Abstract
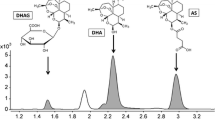
A highly sensitive and rapid liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method was developed and validated for the determination of artemether and its metabolite dihydroartemisinin in human plasma using artemisinin as an internal standard. Chromatographic separation was achieved on a Supelco Discovery HS C18 RP column (150 mm × 4.6 mm, 5 µm; Bellefonte, USA) using acetonitrile and water with 0.1 % formic acid (80:20, v/v) as a mobile phase in isocratic mode. A high-resolution Thermo Electron Corporation LTQ-Orbitrap mass spectrometer (San Jose, USA) was used in single ion monitoring (SIM) mode using atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI) as an interface. The following extracted ion ranges ([M + H]+) were monitored: m/z 267.14–267.16 for artemether, m/z 221.16–221.18 for dihydroartemisinin and m/z 283.14–283.16 for internal standard. The limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantification (LOQ) for artemether were 0.3 and 0.8 ng mL−1, while for dihydroartemisinin were 0.2 and 0.6 ng mL−1, respectively. The validated method was successfully applied to the quantification of artemether and dihydroartemisinin in plasma samples of healthy volunteers participating in pharmacokinetic drug–food interaction studies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wahajuddin, Kanumuri SRR, Isha T (2013) Trend Anal Chem 42: 186–204
Lubbe W, Katya G, Sandra AM, Jennifer N, Peter JS (2013) J Pharm Biomed Anal 55:373–378
Abdoulaye D, Gilbert L Malar. J. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-8-S1-S4
Zhou ZM, Anders JC, Chung H, Theoharides AD (1987) J Chromatogr 414:77–90
Navaratnam V, Mordi MN, Mansor SM (1997) J Chromatogr B 692:157–162
Na-Bangchang K, Congpuong K, Hung LN, Molunto P, Karbwang J (1998) J Chromatogr B 708:201–207
Peys E, Vandenkerckhove J, Hemel JV, Sas B (2005) Chromatographia 61:637–641
Shi B, Yu Y, Li Z, Zhang L, Zhong Y, Su S, Liang S (2006) Chromatographia 64:523–530
Souppart C, Gauducheau N, Sandrenan N, Richard F (2002) J Chromatogr B 774:195–203
Xing J, Yan H, Zhang S, Ren G, Gao Y (2006) Rapid Commun Mass Sp 20:1463–1468
Ortelli D, Rudaz S, Cognard E, Veuthey JL (2000) Chromatographia 52:445–450
Naik H, Murry DJ, Kirsch LE, Fleckenstein L (2005) J Chromatogr B 816:233–242
Lindegardh N, Hanpithakpong W, Kamanikom B, Singhasivanon P, Socheat D, Yi P, Dondorp AM, McGready R, Nosten F, White NJ, Day NPJ (2008) J Chromatogr B 876:54–60
Hilhorst MJ, Hendriks G, Vries R, Hillewaert V, Verhaege T, Merbel NC (2014) J Chromatogr B 965:45–53
Huang L, Jayewardene AL, Li X, Marzan F, Lizak PS, Aweeka FT (2009) J Pharm Biomed Anal 50:959–965
Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (2001) Guidance for industry in Bio-analytical Method Validation. http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/GuidanceComplianceRegulatoryInformation/Guidances/UCM070107.pdf
Du F, Liu T, Shen T, Zhu F, Xing J (2012) J Mass Spectrom 47:246–252
Duthaler U, Keiser J, Huwyler J (2011) J Mass Spectrom 46:172–181
Mordi MN, Mansor SM, Navaratnam V, Wernsdorfer WH (1997) Br J Clin Pharmacol 43:363–365
Agtmael MA, Cheng-Qi S, Qing JX, Mull R, Boxte CJ (1999) Int J Antimicrob Agents 12:151–158
Shabana A, Muzammil HN, Joel T, Niklas L (2010) Malar J 9:275–282
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the University of Peshawar for funding this research project. Novartis Pharma is acknowledged for kind donation of artemether and dihydroartemisinin.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The clinical trials were conducted according to the guidelines of “World Medical Associations, Declaration of Helsinkiethical principles for medical research involving human subjects” and were approved by the Ethics Committee of the Department of Pharmacy, University of Peshawar (Trial number 02/EC-12/Pharm).
Ethical approval
A written informed consent was obtained from all the participants enrolled in the study.
Informed consent
There are no competing interests to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khuda, F., Iqbal, Z., Shah, Y. et al. A High-Resolution LC–MS/MS Method for the Quantitative Determination of Artemether and Its Metabolite Dihydroartemisinin in Human Plasma and Its Application to Pharmacokinetic Studies. Chromatographia 79, 609–618 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-016-3064-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-016-3064-6