Abstract
Objective
This work presents a highly-accelerated, self-gated, free-breathing 3D cardiac cine MRI method for cardiac function assessment.
Materials and methods
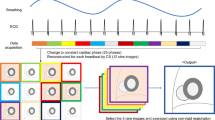
A golden-ratio profile based variable-density, pseudo-random, Cartesian undersampling scheme was implemented for continuous 3D data acquisition. Respiratory self-gating was achieved by deriving motion signal from the acquired MRI data. A multi-coil compressed sensing technique was employed to reconstruct 4D images (3D+time). 3D cardiac cine imaging with self-gating was compared to bellows gating and the clinical standard breath-held 2D cine imaging for evaluation of self-gating accuracy, image quality, and cardiac function in eight volunteers. Reproducibility of 3D imaging was assessed.
Results
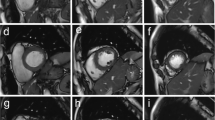
Self-gated 3D imaging provided an image quality score of 3.4 ± 0.7 vs 4.0 ± 0 with the 2D method (p = 0.06). It determined left ventricular end-systolic volume as 42.4 ± 11.5 mL, end-diastolic volume as 111.1 ± 24.7 mL, and ejection fraction as 62.0 ± 3.1%, which were comparable to the 2D method, with bias ± 1.96 × SD of −0.8 ± 7.5 mL (p = 0.90), 2.6 ± 3.3 mL (p = 0.84) and 1.4 ± 6.4% (p = 0.45), respectively.
Conclusion
The proposed 3D cardiac cine imaging method enables reliable respiratory self-gating performance with good reproducibility, and provides comparable image quality and functional measurements to 2D imaging, suggesting that self-gated, free-breathing 3D cardiac cine MRI framework is promising for improved patient comfort and cardiac MRI scan efficiency.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Uribe S, Muthurangu V, Boubertakh R, Schaeffter T, Razavi R, Hill DL, Hansen MS (2007) Whole-heart cine MRI using real-time respiratory self-gating. Magn Reson Med 57:606–613
Manka R, Buehrer M, Boesiger P, Fleck E, Kozerke S (2010) Performance of simultaneous cardiac-respiratory self-gated three-dimensional MR imaging of the heart: initial experience. Radiology 255:909–916
Liu J, Spincemaille P, Codella NC, Nguyen TD, Prince MR, Wang Y (2010) Respiratory and cardiac self-gated free-breathing cardiac CINE imaging with multiecho 3D hybrid radial SSFP acquisition. Magn Reson Med 63:1230–1237
Spincemaille P, Liu J, Nguyen T, Prince MR, Wang Y (2011) Z intensity-weighted position self-respiratory gating method for free-breathing 3D cardiac CINE imaging. Magn Reson Imaging 29:861–868
Henningsson M, Chan RH, Goddu B, Goepfert LA, Razavi R, Botnar RM, Schaeffter T, Nezafat R (2013) Contrast-enhanced specific absorption rate-efficient 3D cardiac cine with respiratory-triggered radiofrequency gating. J Magn Reson Imaging 37:986–992
Barkauskas KJ, Rajiah P, Ashwath R, Hamilton JI, Chen Y, Ma D, Wright KL, Gulani V, Griswold MA, Seiberlich N (2014) Quantification of left ventricular functional parameter values using 3D spiral bSSFP and through-time non-Cartesian GRAPPA. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 16:65
Zhu Y, Liu J, Weinsaft JW, Spincemaille P, Nguyen T, Prince MR, Bao S, Xie Y, Wang Y (2015) Free-breathing 3D imaging of right ventricular structure and function using respiratory and cardiac self-gated cine MRI. BioMed Res Int 2015:9. doi:10.1155/2015/819102
Bhat H, Ge L, Nielles-Vallespin S, Zuehlsdorff S, Li D (2011) 3D radial sampling and 3D affine transform-based respiratory motion correction technique for free-breathing whole-heart coronary MRA with 100% imaging efficiency. Magn Reson Med 65:1269–1277
Moghari MH, Roujol S, Chan RH, Hong SN, Bello N, Henningsson M, Ngo LH, Goddu B, Goepfert L, Kissinger KV, Manning WJ, Nezafat R (2013) Free-breathing 3D cardiac MRI using iterative image-based respiratory motion correction. Magn Reson Med 70:1005–1015
Pang J, Sharif B, Fan Z, Bi X, Arsanjani R, Berman DS, Li D (2014) ECG and navigator-free four-dimensional whole-heart coronary MRA for simultaneous visualization of cardiac anatomy and function. Magn Reson Med 72:1208–1217
