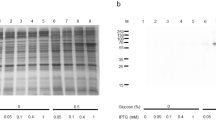
Abstract
Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) is an enzyme involved in catecholamine catabolism that is key for the treatment of different neurologic disorders. Actually, there are still unmet needs concerning the development of more selective membrane-bound COMT (hMBCOMT) downstream strategies, envisaging their application in structural and bio-interaction studies. Therefore, in this work, recombinant hexahistidine-tagged hMBCOMT (hMBCOMT-His6) was expressed from Pichia pastoris methanol-induced cultures in a catalytically active form (27.3 nmol h−1 mg−1 of protein) and successfully solubilized with n-dodecyl β-d-maltoside. Afterward, immobilized-metal affinity chromatography provided the required selectivity for the direct capture of hMBCOMT-His6 from detergent-solubilized P. pastoris membranes, being the target enzyme recovered in a highly purified fraction. Also, despite the relatively low purification fold (1.53), the purity of the target enzyme assessed by SDS-PAGE is high and it is recovered with biological activity (67 nmol h−1 mg−1 of protein). Then, after a final polishing stage using Q-Sepharose, a pure and immunologically active enzyme fraction was obtained. Overall, the strategy herein reported may be applied to obtain pure hMBCOMT fractions, debottlenecking the implementation of bio-interaction studies and relieving the problems associated with hMBCOMT drug discovery pipeline. In a last analysis, these studies may lead to the establishment of new pharmacological therapies, thereby improving the prognosis of neurologic disorders.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonifacio MJ, Palma PN, Almeida L, Soares-da-Silva P (2007) Catechol-O-methyltransferase and its inhibitors in Parkinson’s disease. CNS Drug Rev 13:352–379
Ma Z, Liu H, Wu B, Brit J (2013) Structure-based drug design of catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitors for CNS inhibitors. Clin Pharmacol 77:410–420
Wu W, Wu Q, Hong X, Xiong G, Xiao Y, Zhou J, Wang W, Wu H, Zhou L, Song W, Dai H, Qiu H, Zhao Y (2015) Catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibits colorectal cancer cell proliferation and invasion. Arch Med Res 46:17–23
Apud JA, Weinberger DR (2007) Treatment of cognitive deficits associated with schizophrenia: potential role of catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitors. CNS Drugs 21:535–557
Harrison ST, Poslusney MS, Mulhearn JJ, Zhao Z, Kett NR, Schubert JW, Melamed JY, Allison TJ, Patel SB, Sanders JM, Sharma S, Smith RF, Hall DL, Robinson RG, Sachs NA, Hutson PH, Wolkenberg SE, Barrow JC (2015) Synthesis and evaluation of heterocyclic catechol mimics as inhibitors of catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT). ACS Med Chem Lett 6:318–323
Bonifácio MJ, Soares-da-Silva P (2003) Purification of membrane-bound catechol-O-methyltransferase. Methods Mol Biol 228:231–238
Correia FF, Santos FM, Pedro AQ, Bonifacio MJ, Queiroz JA, Passarinha LA (2014) Recovery of biological active catechol-O-methyltransferase isoforms from Q-sepharose. J Sep Sci 37:20–29
Santos FM, Pedro AQ, Soares RF, Martins R, Bonifácio MJ, Queiroz JA, Passarinha LA (2013) Performance of hydrophobic interaction ligands for human membrane-bound catechol-O-methyltransferase purification. J Sep Sci 36:1693–1702
Pedro AQ, Pereira P, Bonifácio MJ, Queiroz JA, Passarinha LA (2015) Purification of membrane-bound catechol-O-methyltransferase by arginine-affinity chromatography. Chromatographia 78:1339–1348
Lantez V, Nikolaidis I, Rechenmann M, Vernet T, Noirclerc-Savoye M (2015) Rapid automated detergent screening for the solubilization and purification of membrane proteins and complexes. Eng Life Sci 15:39–50
Porath J, Carlsson J, Olsson I, Belfrage G (1975) Metal chelate affinity chromatography, a new approach to protein fractionation. Nature 258:598–599
Cheung RCF, Wong JH, Bun Ng T (2012) Immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography: a review on its applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 96:1411–1420
Mooney JT, Fredericks DP, Zhang C, Christensen T, Jespergaard C, Schiodt CB, Hearn MT (2014) Purification of a recombinant human growth hormone by an integrated IMAC procedure. Protein Expr Purif 94:85–94
