Abstract
Objective
The aim of our study was to investigate the biological effects of Bcl-XL antisense oligodeoxynucleotide (ASODN) transfected into cultured esophageal carcinoma cells and human esophageal carcinoma xenograft in nude mice.
Methods
Cationic liposome-mediated ASODN was used to transfect esophageal carcinoma cells. RT-PCR, Western blot, MTT assay, flow cytometry, and in situ apoptosis cells detection (TUNEL detection) were used to systematically study the biological effects of transfected cells both in vitro and in vivo.
Results
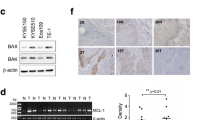
In this study, the results showed that the proliferation of esophageal carcinoma cells in ASODN group decreased significantly when compared with the control group (P < 0.05), at 57.3% Bcl-XL mRNA inhibitory rate, and a significant decreasing of Bcl-XL protein expression, at the apoptosis rates of (31.1 ± 5.8)% and 35.0% by flow cytometry and TUNEL assay respectively (P < 0.01, when compared with control groups). It also showed that the growth of human esophageal carcinoma in nude mice of ASODN group was significantly inhibited (P < 0.05), together with a significant decreased expression level of Bcl-XL mRNA and protein, and an induced tumor cell apoptosis in nude mice.
Conclusion
Our result indicates Bcl-XL ASODN can effectively inhibit the proliferation of esophageal carcinoma cells in vitro and tumor growth in vivo. The suppression of Bcl-XL expression by ASODN may offer both a therapeutic approach and an important theoretic foundation for gene therapy against esophageal carcinoma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krecicki T, Fraczek M, Kozlak J, et al. Bcl-XL protein expression in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci, 2004, 29: 55–58.
Zhao WL, Daneshpouy ME, Mounier N, et al. Prognostic significance of bcl-xL gene expression and apoptotic cell counts in follicular lymphoma. Blood, 2004, 103: 695–697.
Leech SH, Olie RA, Gautschi O, et al. Induction of apoptosis in lungcancer cells following Bcl-XL, anti-sense treatment. Int J Cancer, 2000, 86: 570–576.
Lin WM. Guide of operation and application on PCR technic. Beijing: Science Technic Publishing House of China, 1991. 69–72.
Arriola EL, Rodriguez-Lopez AM, Hickman JA, et al. Bcl-2 overexpression results in reciprocal downregulation of Bcl-X(L) and sensitized human testicular germ cell tumours to chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Oncogene, 1999, 18: 1457–1464.
Mizutani Y, Kamoi K, Ukimura O, et al. Synergistic cytotoxicity and apoptosis of JTE-522, a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, and 5-fluorouracil against bladder cancer. J Urol, 2002, 168: 2650–2654.
Wang T, Chen F, Chen Z. Honokiol induces apoptosis through p53-independent pathway in human colorectal line RKO. World J Gastroenterol, 2004, 10:2205–2208.
Watanabe J, Kushihata F, Honda K, et al. Prognostic significance of Bcl-xL in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Surgery, 2004, 135: 604–612.
Chu R, Upreti M, Ding WX, et al. Regulation of Bax by C-Jun NH2-terminal kinase and Bcl-xL in vinblastine-induced apoptosis. Biochem Pharmacol, 2009, 78: 241–248.
Wang X, Xing D, Liu L, et al. BimL directly neutralizes Bcl-xL to promote Bax activation during UV-induced apoptosis. FEBS Lett, 2009, 583: 1873–1879.
Soltani-Arabshahi R, Leboeuf C, Rivet J, et al. Bcl-xL gene expression correlated with lower apoptotic cell numbers and shorter progressionfree survival in PCFCL. J Invest Dermatol, 2009, 129: 1703–1709.
Xing LN, Qi L. Effects of antisense oligonucleotides targeting VEGF on radio sensitivity of uterine cervix cancer Hela cells. Chinese-German J Clin Oncol, 2009, 8: 50–54.
Okumura M, Kajiyama Y, Takeda K, et al. Correlation between loss of Bcl-XL expression and improved prognosis in advanced esophageal cancer treated by preoperative chemoradiotherapy. Eur Surg Res, 2008, 41: 260–266.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by a grant from the Henan Innovation Project for University Prominent Research Talents (No. 2007KYCX005).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Wen, H., Zhang, L. et al. Inhibitory effects of transfected Bcl-XL antisense oligodeoxynucleotide to proliferation and growth in esophageal carcinoma cell line and human esophageal carcinoma xenograft of nude mice. Chin. -Ger. J. Clin. Oncol. 9, 169–174 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10330-010-0006-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10330-010-0006-x