Abstract
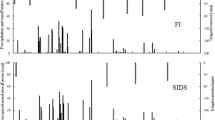
While many water-saving rice production techniques have been adopted in China, the environmental effects of these techniques require further investigation. This study aims to assess nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) leaching losses under real conditions in different water and N managements. Two water and three N treatments are conducted in the Taihu Lake region of China. Results show that the total N leaching losses during the rice season under flooding irrigation (FI) are 12.4, 9.31, and 7.17 kg ha−1 for farmers’ fertilization practices (FFP), site-specific N management (SSNM), and controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer management (CRN), respectively. Under controlled irrigation (CI), the respective losses were 7.40, 5.86, and 3.79 kg ha−1 for the same management methods. The total P leaching losses during the rice season under FI were 0.939, 0.927, and 0.353 kg ha−1 for FFP, SSNM, and CRN, respectively. Under CI, the losses were 0.424, 0.433, and 0.279 kg ha−1, respectively, for the same management methods. Ammonium and nitrate N accounted for 42.2–65.5% and 11.8–14.7% of the total nitrogen leaching losses under different water and N management methods, respectively. Due to significant decrease of volumes of percolation water and nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations in percolation water, N and P leaching losses were reduced in the CI treatment compared to the FI treatment under the same N management. The reduction of N input and application of controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer can reduce N and P leaching losses from paddy fields.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apthorp JN, Hedley MJ, Tillman RW (1987) The effects of nitrogen fertilizer form on the plant availability of phosphate from soil, phosphate rock and mono-calcium phosphate. Fertil Res 12:269–284
Barker R, Dawe D, Tuong TP, Bhuiyan SI, Guerra LC (2000) The outlook for water resources in the year 2020: challenges for research on water management in rice production. Int Rice Comm Newslett 49:7–21
Belder P, Bouman BAM, Cabangon R, Guoan L, Quilang EJP, Li YH, Spiertz JHJ, Tuong TP (2004) Effect of water-saving irrigation on rice yield and water use in typical lowland conditions in Asia. Agric Water Manage 65:193–210
Bouman BAM, Tuong TP (2001) Field water management to save water and increase its productivity in irrigated lowland rice. Agric Water Manage 49:11–30
Chirinda N, Cater MS, Albertb KR, Ambus P, Olesen JE, Porter JR, Petersen SO (2010) Emissions of nitrous oxide from arable organic and conventional cropping systems on two soil types. Agric Ecosyst Environ 136:199–208
Cui YL, Li YH, Lu GA, Sha ZR (2004) Nitrogen movement and transformation with different water supply for paddy rice. Adv Water Sci 15(3):280–285 (in Chinese)
Fan AM, Willhite CC, Book SA (1987) Evaluation of the nitrate drinking water standard with reference to infant methemoglobinemia and potential reproductive toxicity. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 7(2):135–148
Ji XH, Zheng SX, Shi LH, Liao YL (2008) Effect of fertilization on nutrient leaching loss from different paddy soils in Dongting Lake Area. Acta Pedol Sin 45(4):663–671 (in Chinese)
Ju XT, Xing GX, Chen XP, Zhang SL, Zhang LJ, Liu XJ, Cui ZL, Yin B, Christie P, Zhu ZL, Zhang FS (2009) Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive Chinese agricultural systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(9):3041–3046
Lage M, Bamouh A, Karrou M, Mourid ME (2003) Estimation of rice evapotranspiration using a microlysimeter technique and comparison with FAO Penman-Monteith and Pan Evaporation methods under Moroccan conditions. Agronomie 23:625–631
Le C, Zha Y, Li Y, Sun D, Lu H, Yin B (2010) Eutrophication of Lake Waters in China: cost, causes, and control. Environ Manage 45:662–668
Li YH (2001) Research and practice of water saving irrigation for rice in China. In: Proceedings of the international workshop on water saving irrigation for rice, pp 1–9
Li SS, Peng SZ (1991) Rice controlled irrigation. In: Proceedings of international commission on irrigation and drainage, special technical session, Beijing, pp 71–84
Li HP, Yang GS, Li Y (2006) Simulation of nutrient fluxes response of land use change in Taihu Basin. J Soil Water Conserv 20(4):179–182 (in Chinese)
Li H, Liang XQ, Chen YX, Tian GM, Zhang ZJ (2008) Ammonia volatilization from urea in rice fields with zero-drainage water management. Agric Water Manage 95:887–894
