Abstract
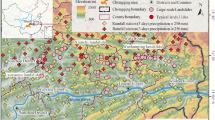
The torrential rains that hit northern Kyushu, Japan, on July 5–6, 2017, caused serious damage, especially in Asakura City, Fukuoka Prefecture, and in Hita City, Oita Prefecture. The primary meteorological mechanism that caused these torrential rains can be summarized as record-breaking heavy rains caused by linear rainbands in northern Kyushu. These heavy rains triggered hillside collapse, with the massive volume of driftwood and soil destroying downstream areas. Shortly after the immediate damage caused by the torrential rains was confirmed, the agricultural reservoirs were suspected to have exacerbated the flood damage in downstream areas. However, it is considered that the reservoirs helped mitigate flood impacts. To verify the disaster mitigation effect of the reservoirs on these torrential rains, the Japan Society of Irrigation, Drainage and Rural Engineering organized a survey team to investigate the damaged agricultural reservoirs in Asakura City. From the survey, four of 11 surveyed reservoirs were confirmed ravaged because of the massive driftwood and soil volume from the hillside area. However, the other reservoirs remained intact, and two distinctive characteristics were found to have helped prevent the flood from worsening. One was the reservoirs’ capacity to store soil; they had a large water capacity, and their strong walls kept the soil inside at their full water level. The other was spillway type and location. The reservoirs that had side-overflow spillways were able to discharge driftwood. Therefore, the water storage capacity of the reservoirs, dike strength, and spillway type and location are important factors that may help mitigate flooding.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fire and Disaster Management Agency of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communication, Japan (2017) Damage situation by torrential rains and typhoon caused by seasonal rain front on 30 June 2017. http://www.fdma.go.jp/bn/8d69db20cdee708269ce9f543bad1dbf0fb6be3b.pdf. Accessed 28 Dec 2018. (in Japanese)
Hori T (2015) Impact and safety of reservoirs in case of debris flow into the reservoirs. Found Eng Equip Mon 43(6):101–104 (in Japanese)
Izumi A, Hori T, Syoda D, Yoshisako H, Kajihara Y (2018) Disaster cause of small earthfill dam damaged by northern Kyushu torrential rain in July 2017. Bull NARO River Eng 2:121–136 (in Japanese)
Japan Meteorological Agency (2017a) Information of torrential rains in northern Kyushu on July 2017. http://www.jma.go.jp/jma/press/1707/19a/20170719_sankou.pdf. Accessed 26 Dec 2018. (in Japanese)
Japan Meteorological Agency (2017b) Dairy weather chart. No 186. http://www.data.jma.go.jp/fcd/yoho/data/hibiten/2017/1707.pdf Accessed 28 Dec 2018. (in Japanese)
Japan Meteorological Agency (2017c) Search for the past weather information in Japan. https://www.data.jma.go.jp/obd/stats/etrn/index.php. Accessed 26 Dec 2018. (in Japanese)
Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Japan (2018) Overview of agricultural reservoirs. http://www.maff.go.jp/j/nousin/bousai/bousai_saigai/b_tameike/. Accessed 26 Dec 2018. (in Japanese)
Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism Kyushu Regional Development Bureau (2017) Report on research committee on restoration technology of river and erosion control at right bank catchment of Chikugo River Basin. http://www.qsr.mlit.go.jp/site_files/file/bousai_joho/tecforce/H29hokubugouu_data/171122houkokusyo11.pdf. Accessed 26 Dec 2018. (in Japanese)
Oda T, Miwa A, Nomura Y, Tanakamaru H (2015) Sediment disaster of irrigation ponds by heavy rainfall in August 2014 in Tanba city, Hyogo Prefecture. Water Land Environ Eng 8(83):39–42 (in Japanese)
Takemi T (2018) Generating factor of torrential rains in northern Kyushu 2017 and possibility of its prediction. Q J Sci Approach Fire Disaster 182:17–24 (in Japanese)
Tsuguchi H (2016) Linear rainbands. Tenki 63:727–729 (in Japanese)
Acknowledgements
This paper summarizes the results of the JSIDRE survey on the 2017 torrential rains in northern Kyushu, Japan. For the survey, we were fortunate to have the cooperation of the Disaster Prevention and Restoration Division, Rural Infrastructure Department, Rural Development Bureau of the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Japan, and the Rural Environment Division, Rural Development Bureau, of the Kyushu Regional Agricultural Administration Office. Moreover, we obtained valuable information from the Institute for Rural Engineering, NARO. We would like to express our gratitude to these agencies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozaki, A., Hiramatsu, K. & Hama, T. Survey of agricultural reservoirs damaged by the July 2017 torrential rains in northern Kyushu, Japan. Paddy Water Environ 17, 237–246 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-019-00716-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-019-00716-3