Santelli C, Nezafat R, Goddu B, Manning WJ, Smink J, Kozerke S, Peters DC (2011) Respiratory bellows revisited for motion compensation: preliminary experience for cardiovascular MR. Magn Reson Med 65:1097–1102
Leung AO, Paterson I, Thompson RB (2008) Free-breathing cine MRI. Magn Reson Med 60:709–717
Hu P, Hong S, Moghari MH, Goddu B, Goepfert L, Kissinger KV, Hauser TH, Manning WJ, Nezafat R (2011) Motion correction using coil arrays (MOCCA) for free-breathing cardiac cine MRI. Magn Reson Med 66:467–475
Feng L, Axel L, Chandarana H, Block KT, Sodickson DK, Otazo R (2016) XD-GRASP: Golden-angle radial MRI with reconstruction of extra motion-state dimensions using compressed sensing. Magn Reson Med 75:775–788
Mascarenhas NB, Muthupillai R, Cheong B, Pereyra M, Flamm SD (2006) Fast 3D cine steady-state free precession imaging with sensitivity encoding for assessment of left ventricular function in a single breath-hold. AJR Am J Roentgenol 187:1235–1239
Liu J, Wieben O, Jung Y, Samsonov AA, Reeder SB, Block WF (2010) Single breathhold cardiac CINE imaging with multi-echo three-dimensional hybrid radial SSFP acquisition. J Magn Reson Imaging 32:434–440
Coppo S, Piccini D, Bonanno G, Chaptinel J, Vincenti G, Feliciano H, van Heeswijk RB, Schwitter J, Stuber M (2015) Free-running 4D whole-heart self-navigated golden angle MRI: initial results. Magn Reson Med 74:1306–1316
Tsao J, Boesiger P, Pruessmann KP (2003) k–t BLAST and k–t SENSE: dynamic MRI with high frame rate exploiting spatiotemporal correlations. Magn Reson Med 50:1031–1042
Kozerke S, Tsao J, Razavi R, Boesiger P (2004) Accelerating cardiac cine 3D imaging using k–t BLAST. Magn Reson Med 52:19–26
Greil GF, Germann S, Kozerke S, Baltes C, Tsao J, Urschitz MS, Seeger A, Tangcharoen T, Bialkowsky A, Miller S, Sieverding L (2008) Assessment of left ventricular volumes and mass with fast 3D cine steady-state free precession k–t space broad-use linear acquisition speed-up technique (k–t BLAST). J Magn Reson Imaging 27:510–515
Wech T, Pickl W, Tran-Gia J, Ritter C, Beer M, Hahn D, Kostler H (2014) Whole-heart cine MRI in a single breath-hold—a compressed sensing accelerated 3D acquisition technique for assessment of cardiac function. Rofo 186:37–41
Han F, Zhou Z, Han E, Gao Y, Nguyen KL, Finn JP, Hu P (2016) Self-gated 4D multiphase, steady-state imaging with contrast enhancement (MUSIC) using rotating cartesian K-space (ROCK): validation in children with congenital heart disease. Magn Reson Med. doi:10.1002/mrm.26376
Donoho DL (2006) Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 52:1289–1306
Candes EJ, Romberg J, Tao T (2006) Robust uncertainty principles: exact signal reconstruction from highly incomplete frequency information. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 52:489–509
Candes EJ, Tao T (2006) Near-optimal signal recovery from random projections: universal encoding strategies? IEEE Trans Inf Theory 52:5406–5425
Lustig M, Donoho D, Pauly JM (2007) Sparse MRI: the application of compressed sensing for rapid MR imaging. Magn Reson Med 58:1182–1195
Pruessmann KP, Weiger M, Scheidegger MB, Boesiger P (1999) SENSE: sensitivity encoding for fast MRI. Magn Reson Med 42:952–962
Griswold MA, Jakob PM, Heidemann RM, Nittka M, Jellus V, Wang J, Kiefer B, Haase A (2002) Generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisitions (GRAPPA). Magn Reson Med 47:1202–1210
Lustig M, Pauly JM (2010) SPIRiT: iterative self-consistent parallel imaging reconstruction from arbitrary k-space. Magn Reson Med 64:457–471
Piccini D, Feng L, Bonanno G, Coppo S, Yerly J, Lim RP, Schwitter J, Sodickson DK, Otazo R, Stuber M (2016) Four-dimensional respiratory motion-resolved whole heart coronary MR angiography. Magn Reson Med. doi:10.1002/mrm.26221
Cheng JY, Zhang T, Ruangwattanapaisarn N, Alley MT, Uecker M, Pauly JM, Lustig M, Vasanawala SS (2015) Free-breathing pediatric MRI with nonrigid motion correction and acceleration. J Magn Reson Imaging 42:407–420
