Abstract
Purpose
Compare fourT1-mapping pulse sequences for T1 relaxometry and extracellular volume (ECV) fraction of the pancreas and liver
Materials and methods
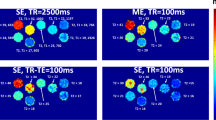
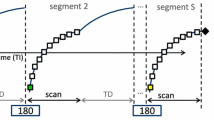
In vitro phase of this prospective study was performed on a T1 phantom, followed by imaging 22 patients. Variable flip angle (VFA), modified Look-Locker inversion recovery (MOLLI), prototype saturation recovery single-shot acquisition (SASHA), and prototype inversion recovery (IR-SNAPSHOT) pulse sequences were used to obtain T1 and ECV maps on the same 1.5 T MR scanner using the same imaging protocol.
Results
In vitro tests showed almost perfect precision of MOLLI (ρc = 0.9998), SASHA (ρc = 0.9985), and IR-SNAPSHOT (ρc = 0.9976), while VFA showed relatively less, however, substantial precision (ρc = 0.9862). Results of patient scans showed similar ECV fraction of the liver (p = 0.08), pancreas (p = 0.43), and T1 of the liver (p = 0.08) with all pulse sequences. T1 of the pancreas with MOLLI, SASHA, and IR-SNAPSHOT was statistically similar (p > 0.05).
Conclusion
MOLLI, SASHA, and IR-SNAPSHOT provided almost perfect in vitro precision and similar T1 during in vivo scans. Similar ECV fractions of the liver and pancreas were obtained with all sequences. More refinement of pulse sequences to provide sufficient spatial coverage in one breath hold together with high precision would be desirable in abdominal imaging.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- VFA:
-
Variable flip angle
- IR-SNAPSHOT:
-
Look-Locker inversion recovery
- SASHA:
-
Saturation recovery single-shot acquisition
- MOLLI:
-
Modified Look-Locker inversion recovery
- ECV:
-
Extracellular volume
- RF:
-
Radio frequency
References
Messroghli DR, Radjenovic A, Kozerke S, Higgins DM, Sivananthan MU, Ridgway JP (2004) Modified Look-Locker inversion recovery (MOLLI) for high-resolution T 1 mapping of the heart. Magn Reson Med 52(1):141–146
Moon JC, Messroghli DR, Kellman P, Piechnik SK, Robson MD, Ugander M, Gatehouse PD, Arai AE, Friedrich MG, Neubauer S, Schulz-Menger J, Schelbert EB, Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance I, Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Working Group of the European Society of C (2013) Myocardial T 1 mapping and extracellular volume quantification: a Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (SCMR) and CMR Working Group of the European Society of Cardiology consensus statement. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 15:92
Ou HY, Bonekamp S, Bonekamp D, Corona-Villalobos CP, Torbenson MS, Geiger B, Kamel IR (2013) MRI arterial enhancement fraction in hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis. Am J Roentgenol 201(4):W596–602
Tirkes T, Lin C, Fogel EL, Sherman SS, Wang Q, Sandrasegaran K (2017) T1 mapping for diagnosis of mild chronic pancreatitis. J Magn Reson Imaging 45(4):1171–1176
Kim KA, Park MS, Kim IS, Kiefer B, Chung WS, Kim MJ, Kim KW (2012) Quantitative evaluation of liver cirrhosis using T 1 relaxation time with 3 tesla MRI before and after oxygen inhalation. J Magn Reson Imaging 36(2):405–410
Luetkens JA, Klein S, Traber F, Schmeel FC, Sprinkart AM, Kuetting DLR, Block W, Uschner FE, Schierwagen R, Hittatiya K, Kristiansen G, Gieseke J, Schild HH, Trebicka J, Kukuk GM (2018) Quantification of liver fibrosis at T 1 and T 2 mapping with extracellular volume fraction MRI: preclinical results. Radiology 288(3):748–754
Banerjee R, Pavlides M, Tunnicliffe EM, Piechnik SK, Sarania N, Philips R, Collier JD, Booth JC, Schneider JE, Wang LM, Delaney DW, Fleming KA, Robson MD, Barnes E, Neubauer S (2014) Multiparametric magnetic resonance for the non-invasive diagnosis of liver disease. J Hepatol 60(1):69–77
Hoad CL, Palaniyappan N, Kaye P, Chernova Y, James MW, Costigan C, Austin A, Marciani L, Gowland PA, Guha IN, Francis ST, Aithal GP (2015) A study of T(1) relaxation time as a measure of liver fibrosis and the influence of confounding histological factors. NMR Biomed 28(6):706–714
Pavlides M, Banerjee R, Sellwood J, Kelly CJ, Robson MD, Booth JC, Collier J, Neubauer S, Barnes E (2016) Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging predicts clinical outcomes in patients with chronic liver disease. J Hepatol 64(2):308–315
Huang Y, Sadowski EA, Artz NS, Seo S, Djamali A, Grist TM, Fain SB (2011) Measurement and comparison of T 1 relaxation times in native and transplanted kidney cortex and medulla. J Magn Reson Imaging 33(5):1241–1247
Tirkes T, Lin C, Cui E, Deng Y, Territo PR, Sandrasegaran K, Akisik F (2018) Quantitative MR evaluation of chronic pancreatitis: extracellular volume fraction and MR relaxometry. Am J Roentgenol 210(3):533–542
