Abstract
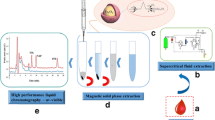
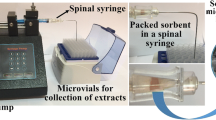
Iron nanoparticles were synthesized by green technology. These were functionalized with 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide (ionic liquid) to enhance specificity and selectivity. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence, X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy were used for characterization. 1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide-functionalized iron nanoparticles (BMIF-INPs) were applied in nano dispersive solid-phase extraction for the extraction of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) from the plasma prior. The different extraction parameters such as type and amount of sorbents, agitation time, pH, desorbing solvents, desorbing volume, and desorption times were optimized. Optimum conditions were 1.5 mg mL−1 of BMIF-INP sorbent, 20 min of agitation time, pH of 5.0, acetonitrile + 0.1 % acetic acid desorbing solvent, 600 µL of desorbing volume and 2 min of desorbing time. The percentage recoveries of all the six NSAIDs ranged from 87.4 to 94.98 %. High-performance liquid chromatography was developed using a pentafluorophenyl column (100 × 4.6 mm; 2.6 µm) and water–acetonitrile–acetic acid (70:30, v/v) of pH 3.0 with acetic acid as the mobile phase. The flow rate was 1.0 mL min−1 with detection at 240 nm. The values of k, α and R s ranged from 0.83 to 19.0, 1.16 to 6.13 and 1.0 to 5.76, respectively. The developed sample preparation and chromatographic methods were fast, selective, inexpensive, economical and reproducible. These methods have good applications and may be used for analyzing these drugs in biological, environmental and industrial matrices.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization (2011) World report on disability. WHO. ISBN 978 92 4 068637 3 (Daisy)
American Gastroenterological Association. Study Shows Long-term Use Of NSAIDs Causes Severe Intestinal Damage. ScienceDaily. ScienceDaily, 16 January 2005. http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2005/01/050111123706.htm
Rochon PA, Gurwitz JH, Simms RW, Fortin PR, Felson DT, Minaker KL, Chalmers TC (1994) A study of manufacturer-supported trials of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the treatment of arthritis. Arch Intern Med 154:157–163
Tracy TS, Krohn K, Jones DR, Bradley JD, Hall SD, Brater DC (1992) The effects of a salicylate, ibuprofen, and naproxen on the disposition of methotrexate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 42:121–125
Anderson JA, Lee P, Webb J, Buchanan WW (1974) Evaluation of the therapeutic potential of ketoprofen in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Med Res Opin 2:189–197
Smolinske SC, Hall AH, Vandenberg SA, Spoerke DG, McBride PV (1990) Toxic effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in overdose. Drug Saf 5:252–274
Higuchi K, Umegaki E, Watanabe T, Yoda Y, Morita E, Murano M, Tokioka S, Arakawa T (2009) Present status and strategy of NSAIDs-induced small bowel injury. J Gastroenterol 44:879–888
Whelton A (1999) Nephrotoxicity of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: physiologic foundations and clinical implications. Am J Med 106:13S–24S
Antman EM, Bennett JS, Daugherty A, Furberg C, Roberts H, Taubert KA (2007) Use of nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory drugs an update for clinicians: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 115:1634–1642
Singh G (1998) Recent considerations in nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug gastropathy. Am J Med 105:31S–38S
Ali I, Aboul-Enein HY, Gupta VK (2009) Nano chromatography and capillary electrophoresis, pharmaceutical and environmental analyses. Wiley, Hoboken
Halling-Sørensen B, Nielsen SN, Lanzky PF, Ingerslev F, Holten Lützhøft HC, Jørgensen SE (1998) Occurrence, fate and effects of pharmaceutical substances in the environment—a review. Chemosphere 36:357–393
Lin AYC, Tsai YT, Yu TH, Wang XH, Lin CF (2011) Occurrence and fate of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in Taiwan’s aquatic environment. Desalin Water Treat 32:57–64