Prieto C, Doneva M, Usman M, Henningsson M, Greil G, Schaeffter T, Botnar RM (2015) Highly efficient respiratory motion compensated free-breathing coronary MRA using golden-step Cartesian acquisition. J Magn Reson Imaging 41:738–746
Zhu Y, Guo Y, Lingala SG, Lebel RM, Law M, Nayak KS (2016) GOCART: GOlden-angle CArtesian randomized time-resolved 3D MRI. Magn Reson Imaging 34:940–950
Piccini D, Littmann A, Nielles-Vallespin S, Zenge MO (2011) Spiral phyllotaxis: the natural way to construct a 3D radial trajectory in MRI. Magn Reson Med 66:1049–1056
Küstner T, Würslin C, Gatidis S, Martirosian P, Nikolaou K, Schwenzer NF, Schick F, Yang B, Schmidt H (2016) MR image reconstruction using a combination of compressed sensing and partial Fourier acquisition: ESPReSSo. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 35:2447–2457
Liu J, Saloner D (2014) Accelerated MRI with CIRcular Cartesian UnderSampling (CIRCUS): a variable density Cartesian sampling strategy for compressed sensing and parallel imaging. Quant Imaging Med Surg 4:57–67
Liu J, Pedoia V, Heilmeier U, Ku E, Su F, Khanna S, Imboden J, Graf J, Link T, Li X (2016) High-temporospatial-resolution dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) wrist MRI with variable-density pseudo-random circular Cartesian undersampling (CIRCUS) acquisition: evaluation of perfusion in rheumatoid arthritis patients. NMR Biomed 29:15–23
Liu J, Faraji F, Kefayati S, Haraldsson H, Saloner D (2015) Highly accelerated intracranial 4D flow MRI with CIRcular Cartesian Undersampling (CIRCUS). In: Proceedings of the 23rd Annual Meeting of ISMRM, Toronto, Canada, p 458
Otazo R, Kim D, Axel L, Sodickson DK (2010) Combination of compressed sensing and parallel imaging for highly accelerated first-pass cardiac perfusion MRI. Magn Reson Med 64:767–776
Feng L, Srichai MB, Lim RP, Harrison A, King W, Adluru G, Dibella EV, Sodickson DK, Otazo R, Kim D (2013) Highly accelerated real-time cardiac cine MRI using k–t SPARSE-SENSE. Magn Reson Med 70:64–74
Winkelmann S, Schaeffter T, Koehler T, Eggers H, Doessel O (2007) An optimal radial profile order based on the Golden Ratio for time-resolved MRI. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 26:68–76
Larson AC, Kellman P, Arai A, Hirsch GA, McVeigh E, Li D, Simonetti OP (2005) Preliminary investigation of respiratory self-gating for free-breathing segmented cine MRI. Magn Reson Med 53:159–168
Rosset A, Spadola L, Ratib O (2004) OsiriX: an open-source software for navigating in multidimensional DICOM images. J Digit Imaging 17:205–216
Wetzl J, Schmidt M, Zenge MO, Lugauer F, Lazar L, Nadar M, Maier A, Hornegger J, Forman C (2015) Isotropic 3-D CINE imaging with Sub-2 mm resolution in a single breath-hold. In: Proceedings of the 24th Annual Meeting of ISMRM, Singapore, May 2016, p 1011
Usman M, Cruz G, Prieto C (2016) Highly-efficient free breathing whole heart CINE MRI with self gated 3D CASPR-TIGER trajectory. In: Proceedings of the 24th Annual Meeting of ISMRM, Singapore, May 2016, p 1814
Nezafat R, Herzka D, Stehning C, Peters DC, Nehrke K, Manning WJ (2008) Inflow quantification in three-dimensional cardiovascular MR imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 28:1273–1279
Srinivasan S, Ennis DB (2014) Variable flip angle balanced steady-state free precession for lower SAR or higher contrast cardiac cine imaging. Magn Reson Med 71:1035–1043
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by Grant from the NIH K25EB014914 (JL), NIH R56HL133663 (JL), GE Healthcare (JL), NIH R01NS059944 (DS), R01HL114118 (DS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This study was conducted under IRB approvals (#12-09781, #14-14769) at University of California San Francisco.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Feng, L., Shen, HW. et al. Highly-accelerated self-gated free-breathing 3D cardiac cine MRI: validation in assessment of left ventricular function. Magn Reson Mater Phy 30, 337–346 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-017-0607-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-017-0607-2