Abstract
Objective
To investigate the anti-proliferative effect of histone deacetylases-1 (HDAC-1) knockdown in Hela cells.
Methods
The HDAC-1 protein was knockdowned using siRNA. The expression of HDAC-1 was detected by Western blotting. Apoptosis was assessed by flow cytometry. The inhibition of cell growth was assesses by MTT assay.
Results
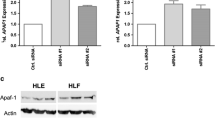
HDAC-1 siRNA knockdowned the expression of HDAC-1 protein. HDAC siRNA inhibited the proliferation of Hela cells. HDAC-1 siRNA induced apoptosis.
Conclusion
HDAC-1 siRNA may inhibit the growth of Hela cells by inducing apoptosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khan N, Jeffers M, Kumar S, et al. Determination of the class and isoform selectivity of small-molecule histone deacetylase inhibitors. Biochem J, 2008, 409: 581–589.
Nome RV, Bratland A, Harman G, et al. Cell cycle checkpoint signaling involved in histone deacetylase inhibition and radiation-induced cell death. Mol Cancer Ther, 2005, 4: 1231–1238.
Wang AD, Ji XY, Huang Q, et al. Studies on the target cells and molecules with sodium valproate induced differential of human glioma cells. Chin J Surg (Chinese), 2007, 45: 1121–1124.
Thelen P, Schweyer S, Hemmerlein B, et al. Expressional changes after histone deacetylase inhibition by valproic acid in LNCaP human prostate cancer cells. Int J Oncol, 2004, 24: 25–31.
Chopin V, Toillon RA, Jouy N, et al. P21 (WAF1/CIP1) is dispensable for G1 arrest, but indispensable for apoptosis induced by sodium butyrate in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Oncogene, 2004, 23: 21–29.
Huang X, Guo B. Adenomatous polyposis coli determines sensitivity to histone deacetylase inhibitor-induced apoptosis in colon cancer cells. Cancer Res, 2006, 66: 9245–9251.
Park H, Im JY, Kim J, et al. Effects of apicidin, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, on the regulation of apoptosis in H-ras-transformed breast epithelial cells. Int J Mol Med, 2008, 21: 325–333.
Komata T, Kanzawa T, Nashimoto T, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors, N-butyric acid and trichostatin A, induce caspase-8-but not caspase-9-dependent apoptosis in human malignant glioma cells. Int J Oncol, 2005, 26: 1345–1352.
Halkidou K, Gaughan L, Cook S, et al. Upregulation and nuclear recruitment of HDAC1 in hormone refractory prostate cancer. Prostate, 2004, 59: 177–189.
Weichert W, Röske A, Gekeler V, et al. Histone deacetylases 1, 2 and 3 are highly expressed in prostate cancer and HDAC2 expression is associated with shorter PSA relapse time after radical prostatectomy. Br J Cancer, 2008, 98: 604–610.
Rikimaru T, Taketomi A, Yamashita Y, et al. Clinical significance of histone deacetylase 1 expression in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology, 2007, 72: 69–74.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, N., Yu, S. The proliferation inhibition of Hela cells by histone deacetylases-1 siRNA. Chin. -Ger. J. Clin. Oncol. 7, 365–367 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10330-008-0034-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10330-008-0034-y