraction using stabilized constant D.C. electric current—a simple tool for improvement of extraction performance. J Chromatogr A 1234:32–37
Rezazadeh M, Yamini Y, Seidi S, Esrafili A (2012) Pulsed electromembrane extraction: a new concept of electrically enhanced extraction. J Chromatogr A 1262:214–218
Arjomandi-Behzad L, Yamini Y, Rezazadeh M (2013) Pulsed electromembrane method for simultaneous extraction of drugs with different properties. Anal Biochem 438:136–143
Rezazadeh M, Yamini Y, Seidi S, Esrafili A (2013) One-way and two-way pulsed electromembrane extraction for trace analysis of amino acids in foods and biological samples. Anal Chim Acta 773:52–59
Rezazadeh M, Yamini Y, Seidi S, Arjomandi-Behzad L (2014) Voltage-step pulsed electromembrane as a novel view of electrical field-induced liquid-phase microextraction. J Chromatogr A 1324:21–28
Moazami HR, Nojavan S, Zahedi P, Davarani SSH (2014) Electronic simulation of the supported liquid membrane in electromembrane extraction systems: improvement of the extraction by precise periodical reversing of the field polarity. Anal Chim Acta 841:24–32
Zahedi P, Davarani SSH, Moazami HR, Nojavan S (2016) Surfactant assisted pulsed two-phase electromembrane extraction followed by GC analysis for quantification of basic drugs in biological samples. J Pharm Biomed 117:485–491
Davarani SSH, Moazami HR, Memarian E, Nojavan S (2016) Electromembrane extraction through a virtually rotating supported liquid membrane. Electrophoresis 37:339–346
Rezazadeh M, Yamini Y, Seidi S, Aghaei A (2015) Pulsed electromembrane extraction for analysis of derivatized amino acids: a powerful technique for determination of animal source of gelatin samples. Talanta 136:190–197
Kamyabi MA, Aghaei A (2016) Electromembrane extraction and spectrophotometric determination of As(V) in water samples. Food Chem 212:65–71
Huang C, Seip KF, Gjelstad A, Pedersen-Bjergaard S (2015) Electromembrane extraction for pharmaceutical and biomedical analysis—Quo vadis. J Pharm Biomed 113:97–107
Mohammadi J, Davarani SSH, Moazami HR (2016) Impedometric monitoring of the behavior of the supported liquid membrane in electromembrane extraction systems: an insight into the origin of optimized experimental parameters. Anal Chim Acta 934:98–105
Asl YA, Yamini Y, Rezazadeh M, Seidi S (2015) Electromembrane extraction using cylindrical electrode: a new view for augmentation of extraction efficiency. Anal Methods 7:197–204
Moazami HR, Davarani SSH, Mohammadi J, Nojavan S, Abrari M (2015) The effect of electric field geometry on the performance of electromembrane extraction systems: footprints of a third driving force along with migration and diffusion. Anal Chim Acta 891:151–159
Asadi S, Tabani H, Khodaei K, Asadian F, Nojavan S (2016) Rotating electrode in electro membrane extraction: a new and efficient methodology to increase analyte mass transfer. RSC Adv 6:101869–101879
Huang C, Gjelstad A, Seip KF, Jensen H, Pedersen-Bjergaard S (2015) Exhaustive and stable electromembrane extraction of acidic drugs from human plasma. J Chromatogr A 1425:81–87
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moazami, H.R., Davarani, S.S.H., Abrari, M. et al. Electromembrane Extraction Using a Round-Headed Platinum Wire as the Inner Electrode: A Simple and Practical Way to Enhance the Performance of Extraction. Chromatographia 81, 1023–1033 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-018-3537-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-018-3537-x