Liu W, Qiu RL (2007) Mini-review Water eutrophication in China and the combating strategies. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 82:781–786
Mao Z (2001) Water efficient irrigation and environmentally sustainable irrigated rice production in china. International Commission on Irrigation and Drainage
Ni WZ, Li JP, Zhu ZL (2007) Occurrence of nitrification-denitrification and gaseous nitrogen loss process in flooded rice soil. Prog Nat Sci 17(1):6–10
Pathak BK, Kazama F, Toshiaki I (2004) Monitoring of nitrogen leaching from a tropical paddy in Thailand. Agricultural Engineering International the CIGR. J Sci Res Dev VI:1–11
Peng SZ (1992) The new characters of rice water requirement in water-saving irrigation. Chin Rural Water Hydropower 10(3):401–412 (in Chinese)
Shan YH, Yang LZ, Yan TM, Wang JG (2005) Downward movement of phosphorus in paddy soil installed in large-scale monolith lysimeters. Agric Ecosyst Environ 111:270–278
State Environmental Protection Administration of China (2002) Standard methods for water and wastewater monitoring and analysis, 4th edn. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing, pp 243–281 (in Chinese)
Stoop WA, Uphoff N, Kassam A (2002) A review of agricultural research issues raised by the system of rice intensification (SRI) from Madagascar: opportunities for improving farming system for resource-poor farmers. Agric Syst 71:249–274
Tabbal DF, Bouman BAM, Bhuiyan SI, Sibayan EB, Sattar MA (2002) On-farm strategies for reducing water input in irrigated rice; case studies in the Philippines. Agric Water Manage 56:93–112
Tian YH, Yin B, Yang LZ, Yin SX, Zhu ZL (2007) Nitrogen runoff and leaching losses during rice-wheat rotations in Taihu Lake region, China. Pedophere 17(4):445–456
Wang DJ, Liu Q, Lin JH, Sun RJ (2004) Optimum nitrogen use and reduced nitrogen loss for production of rice and wheat in the Yangtse Delta region. Environ Geochem Health 26:221–227
Wortmann CS, Walters DT (2006) Phosphorus runoff during four years following composted manure application. J Environ Qual 35(2):651–657
Wu JF, Zhang ML, Liu JR, Wang HH (2001) Effect of different structure of fertilizer on the migration of nitrogen in red rice soil. Plant Nutr Fertil Sci 7(4):368–373 (in Chinese)
Xie XJ, Ran W, Shen QR, Yang CY, Yang JJ, Cao ZH (2004) Field studies on 32P movement and P leaching from flooded paddy soils in the region of Taihu Lake, China. Environ Geochem Health 26:237–243
Xing GX, Zhu ZL (2000) An assessment of N loss from agricultural fields to the environment in China. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 57:67–73
Yoon KS, Choi JK, Son JG, Cho JY (2006) Concentration profile of nitrogen and phosphorus in leachate of a paddy plot during the rice cultivation period in southern Korea. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 37:957–972
Yoshinaga L, Miuraa A, Hitomia T, Hamada K, Shiratani E (2007) Runoff nitrogen from a large sized paddy field during a crop period. Agric Water Manage 87:217–222
Yu SE, Zhang ZY (2002) Technical system of water saving irrigation for rice planting in Jiangsu Province. J Hohai Univ (Nat Sci) 30(6):30–34 (in Chinese)
Zhang HC, Cao ZH, Shen QR, Wong MH (2003) Effect of phosphate fertilizer application on phosphorus (P) losses from paddy soils in Taihu Lake Region: I. Effect of phosphate fertilizer rate on P losses from paddy soil. Chemosphere 50(6):695–701
Zhao MQ, Chen X, Shi Y, Lu CY (2009a) Phosphorous loss potential of lowland rice soil in Liaohe River Plain of Northeast China under effects of phosphorous fertilization. Fresenius Environ Bull 18(11):2146–2150
Zhao X, Xie YX, Xiong ZQ, Yan XY, Xing GX, Zhu ZL (2009b) Nitrogen fate and environmental consequence in paddy soil under rice-wheat rotation in the Taihu lake region, China. Plant Soil 319:225–234
Zhou S, Nishiyama K, Watanabe Y, Hosomi M (2009) Nitrogen budget and ammonia volatilization in paddy fields fertilized with liquid cattle waste. Water Air Soil Pollut 201:135–147
Zhu ZL, David N, Sun B (2006) Policy for reducing non-point pollution from crop production in China. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing, pp 135–136
Acknowledgments
The research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 50839002, 50809022) and the National Key Technologies R&D Program of China during the 11th Five-year Plan Period (No. 2006BAD11B09).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, SZ., Yang, SH., Xu, JZ. et al. Nitrogen and phosphorus leaching losses from paddy fields with different water and nitrogen managements. Paddy Water Environ 9, 333–342 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-010-0246-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-010-0246-y