Abstract
Objective
The aim of the present study was to further evaluate the clinical value of single or joint of golgi protein 73 (GP73) and alphafetoprotein (AFP) in diagnosis of hepatocellular (HCC).
Methods
One hundred and eighteen, 94 and 47 serum samples from the patients with HCC, chronic liver disease (CLD) and liver cirrhosis (LC) were collected, respectively. Serum levels of AFP and GP73 were assayed with commercial kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Results
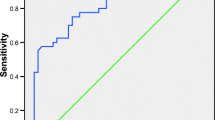
Patients with HCC had higher serum concentration of AFP than that of the patients with CLD (P < 0.01), but was similar to that of the patients with LC. Serum GP73 levels in the patients with CLD or LC were significantly lower than that in the patients from HCC group (P < 0.01). Among 118 HCC patients, the positive rate of GP73 and AFP was 80.5% and 48.3%, respectively (P < 0.001). The ROC curve analysis showed that the AUC value of GP73 was higher than that of serum AFP. Moreover, the sensitivity and the accuracy of GP73 were 77.1% and 82.6%, respectively, which were greater more than that of AFP at 90% specificity (28.8% and 59.8%, respectively). The AUC, the sensitivity and the accuracy of GP73 in combination of AFP (AFP/GP73) were 0.855, 78.0% and 83.0%, respectively, which were similar to that of GP73 alone but were much higher than that of the single marker AFP.
Conclusion
For HCC diagnosing, GP73 was more sensitive and specific than AFP. The diagnostic value of AFP/GP73 was similar to GP73 but was much higher than AFP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu MC. Clinical and experimental research of primary liver cancer in China. Chinese-German J Clin Oncol, 2002, 1: 1–4.
Yang SL, Pan XL, Xiong ZF, et al. The influence of hepatitis B virus X protein on the clock genes in liver cells and its significance. Chinese-German J Clin Oncol, 2011, 10: 468–471.
Forner A, Llovet JM, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet, 2012, 379: 1245–1455.
Ochiai T, Ikoma H, Murayama Y, et al. Factors resulting in 5-year disease-free survival after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Anticancer Res, 2012, 32: 1417–1422.
Chen XM, Luo PF, Lin HH, et al. Protocol of interventional treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Chinese-German J Clin Oncol, 2005, 4: 112–115
Yamashita T, Kaneko S. Treatment strategies for hepatocellular carcinoma in Japan. Hepatol Res, 2012 April 13.
Kudo M. Diagnostic imaging of hepatocellular carcinoma: recent progress. Oncology, 2011, 81: 73–85.
Tan W, Wu GY, Zheng CS. Imaging finding of primary hepatic leiomyoma. Chinese-German J Clin Oncol, 2009,8: 134–136.
Wang Y, Shen Z, Zhu Z, et al. Clinical values of AFP, GPC3 mRNA in peripheral blood for prediction of hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence following OLT: AFP, GPC3 mRNA for prediction of HCC. Hepat Mon, 2011, 11: 195–199.
El-Serag HB, Kramer JR, Chen GJ, et al. Effectiveness of AFP and ultrasound tests on hepatocellular carcinoma mortality in HCV-infected patients in the USA. Gut, 2011, 60: 992–997.
Bertino G, Neri S, Bruno CM, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of alpha-fetoprotein, des-γ-carboxy prothrombin and squamous cell carcinoma antigen immunoglobulin M complexes in hepatocellular carcinoma. Minerva Med, 2011, 102: 363–371.
Zhou L, Rui JA, Wang SB, et al. The significance of serum AFP cut-off values, 20 and 400 ng/mL in curatively resected patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and cirrhosis might be of difference. Hepatogastroenterology, 2012, 59: 840–843.
Hu JS, Wu DW, Liang S, et al. GP73, a resident Golgi glycoprotein, is sensibility and specificity for hepatocellular carcinoma of diagnosis in a hepatitis B-endemic Asian population. Med Oncol, 2010, 27: 339–345.
Kladney RD, Cui X, Bulla GA, et al. Expression of GP73, a resident Golgi membrane protein, in viral and nonviral liver disease. Hepatology, 2002, 35: 1431–1440.
Liu X, Wan X, Li Z, et al. Golgi protein 73 (GP73), a useful serum marker in liver diseases. Clin Chem Lab Med, 2011, 49: 1311–1316.
Marrero JA, Romano PR, Nikolaeva O, et al. GP73, a resident Golgi glycoprotein, is a novel serum marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol, 2005, 43: 1007–1012.
Hann HW, Wang M, Hafner J, et al. Analysis of GP73 in patients with HCC as a function of anti-cancer treatment. Cancer Biomark, 2010, 7: 269–273.
Yamamoto K, Imamura H, Matsuyama Y, et al. AFP, AFP-L3, DCP, and GP73 as markers for monitoring treatment response and recurrence and as surrogate markers of clinicopathological variables of HCC. J Gastroenterol, 2010, 45: 1272–1282.
Gu Y, Chen W, Zhao Y, et al. Quantitative analysis of elevated serum Golgi protein-73 expression in patients with liver diseases. Ann Clin Biochem, 2009, 46: 38–43.
Ozkan H, Erdal H, Tutkak H, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic validity of Golgi protein 73 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Digestion, 2011, 83: 83–88.
LU Y, Xia Y, Wang YH, et al. Expression of PADI4 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Chinese-German J Clin Oncol, 2009, 8: 453–455.
Shams M, Al-Gayyar M, Barakat E, et al. Circulating adiponectin: a potential prognostic marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Chinese-German J Clin Oncol, 2011, 10: 570–574
Zhang G, Ha SA, Kim HK, et al. Combined analysis of AFP and HCCR-1 as an useful serological marker for small hepatocellular carcinoma: a prospective cohort study. Dis Markers, 2012, 32: 265–271.
Liu AM, Yao TJ, Wang W, et al. Circulating miR-15b and miR-130b in serum as potential markers for detecting hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective cohort study. BMJ Open, 2012, 2: e000825.
Zhou Y, Yin X, Ying J, et al. Golgi protein 73 versus alpha-fetoprotein as a biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma: a diagnostic meta-analysis. BMC Cancer, 2012, 12: 17.
Shi Y, Chen J, Li L, et al. A study of diagnostic value of golgi protein GP73 and its genetic assay in primary hepatic carcinoma. Technol Cancer Res Treat, 2011, 10: 287–294.
Tian L, Wang Y, Xu D, et al. Serological AFP/golgi protein 73 could be a new diagnostic parameter of hepatic diseases. Int J Cancer, 2011, 129: 1923–1931.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by a grant from the International Collaboration Program from Nanjing Science and Technology Bureau (No. 201001139).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Z., Xia, D., Wang, C. et al. Clinical evaluation of single or joint of golgi protein 73 and alpha-fetoprotein in hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosing. Chin. -Ger. J. Clin. Oncol. 11, 650–654 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10330-012-1072-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10330-012-1072-z