Abstract
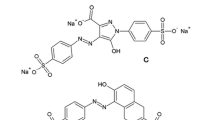
Due to the toxic and carcinogenic effects of some synthetic food colorants, their utilization is limited by food and health regulations. Synthetic colorants are preferred for their stability and low cost in food processing but their misuse may cause health hazards. The aim of this study is to determine food colorants by fast, accurate and applicable methods and inform consumers about the limitations of these substances. Thus, spectrophotometric CUPRAC (cupric ion reducing antioxidant capacity) assay was adapted for the determination of synthetic food colorants so as to define PECC (ponceau 4R equivalent colorant content) coefficients for the calculation of total colorant content of powder beverage samples. The PECC coefficients of the tested colorants were found in the following order: PECCerythrosine > PECCsunsetyellow > PECCtartrazine > PECCindigocarmine. HPLC and on-line HPLC derivatization techniques were developed for synthetic colorants. Total colorant content of synthetic and real (orange and rosehip powder beverage) samples were found and critically compared with the use of three methods, namely spectrophotometric CUPRAC, HPLC (with CUPRAC calculation) and on-line HPLC–post column CUPRAC assays. On-line HPLC–CUPRAC assay yielded low detection limits for colorants. Statistical analyses of the findings of these three methods using the two-way ANOVA test proved that the developed methods for determining synthetic food colorants are accurate, diversely applicable, and well-correlating.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eigenmann PA, Haenggeli CA (2007) Food colourings, preservatives, and hyperactivity. Lancet 370(9598):1524–1525
Culzoni MJ, Schenone V, Llamas NE (2009) Fast chromatographic method for the determination of dyes in beverages by using high performance liquid chromatography—diode array detection data and second order algorithms. J Chromatogr A 12(16):7063–7070
Minioti K, Sakellariou CF, Nikolas ST (2007) Determination of 13 synthetic food colorants in water-soluble foods. Anal Chim Acta 583:103–110
Dossi N, Toniolo R, Susmel S, Pizzariello A, Bontempelli G (2006) Simultaneous RP-LC determination of additives in soft drinks. Chromatographia 63:557–562
Kirschbaum J, Krause C, Brückner H (2006) Liquid chromatographic quantification of synthetic food colorants in fish roe and caviar. Eur Food Res Technol 222:572–579
Ni Y, Qi M, Kokot S (2001) Simultaneous spectrophotometric determination of ternary mixture of Tartrazine, Sunset yellow and Ponceau 4R by H-point standard addition method. Anal Lett 34:2585–2596
Lachenmeier DW, Kessler W (2008) Multivariate curve resolution of spectrophotometric data for the determination of artificial food colour. J Agric Food Chem 56(14):5463–5468
Blois MS (1958) Antioxidant determinations by the use of a stable free radical. Nature 181:1199–1200
Benzie IFF, Strain JJ (1996) The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of antioxidant power: the FRAP assay. Anal Biochem 239:70–76
Miller NJ, Diplock AT, Rice-Evans C, Davies MJ, Gopinathan V, Milner AA (1993) A novel method for measuring antioxidant capacity. Clin Sci (Lond) 84:407–412
Ozdemir Olgun FA, Demirata B, Apak R (2012) Determination of synthetic food colorants in water-soluble beverages individually by HPLC and totally by Ce(IV)-oxidative spectrophotometry. Food Anal Methods 5(6):1335–1341
Wen J, Kong W, Wang J, Yang M (2013) Simultaneous determination of four aflatoxins and ochratoxin A in ginger and related products by HPLC with fluorescence detection after immunoaffinity column clean-up and postcolumn phtochemical derivatization. J Seperation Sci 36(23):3709–3716
Celik SE, Ozyurek M, Guclu K, Apak R (2010) Determination of antioxidants by a novel on-line HPLC-cupric reducing antioxidant capacity (CUPRAC) assay with post-column detection. Anal Chim Acta 674:79–88
Ou Z, Schmierer D, Radesc T, Larsen L, McDowell A (2013) Application of an online post-column derivatization HPLC–DPPH assay to detect compounds responsible for antioxidant activity in Sonchus oleraceus L. leaf extracts Royal pharmaceutical society. J Pharm Pharmacol 65:271–279
Raudonis R, Raudone L, Jakstas V, Janulis V (2012) Comperative evaluation of post column free radical scavenging and ferric reducing antioxidant power assays for screening of antioxidants in strawberries. J Chroma 13(1233):8–15
Apak R, Güçlü K, Özyürek M, Karademir SE (2004) A novel total antioxidant capacity index for dietary polyphenols, vitamin C and E, using their cupric ion reducing capability in the presence of neocuproine: CUPRAC method. J Agric Food Chem 52:7970–7981
Miller R, Hotz J (1993) Conditional choice probabilities and the estimation of dynamic models. Rev Econ Stud 60:497–529
Jones A, Pravadali-Cekic S, Dennis GR, Shalliker RA (2015) Post column derivatisation analyses review. Is post-column derivatisation incompatible with modern HPLC columns? Anal Chim Acta 889:58–70
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozdemir Olgun, F.A., Demirata Ozturk, B. & Apak, R. Determination of Synthetic Food Colorants in Powder Beverage Samples by On-line HPLC–Cupric Reducing Antioxidant Capacity (CUPRAC) Assay with Post-Column Detection. Chromatographia 79, 199–208 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-015-3018-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-015-3018-4