Abstract
Objective
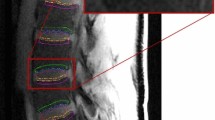
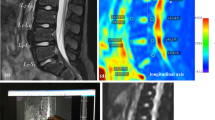
A decreased supply of nutrition to the intervertebral disc can lead to disc degeneration. Nutrient supply can be simulated in vivo by measuring gadolinium enhancement of the disc. We aimed to study the changes associated with disc degeneration that may have effect on the nutrition of the disc, i.e. lumbar artery narrowing, Modic changes, endplate defects, and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) in nucleus pulposus.
Patients and methods
Twenty male volunteers underwent a lumbar spine examination at 1.5 T for anatomical imaging, diffusion weighted imaging, magnetic resonance angiography, and for T1 relaxation time quantification of contrast enhancement of intervertebral disc.
Results
Enhancement of the disc increased with degeneration. Disc space narrowing associated strongly with the enhancement (Pearson’s correlation coefficient 0.46, P < 0.001). The enhancement rate in discs adjacent to Modic type 2 changes was 24%, adjacent to type 1/2 changes 58%, and 13% in the absence of Modic changes. Discs adjacent to endplate defects enhanced 32% compared to 10% of normal endplates. Lumbar artery narrowing or ADC in the disc were not associated with the enhancement.
Conclusion
Increased enhancement of a degenerated disc is associated mostly with disc space narrowing and with the presence of degenerative endplate changes and endplate defects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Urban JP, Smith S, Fairbank JC (2004) Nutrition of the intervertebral disc. Spine 29(23): 2700–2709
Niinimaki JL, Parviainen O, Ruohonen J, Ojala RO, Kurunlahti M, Karppinen J, Tervonen O, Nieminen MT (2006) In vivo quantification of delayed gadolinium enhancement in the nucleus pulposus of human intervertebral disc. J Magn Reson Imaging 24(4): 796–800
Rajasekaran S, Babu JN, Arun R, Armstrong BR, Shetty AP, Murugan S (2004) ISSLS prize winner: a study of diffusion in human lumbar discs: a serial magnetic resonance imaging study documenting the influence of the endplate on diffusion in normal and degenerate discs. Spine 29(23): 2654–2667
Nguyen-minh C, Haughton VM, Papke RA, An H, Censky SC (1998) Measuring diffusion of solutes into intervertebral disks with MR imaging and paramagnetic contrast medium. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19(9): 1781–1784
Nguyen-minh C, Riley L 3rd, Ho KC, Xu R, An H, Haughton VM (1997) Effect of degeneration of the intervertebral disk on the process of diffusion. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 18(3): 435–442
Tokuda O, Okada M, Fujita T, Matsunaga N (2007) Correlation between diffusion in lumbar intervertebral disks and lumbar artery status: evaluation with fresh blood imaging technique. J Magn Reson Imaging 25(1): 185–191
Kurunlahti M, Kerttula L, Jauhiainen J, Karppinen J, Tervonen O (2001) Correlation of diffusion in lumbar intervertebral disks with occlusion of lumbar arteries: a study in adult volunteers. Radiology 221(3): 779–786
Kauppila LI, Tallroth K (1993) Postmortem angiographic findings for arteries supplying the lumbar spine: their relationship to low-back symptoms. J Spinal Disord 6(2): 124–129
Modic MT, Steinberg PM, Ross JS, Masaryk TJ, Carter JR (1988) Degenerative disk disease: assessment of changes in vertebral body marrow with MR imaging. Radiology 166(1 Pt 1): 193–199
Kealey SM, Aho T, Delong D, Barboriak DP, Provenzale JM, Eastwood JD (2005) Assessment of apparent diffusion coefficient in normal and degenerated intervertebral lumbar disks: initial experience. Radiology 235(2): 569–574
Kerttula LI, Jauhiainen JP, Tervonen O, Suramo IJ, Koivula A, Oikarinen JT (2000) Apparent diffusion coefficient in thoracolumbar intervertebral discs of healthy young volunteers. J Magn Reson Imaging 12(2): 255–260
Bammer R, Herneth AM, Maier SE, Butts K, Prokesch RW, Do HM, Atlas SW, Moseley ME (2003) Line scan diffusion imaging of the spine. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24(1): 5–12
Kuisma M, Karppinen J, Niinimaki J, Ojala R, Haapea M, Heliovaara M, Korpelainen R, Taimela S, Natri A, Tervonen O (2007) Modic changes in endplates of lumbar vertebral bodies: prevalence and association with low back and sciatic pain among middle-aged male workers. Spine 32(10): 1116–1122
Tofts PS, Lloyd D, Clark CA, Barker GJ, Parker GJ, McConville P, Baldock C, Pope JM (2000) Test liquids for quantitative MRI measurements of self-diffusion coefficient in vivo. Magn Reson Med 43(3): 368–374
Pfirrmann CW, Metzdorf A, Zanetti M, Hodler J, Boos N (2001) Magnetic resonance classification of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine 26(17): 1873–1878
Modic MT, Masaryk TJ, Ross JS, Carter JR (1988) Imaging of degenerative disk disease. Radiology 168(1): 177–186
Grunhagen T, Wilde G, Soukane DM, Shirazi-Adl SA, Urban JP (2006) Nutrient supply and intervertebral disc metabolism. J Bone Joint Surg Am 88(suppl 2): 30–35
Urban JP, Winlove CP (2007) Pathophysiology of the intervertebral disc and the challenges for MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 25(2): 419–432
Nerlich AG, Schaaf R, Walchli B, Boos N (2007) Temporo-spatial distribution of blood vessels in human lumbar intervertebral discs. Eur Spine J 16(4): 547–555
Ibrahim MA, Haughton VM, Hyde JS (1995) Effect of disk maturation on diffusion of low-molecular-weight gadolinium complexes: an experimental study in rabbits. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 16(6): 1307–1311
Akansel G, Haughton VM, Papke RA, Censky S (1997) Diffusion into human intervertebral disks studied with MR and gadoteridol. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 18(3): 443–445
Moore RJ (2000) The vertebral end-plate: what do we know?. Eur Spine J 9(2): 92–96
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niinimäki, J., Korkiakoski, A., Parviainen, O. et al. Association of lumbar artery narrowing, degenerative changes in disc and endplate and apparent diffusion in disc on postcontrast enhancement of lumbar intervertebral disc. Magn Reson Mater Phy 22, 101–109 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-008-0151-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-008-0151-1