Abstract
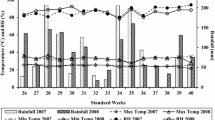
This study was conducted in an attempt to determine the proper nitrogen and phosphorus application levels, nitrogen split application ratio, and application method for environmental-friendly rice production in a salt-affected rice paddy field, which was located in the Saemangeum reclaimed tidal belt on the western coast of South Korea, between April 1, 2003 and October 10, 2004. All treatments were replicated three times in a randomized block design (5 m × 4 m plot) with 11 treatments (total 33 plots). We designed three treatments for the evaluation of reasonable application levels of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers (A1–A3); five treatments to evaluate the nitrogen split application system (T1–T5); and three treatments to determine the proper application for chemical fertilizer (M1–M3). There was no significant difference of amylose and protein content among the application levels, application methods, and nitrogen split application ratios (P < 0.05). No significant differences in grain yield and yield components of rice were observed among the different application levels, application methods, and nitrogen split application ratios (P < 0.05). In order to save labor in agricultural households, preserve or enhance the grain quality of rice, and reduce nutrient losses, we determined that the optimum application level of nitrogen fertilizer was 140 kg ha−1; the application split ratio of nitrogen fertilizer at four different periods was 40% for basal fertilization, 20% for maximum tilling stage, 30% for the panicle formation stage, and 10% for the booting stage; and the best application methods were deep layer application and whole layer application.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Back NH, Choi WY, Ko JC, Kim JK, Park HK, Choung JI, Kim SS, Park KG (2005a) Proper nitrogen fertilizer level for improving the rice quality at reclaimed saline land in the Southwestern area. Korean J Crop Sci 50:46–50 (in Korean, with English abstract)
Back NH, Choi WY, Ko JC, Nam JK, Park HK, Choung JI, Kim SS, Park KG (2005b) Proper transplanting time for improving the rice quality at reclaimed saline land in southwestern Area. Korean J Crop Sci 50:41–45 (in Korean, with English abstract)
Chae JC, Jung MS, Jun DK, Son YM (2002) Relationship between yield and quality of rice varieties grown in reclaimed saline paddy field. Korean J Crop Sci 47:259–262 (in Korean, with English abstract)
Cho JY (2003) Seasonal runoff estimation of N and P in a paddy field of central Korea. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 65:43–52
Cho JY, Choi JK (2001) Nitrogen and phosphorus losses from a broad paddy field in central Korea. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 32:2395–2410
Cho JY, Han KW (2002) Nutrient losses from a paddy field plot in central Korea. Water Air Soil Pollut 134:215–228
Cho JY, Han KW, Choi JK (2000a) Loads of nitrogen and phosphorus from the agricultural watershed in central Korea. Agric Chem Biotechnol 43:254–257
Cho JY, Han KW, Choi JK (2000b) Balance of nitrogen and phosphorus in a paddy filed of central Korea. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 46:343–354
Cho JY, Han KW, Yoon KS, Choi JK, Kim YJ (2002) N and P losses from a paddy field plot in central Korea. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 48:301–306
Cho JY, Son JG, Choi JK, Song CH (2008) Surface and subsurface losses of N and P from salt-affected rice paddy fields of reclaimed land in South Korea. Paddy Water Environ (in press)
Choi WY, Lee KS, Ko JC, Choi SY, Choi DH (2003) Critical saline concentration of soil and water for rice cultivation on a reclaimed saline soil. Korean J Crop Sci 48:238–242 (in Korean, with English abstract)
Choi WY, Lee KS, Ko JC, Park HK, Kim SS, Kim BK, Kim CK (2004) Nitrogen fertilizer management for improving rice quality under different salinity conditions in tidal reclaimed area. Korean J Crop Sci 49:194–198 (in Korean, with English abstract)
Choi WY, Lee KS, Park HK, Choung JI, Kim CK (2005) Optimum nitrogen split application system for grain of rice quality in tidal reclaimed area. Korean J Intl Agric 17:177–181 (in Korean, with English abstract)
Eaton AD, Clesceri LS, Greenberg AE (1995) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Hill JP (1993) The relationship between beta-lactoglobulin phenotypes and milk-composition in New-Zealand dairy-cattle. J Dairy Sci 76:281–286
Jackson ML (1967) Soil chemical analysis. Prentice-Hall, New Delhi
Koo JW, Choi JK, Son JG (1998) Soil properties of reclaimed tidel lands and tidelands of western sea coast in Korea. J Korean Soc Soil Sci Fertil 31:120–127 (in Korean, with English abstract)
Korea Rural Community & Agriculture Corporation (2004) Optimal farmland use and environment-friendly farming in the Saemangeum reclaimed farmland. Ansan, Korea (in Korean)
Lee HS, Kim OB (1997) Studies on salinity and growth of rice at Seosan reclaimed land. Korean J Ecol 20:367–373 (in Korean, with English abstract)
Lee SH, Lee HJ, Kim YI, Hong BD, An Y, Oh KS, Seo SK (2005) Fertilizer recommendation based on soil testing for environmentally friendly agriculture at the demonstration area in Dae-ho reclaimed tideland. Korean J Crop Sci International symposium, pp 114–115 (in Korean, with English abstract)
Ministry of environment (1999) Water quality standards. Seoul, Korea (in Korean)
Moon HT, Cho SR, Kim KH (1996) Changes of physico-chemical properties of soil in reclaimed area by cultivation. Korean J Environ Biol 14:149–153 (in Korean, with English abstract)
National Institute of Agricultural Science and Technology (NIAST) (1999) Standard application of chemical fertilizer in the crops. Suwon, Korea (in Korean)
National Institute of Agricultural Science and Technology (NIAST) (2000) Agricultural soil information system (ASIS). Suwon, Korea (in Korean)
Park CK, Yuk CS, Cho GD (1984) Application effects of some nitrogen fertilizers forms for the growth and yield of rice plant. J Korean Soc Soil Sci Fertil 18:78–88 (in Korean, with English abstract)
Perez CM, Juliano BO (1978) Modification of the simplified amylose test for milled rice. Starch 30:424–426
Shukla BD, Misra AK, Gupta RK (1998) Application of nitrogen in production and post-production systems of agriculture and its effect on environment in India. Environ Pollut 102:115–122
Yoon KS, Cho JY, Choi JK, Son JG (2006) Water management and N, P losses from paddy fields in Southern Korea. J Am Water Resour Assoc 42:1205–1216
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, J.Y., Son, J.G., Song, C.H. et al. Integrated nutrient management for environmental-friendly rice production in salt-affected rice paddy fields of Saemangeum reclaimed land of South Korea. Paddy Water Environ 6, 263–273 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-008-0124-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-008-0124-z