Ali I, Hussain I, Saleem K, Aboul-Enein HY, Bazylak G (2008) Supramolecular chiro-biomedical assays and enantioselective HPLC analyses for evaluation of profens as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, potential anti cancer agents and common xenobiotic. Curr Drug Discov Technol 5:105–120
Ali I, Hussain I, Saleem K, Aboul-Enein HY (2012) Enantiomeric resolution of ibuprofen and flurbiprofen in human plasma by SPE-chiral HPLC methods. Combin Chem High Throughput Screen 15:509–514
Ali I, Singh P, Aboul-Enein HY, Sharma B (2009) Chiral analyses of ibuprofen residues in water and sediment. Anal Lett 42:1747–1760
Caro E, Marc RM, Cormack PAG, Sherrington DC, Borrull F (2005) Selective enrichment of anti-inflammatory drugs from river water samples by solid-phase extraction with a molecularly imprinted polymer. J Sep Sci 28:2080–2085
Debska J, Kot-Wasik A, Namiesnik J (2005) Determination of nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory drugs in water samples using liquid chromatography coupled with diode-array detector and mass spectrometry. J Sep Sci 28:2419–2426
Ppadoyannis IN (1990) HPLC in clinical chemistry, vol 54. Marcel Dekker Inc., New York
Banaker UV (ed) (1992) Pharmaceutical dissolution testing, 1st edn. Marcel Dekker Inc., New York
Starek M, Dąbrowska M (2012) Chromatographic techniques in analysis of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors in drugs and biological samples. Cent Eur J Chem 10:711–730
Aboul-Enein HY, Ali I (2003) Chiral separations by liquid chromatography and related technologies. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, USA, ISBN:0-8247-4014-9
Grob RL (1983) Chromatographic analysis of the environment, 2nd edn. Marcel Dekker, New York
Gooding KM, Regnier FE (1990) HPLC of biological macromolecules methods and applications. Chromatographic science series, vol 51. Marcel Dekker, New York
Farrar H, Letzig L, Gill M (2002) Validation of a liquid chromatographic method for the determination of ibuprofen in human plasma. J Chromatogr B 780:341–348
Suenami K, Lim LW, Takeuchi T, Sasajima Y, Sato K, Takekoshi Y, Kanno S (2006) Rapid and simultaneous determination of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in human plasma by LC–MS with solid-phase extraction. Anal Bioanal Chem 384:1501–1505
Gallo P, Fabbrocino S, Vinci F, Fiori M, Danese V, Nasi A, Serpe L (2006) Multi-residue determination of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug residues in animal serum and plasma by HPLC and photo-diode array detection. J Chromatogr Sci 44:585–590
González-Barreiro C, Lores M, Casais MC, Cela R (2003) Simultaneous determination of neutral and acidic pharmaceuticals in wastewater by high-performance liquid chromatography-post-column photochemically induced fluorimetry. J Chromatogr A 993:29–37
Debska J, Kot-Wasik A, Namiesnik J (2005) Determination of nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory drugs in water samples using liquid chromatography coupled with diode-array detector and mass spectrometry. J Sep Sci 28:2419–2426
Pedrouzo M, Reverté S, Borrull F, Pocurull E, Marcé RM (2007) Pharmaceutical determination in surface and waste waters using high performance liquid chromatography-(electrospray)–mass spectrometry. J Sep Sci 30:297–303
Mikami E, Goto T, Ohno T, Matsumoto H, Nishida M (2000) Simultaneous analysis of naproxen, nabumetone and its major metabolite 6-methoxy-2-naphthylacetic acid in pharmaceutical and human urine by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Pharm Biomed Anal 23:917–925
Kamaruzaman S, Sanagi MM, Endud S, Ibrahim WAW, Yahaya N (2013) MCM-41 solid phase membrane tip extraction combined with liquid chromatography for the determination of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in human urine. J Chromatogr B 940:59–65
Sharifabadi MK, Tehrani MS, Husain SW, Mehdinia A, Azar PA (2014) Determination of residual non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in aqueous sample using magnetic nanoparticles modified with cetyltrimethylammonium bromide by high performance liquid chromatography. Sci World J 2014:1–8
Cazes J (2001) Encyclopedia of chromatography. Marcel Dekker Inc, New York
Ali I, Kulsum U, AL-Othman ZA, Al-Warthan A, Saleem K (2016) Advances in analyses of profens in biological and environmental samples by liquid chromatography. Cur Pharm Anal 12. doi:10.2174/1573412912999151120155536