Kellman P, Wilson JR, Xue H, Bandettini WP, Shanbhag SM, Druey KM, Ugander M, Arai AE (2012) Extracellular volume fraction mapping in the myocardium, part 2: initial clinical experience. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 14:64
Kellman P, Wilson JR, Xue H, Ugander M, Arai AE (2012) Extracellular volume fraction mapping in the myocardium, part 1: evaluation of an automated method. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 14:63
Ugander M, Oki AJ, Hsu LY, Kellman P, Greiser A, Aletras AH, Sibley CT, Chen MY, Bandettini WP, Arai AE (2012) Extracellular volume imaging by magnetic resonance imaging provides insights into overt and sub-clinical myocardial pathology. Eur Heart J 33(10):1268–1278
Cheng HL, Wright GA (2006) Rapid high-resolution T(1) mapping by variable flip angles: accurate and precise measurements in the presence of radiofrequency field inhomogeneity. Magn Reson Med 55(3):566–574
Nekolla S, Gneiting T, Syha J, Deichmann R, Haase A (1992) T 1 maps by K-space reduced snapshot-FLASH MRI. J Comput Assist Tomogr 16(2):327–332
Chow K, Flewitt JA, Green JD, Pagano JJ, Friedrich MG, Thompson RB (2014) Saturation recovery single-shot acquisition (SASHA) for myocardial T(1) mapping. Magn Reson Med 71(6):2082–2095
Chung S, Kim D, Breton E, Axel L (2010) Rapid B1+ mapping using a preconditioning RF pulse with TurboFLASH readout. Magn Reson Med 64(2):439–446
Lin LI (1989) A concordance correlation coefficient to evaluate reproducibility. Biometrics 45(1):255–268
Roujol S, Weingartner S, Foppa M, Chow K, Kawaji K, Ngo LH, Kellman P, Manning WJ, Thompson RB, Nezafat R (2014) Accuracy, precision, and reproducibility of four T 1 mapping sequences: a head-to-head comparison of MOLLI, ShMOLLI, SASHA, and SAPPHIRE. Radiology 272(3):683–689
Treier R, Steingoetter A, Fried M, Schwizer W, Boesiger P (2007) Optimized and combined T 1 and B1 mapping technique for fast and accurate T 1 quantification in contrast-enhanced abdominal MRI. Magn Reson Med 57(3):568–576
Yoon JH, Lee JM, Kim E, Okuaki T, Han JK (2017) Quantitative liver function analysis: volumetric T 1 mapping with fast multisection B1 inhomogeneity correction in hepatocyte-specific contrast-enhanced liver MR imaging. Radiology 282(2):408–417
Robson MD, Piechnik SK, Tunnicliffe EM, Neubauer S (2013) T 1 measurements in the human myocardium: the effects of magnetization transfer on the SASHA and MOLLI sequences. Magn Reson Med 70(3):664–670
Bandula S, Banypersad SM, Sado D, Flett AS, Punwani S, Taylor SA, Hawkins PN, Moon JC (2013) Measurement of Tissue interstitial volume in healthy patients and those with amyloidosis with equilibrium contrast-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 268(3):858–864
Gai N, Turkbey EB, Nazarian S, van der Geest RJ, Liu CY, Lima JA, Bluemke DA (2011) T 1 mapping of the gadolinium-enhanced myocardium: adjustment for factors affecting interpatient comparison. Magn Reson Med 65(5):1407–1415
Funding
No funding was received directly for this study. Dr. Tirkes is supported by National Cancer Institute and National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases of the National Institutes of Health under award numbers 1R01DK116963-01 and U01DK108323 (Consortium for the Study of Chronic Pancreatitis, Diabetes, and Pancreatic Cancer). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Li is supported by National Cancer Institute and National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases of the National Institutes of Health under award number U01DK108323. Dr. Li also receives support from MD Anderson Cancer Center under grant number P30CA016672.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TT was responsible for study conception and design, analysis and interpretation of data and drafting of the manuscript. CL was responsible for study conception and design, analysis and interpretation of data and critical revision. AJS was responsible for acquisition of data. LL was responsible for the analysis and interpretation of data and critical revision. SG and DN were responsible for study conception and design and critical review.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Institutional review board approved this Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) compliant prospective study. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tirkes, T., Zhao, X., Lin, C. et al. Evaluation of variable flip angle, MOLLI, SASHA, and IR-SNAPSHOT pulse sequences for T1 relaxometry and extracellular volume imaging of the pancreas and liver. Magn Reson Mater Phy 32, 559–566 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-019-00762-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-019-00762-2