Pedro AQ, Correia FF, Santos FM, Espírito-Santo G, Gonçalves AM, Bonifácio MJ, Queiroz JA, Passarinha LA (2016) Biosynthesis and purification of histidine-tagged human soluble catechol-O-methyltransferase. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 91:3035–3044
Wang F, Guo J, Bai Q, Wang L (2004) Refolding and purification of recombinant human (pro)renin receptor from Escherichia coli by ion exchange chromatography. Biotechnol Prog 30:864–871
Pedro AQ, Oppolzer D, Bonifácio MJ, Maia CJ, Queiroz JA, Passarinha LA (2015) Evaluation of MutS and Mut+ Pichia pastoris strains for membrane-bound and catechol-O-methyltransferase biosynthesis. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 175:3840–3855
Pedro AQ, Soares RF, Oppolzer D, Santos FM, Rocha LA, Gonçalves AM, Bonifácio MJ, Queiroz JA, Gallardo E, Passarinha LA (2014) An improved HPLC method for quantification of metanephrine with coulometric detection. J Chromatogr Sep Tech 5:217
Vieira-Coelho MA, Soares-da-Silva P (1999) Effects of tolcapone upon soluble and membrane-bound brain and liver catechol-O-methyltransferase. Brain Res 821:69–78
Pedro AQ, Bonifácio MJ, Queiroz JA, Maia CJ, Passarinha LA (2011) A novel prokaryotic expression system for biosynthesis of recombinant human membrane-bound catechol-O-methyltransferase. J Biotechnol 156:141–146
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Yang J, Kulkami K, Manolaridis I, Zhang Z, Dodd RB, Mas-Droux C (2011) Mechanism of isoprenylcysteine carboxyl methylation from the crystal structure of the integral membrane methyltransferase ICMT. Mol Cell 44:997–1004
Block H, Maertens B, Spriestersbach A, Brinker N, Kubicek J, Fabis R, Labahn J, Schäfer F (2009) Immobilized-metal affinity chromatography (IMAC): a review. Methods Enzymol 463:439–473
Jones C, Patel A, Griffin S, Martin J, Young P, O’Donnell K, Silverman C, Porter T, Chaiken IJ (1995) Current trends in molecular recognition and bioseparation. J Chromatogr A 707:3–22
Halliwell CM, Morgan G, Ou C, Cass AEG (2001) Introduction of a (poly)histidine tag in l-lactate dehydrogenase produces a mixture of active and inactive molecules. Anal Biochem 295:257–261
Seddon AM, Curnow P, Booth PJ (2004) Membrane proteins, lipids and detergents: not just a soap opera. Biochim Biophys Acta 1666:105–117
Arnold T, Linke D (2008) The use of detergents to purify membrane proteins. Curr Protoc Protein Sci 4:4.8.1–4.8.30
Privé GG (2007) Detergents for the stabilization and crystallization of membrane proteins. Methods 41:388–397
Sonoda Y, Cameron A, Newstead S, Omote H, Moriyama Y, Kasahara M, Iwata S, Drew D (2010) Tricks of the trade used to accelerate high-resolution structure determination of membrane proteins. FEBS Lett 584:2539–2547
Le Maire M, Champeil P, Moller JV (2000) Interaction of membrane proteins and lipids with solubilizing detergents. Biochim Biophys Acta 1508:86–111
Nieba L, Nieba-Axmann SE, Persson A, Hamalainen M, Edebratt F, Hansson A, Lidholm J, Magnusson K, Karlsson AF, Pluckthun A (1997) BIACORE analysis of histidine-tagged proteins using a chelating NTA sensor chip. Anal Biochem 252:217–228
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the University of Beira Interior—Health Sciences Research Centre (CICS) and FCT (Portuguese Foundation for Sciences and Technology) by the project “EXPL/BBB478/BQB/0960/2012” and COMPETE: FCOMP-010124-FEDER-027563. A. Q. Pedro acknowledges a doctoral fellowship (SFRH/BD/81222/2011) from FCT. This work is supported by FEDER funds through the POCI—COMPETE 2020—Operational Programme Competitiveness and Internationalisation in Axis I—Strengthening research, technological development and innovation (Project POCI-01-0145-FEDER-007491) and National Funds by FCT—Foundation for Science and Technology (Project UID/Multi/00709/2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pedro, A.Q., Gonçalves, A.M., Queiroz, J.A. et al. Purification of Histidine-Tagged Membrane-Bound Catechol-O-Methyltransferase from Detergent-Solubilized Pichia pastoris Membranes. Chromatographia 81, 425–434 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-017-3453-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-017-3453-5