Ali I, Gupta VK, Aboul-Enein HY, Hussain A (2008) Hyphenation in sample preparation: advancement from the micro to the nano world. J Sep Sci 31:2040–2053
Basheer C, Alnedhary AA, Rao BSM, Valliyaveettil S, Lee HK (2006) Development and application of porous membrane-protected carbon nanotube micro solid-phase extraction combined with gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 78:2853
Asgharinezhad AA, Ebrahimzadeh H, Mirbabaei F, Mollazadeh N, Shekari N (2014) Dispersive micro-solid-phase extraction of benzodiazepines from biological fluids based on polyaniline/magnetic nanoparticles composite. Anal Chim Acta 844:80–89
Mahpishanian S, Sereshti H (2014) Graphene oxide-based dispersive micro-solid phase extraction for separation and preconcentration of nicotine from biological and environmental water samples followed by gas chromatography-flame ionization detection. Talanta 130:71–77
Tian J, Xu J, Zhu F, Lu T, Su C, Ouyang G (2013) Application of nanomaterials in sample preparation. J Chromatogr A 1300:2–16
Wen Y, Chen L, Li J, Liu D, Chen L (2014) Recent advances in solid-phase sorbents for sample preparation prior to chromatographic analysis. Trends Anal Chem 59:26–41
Lucena R, Simonet BM, Cárdenas S, Valcárcel M (2011) Potential of nanoparticles in sample preparation. J Chromatogr A 1218:620–637
Huang L, Weng X, Chen Z, Megharaj M, Naidu R (2014) Green synthesis of iron nanoparticles by various tea extracts: comparative study of the reactivity. Spectrochim Acta Mol Biomol Spectrosc 130:295–301
Hoag GE, Collins JB, Holcomb JL, Hoag JR, Nadagouda MN, Varma RS (2009) Degradation of bromothymol blue by ‘greener’ nano-scale zero-valent iron synthesized using tea polyphenols. J Mater Chem 19:8671–8677
Shahwan T, Abu Sirriah S, Nairat M, Boyaci E, Eroğlu AE, Scott TB, Hallam KR (2011) Green synthesis of iron nanoparticles and their application as a fenton-like catalyst for the degradation of aqueous cationic and anionic dyes. Chem Eng J 172:258–266
Ali I, AL-Othman ZA, Al-Warthan AA (2016) Sorption, Kinetic and Thermodynamics Studies of Atrazine Hericide Removal from water using Iron nanocomposite material. Int J Environ Sci Technol. doi:10.1007/s13762-015-0919-6
Ali I, AL-Othman ZA, Al-Warthan A (2015) Removal of secbumeton herbicide from water on composite nano adsorbent. Desal Water Treat. doi:10.1080/19443994.2015.1041164
Ali I (2012) New generation adsorbents for water treatment. Chem Rev 112:5073–5091
Dethlefs KM, Hobza P (2000) Noncovalent interactions: a challenge for experiment and theory. Chem Rev 100:143–168
Martinez CR, Iverson BL (2012) Rethinking the term “pi-stacking”. Chem Sci 3:2191–2201
Dougherty DA (2007) Cation–π interactions involving aromatic amino acids. J Nutr 137:1504S–1508S
Scrutton NS, Raine ARC (1996) Cation–π bonding and amino–aromatic interactions in the biomolecular recognition of substituted ammonium ligands. Biochem J 319:1–8
Gao J, Chou LW, Auerbach A (1993) The nature of cation–pi binding: interactions between tetramethylammoniumion and benzene in aqueous solution. Biophys J 65:43–47
Mohan N, Vijayalakshmi KP, Koga N, Suresh CH (2010) Comparison of aromatic NH···π, OH···π, and CH···π interactions of alanine using MP2, CCSD, and DFT methods. J Comput Chem 31:2874–2882
Imai YN, Inoue Y, Nakanishi I, Kitaura K (2009) Amide–π-interactions between formamide and benzene. J Comput Chem 30:2267–2276
Ottiger P, Pfaffen C, Leist R, Leutwyler S (2009) Strong N–H···π hydrogen bonding in amide–benzene interactions. J Phys Chem B 113:2937–2943
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their sincere appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for its funding to this Prolific Research Group (PRG-1436-04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, I., Kulsum, U., AL-Othman, Z.A. et al. Analyses of Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs in Human Plasma Using Dispersive Nano Solid-Phase Extraction and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Chromatographia 79, 145–157 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-015-3020-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-015-3020-x