Abstract
Objective
The aim of the study was to establish models of Hep-2 laryngeal cancer cell line of different oxygen supplying, trying to investigate the impact of normoxia, hypoxia, reoxygenation after hypoxia on apoptosis and expression of proteins HIF-1α and p53 to Hep-2 human laryngeal cancer cell line induced by 60Co γ-ray.
Methods
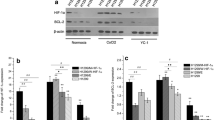
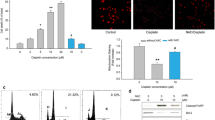
Human laryngeal cancer Hep-2 cells were divided into 3 groups: group A (normoxia), group B (hypoxia), and group C (reoxygenation after hypoxia). All of the cells were exposed to 5 Gy dosage of γ-ray. Flow cytometry (FCM) was used to measure the protein levels of HIF-1α and p53 and to detect cell apoptosis. The protein levels of HIF-1α and p53 were also determined by immunohistochemistry and Western blotting. The expression of HIF-1α mRNA was determined by RT-PCR.
Results
The protein levels of HIF-1α and p53 were evidently increased in group B compared to group A. The protein levels of HIF-1α and p53 in group C were lower compared to group B; the rate of apoptosis in group C was higher than that in group B.
Conclusion
Hypoxia decreased the effect of apoptosis induced by 60Co γ-ray in Hep-2 human laryngeal cancer cell line. The apoptosis pathway maybe related to some other genes or proteins but not p53 in the conditions of hypoxia and reoxygenation after hypoxia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Iida T, Mine S, Fujimoto H, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha induces cell cycle arrest of endothelial cells. Genes Cells, 2002, 7: 143–149.
Comerford KM, Wallace TJ, Karhausen J, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1-dependent regulation of the multidrug resistance (MDR1) gene. Cancer Res, 2002, 62: 3387–3394.
Zhu WG, Aramaki R, Cai Y, et al. Promotion of heat-induced apoptosis in FM3A cells by protease inhibitors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 1996, 225: 924–931.
Jayasurya R, Francis G, Kannan S, et al. p53, p16 and cyclin D1: molecular determinants of radiotherapy treatment response in oral carcinoma. Int J Cancer, 2004, 109: 710–716.
Stephens LC, Ang KK, Schultheiss TE, et al. Apoptosis in irradiated murine tumors. Radiat Res, 1991, 127: 308–316.
Shen WG, Zhu J, Yu ZY, et al. Effect of hypoxia on migration invasion and adhesion to endothelium of human pulmonary adenocarcinoma A549 cells. Chinese-German J Clin Oncol, 2008, 7: 509–514.
Liang L. The expression of protein HIF-α and p53 in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical carcinoma and its significance. J Qiqihar Med Coll (Chinese), 2007, 28: 158–161.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, B., Zhang, J., Song, D. et al. The impact of 60Co γ-ray on apoptosis to Hep-2 human laryngeal cancer cell in the condition of reoxygenation after hypoxia. Chin. -Ger. J. Clin. Oncol. 9, 93–96 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10330-009-0163-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10330-009-0163-y