Abstract
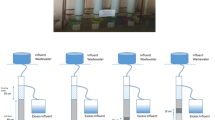
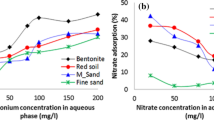
Sodium adsorption ratio (SAR) is one of the water quality indexes that whose is important due to reuse or depletion to environment. Solutes in drain water can be controlled by adsorption, chemical or biological reaction, organic envelope of drainage. Rice husk is the common option of drainage envelops in paddy fields. In this study, the ability of reduction of SAR by rice husk was evaluated in batch scale and physical model of drain envelops. In the batch experiments, the adsorption of SAR parameters was investigated by adding 2 g of rice husk into a 100 ml of sodium chloride solution. The results indicated that rice husk absorbed calcium, magnesium and sodium, respectively. By increasing the temperature, contact time and pH, adsorption of calcium, magnesium and sodium was increased; however, the higher concentration of sodium in soil solution reduced the percentage of adsorption. In a more realistic state, physical models of subsurface drainage in the paddy fields were made. Drainage envelope treatments included of rice husk (H), combination of 20 and 60 % of husk with gravel (H20G80 and H60G40) and a pipe without envelope (NE). Due to higher drain discharge and more sodium removal (lower SAR in drain water), treatment H with the discharge of 16.2 ml/min and SAR of 1.27 (meq/l)0.5 was better in comparison with other treatments.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adeniran KA (2008) Performance of no-filter drainage material on Clayey loam alfisol. J CIGR: 10
Ahalya N, Kanamadi RD, Ramachadra TV (2006) Bio sorption of Iron (III) from aqueous solutions using the husk of Cicer Arientinum. Indian J Chem Technol 13:122–127
Alizade A (2008) Soil, water and plants relationship. Imam Reza University, Mashhad, p 484 (In Farsi)
Antunesa M, Estevesb VI, Guéganc R, Crespoa JS, Fernandesd AN, Giovanelaa M (2012) Removal of diclofenac sodium from aqueous solution by Isabel grape bagasse. Chem Eng J 192:114–121
Arafat HA, Franz M, Pinto NG (1999) Effect of salt on the mechanism of adsorption of aromatics on activated carbon. Langmuir 15:5997–6003
Asadi M, Salehi B (2006) General chemistry, vol 1. Pub Shiraz University, Shiraz, p 1145 (In Farsi)
Bozic D, Gorgievski M, Stankovi V, Strbac N, Serbula S, Petrovic N (2013) Adsorption of heavy metal ions by Beech Sawdust—kinetics, mechanism and equilibrium of the process. Ecol Eng 58:202–206
Bybordi M (2008) Principals of land drainage engineering, vol 10. Pub Tehran University, Tehran, p 641
Cao W, Dang Z, Zhou XQ, Yi XY, Wu PX, Zhu N-W, Lu GN (2011) Removal of sulphate from aqueous solution using modified rice straw: preparation. characterization and adsorption performance. Carbohydr Polym 85(3):571–577
FAO (2010) The wealth of waste: the economics of wastewater use in agriculture. FAO Water Report 35. Rome
Ghane E, Navabian M, Esmaeili Varaki M, Malekpor Estalki A (2015) Investigation of hydraulic and chemical behavior of dual drain envelopes (organic and synthetic) in paddy conditions with two different water qualities. Iran Soil Water Res 46(1):31–39
Inosako K, Ohara K (2004) Desalinization of salt-affected field of Monbo area in Tanzania. Proc Annu Meet JSIDRE: 502–503
Inosako K, Yasunaga K, Takeshita N, Saito T, Inoue M (2012) Desalinization of a salt-affected field using a rice husk under drainage system. J Arid Land Stud 22(1):143–146
IRI Vice Presidency for Planning and Supervision—467 (2009) guidelines for laboratory analysis of soil and water samples. NO. 467. p 255. (In Farsi)
Kaboosi K (2006) The feasibility of rice husk application as an envelope material in subsurface drainage systems. Thesis for Degree of Master of Science, Irrigation and Reclamation Engineering, College of Agriculture and Natural Resources, Tehran University. Karaj (In Farsi)
Kaboosi K, Liaghat A, Hosseini SH (2012) The feasibility of rice husk application as envelope material in subsurface drainage system. Irrig Drain 61(4):490–496
Kamble BM, Rathod SD, Phalke DH (2008) Effect of sub-surface drainage (SSD) system with different filters (envelopes) on improvement of chemical properties of salt affected and water logged soil. Int J Agric Eng 1(2):123–125
Koerner RM (1994) Designing with geosynthetics. Prentice- Hall, Eaglewood Cliffs, p 738
Moslemi Kouchesfahani M (2012) Reduction of Nitrate and salinity of agricultural drained water using zeolite. Thesis for Degree of Master of Science, Irrigation and Drainage Engineering, Water Engineering, University of Guilan, Rasht city. p 81 (In Farsi)
Nadeem M, Mahmood A, Shahid SA (2006) Sorption of lead from aqueous solution by chemically modified carbon adsorbents. J Hazard Mater 138:604–613
Nameni M, AlaviMoghadam MR, Arami M (2008) Adsorption of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions by wheat bran. J Environ Sci Technol 5(2):161–168 (In Farsi)
Neek-Azar M, Alijani H, Haghighati A-H (2009) The removal of mercury from aqueous solutions by wheat husk. J Environ Sci Technol 11(2):111–118 (In Farsi)
Rivera-Utrilla J, Prados-Joya G, Sánchez-Polo M, Ferro-Garcia MA, Bautista-Toledo I (2009) Removal of nitro imidazole antibiotics from aqueous solution by adsorption/bio adsorption on activated carbon. J Hazard Mater 170:298–305
Smedema KL, Vlotman WF, Rycroft WR (2004) Modern land drainage: planning and management of agricultural drainage systems. Taylor & Francis, London, p 449
Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. 2013. 22nd Edition. Publication of the American Public Health Association (APHA), the American Water Works Association (AWWA), and the Water Environment Federation (WEF)
Velásquez L, Dussan J (2009) Bio Sorption and bioaccumulation of heavy metals on dead and living biomass of Bacillus sphaericus. J Hazard Mater 167(1–3):713–716
Vijayaraghavan K, Yun YS (2008) Bacterial bio sorbents and bio sorption. Biotechnol Adv 26(3):266–291
Vlotman WF, Willardson LS, Dierickx W (1999) Envelope design for subsurface drains. Institute for Land Reclamation and Improvement/ILRI, No. 60, Wageningen
Zhang Y, Zheng R, Zhao J, Ma F, Zhang Y, Meng Q (2014) Characterization of—treated rice husk adsorbent and adsorption of copper (ii) from aqueous solution. Biomed Res Int 2014:8
Acknowledgments
This article is extracted from the Master’s Thesis in the field of irrigation and drainage in the University of Guilan. The authors would hereby like to thank the University of Guilan for giving them the research facilities and Sharab Gostar Company for free drains.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Navabian, M., Ghane, E. & Hosseinzade, M. Investigating the reduction of sodium adsorption ratio from agricultural waste by rice husk in batch scale and physical model of drain envelop. Paddy Water Environ 15, 299–306 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-016-0549-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-016-0549-8