Abstract
Objective
To investigate the effects and mechanisms of tumor suppressor gene PTEN on the induction of anoikis of human bladder transitional carcinoma cells BIU-87.
Methods
BIU-87 cells were transfected with GFP plasmids containing wild-type PTEN or phosphatase inactivating mutant PTEN (C124A-PTEN) in vitro. The PTEN expression and the phosphorylation levels of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and protein kinase B (PKB/Akt) were detected by Western blotting. Flow cytometry assay and laser scanning confocal microscopy were used to analyze apoptosis in adherent and non-adherent cells.
Results
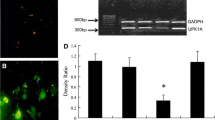
Compared with the control group, PTEN expression in the cells transfected with wild-type PTEN increased to 210%–260%, while the phosphorylation level of FAK and Akt decreased 59% (P < 0.01) and 89% (P < 0.01), respectively. And the anoikis percentage increased from 8.32 ± 0.57% to 37.62 ± 2.12%. In the cells transfected with C124A-PTEN, neither the phosphorylation of FAK and Akt nor the anoikis percentage had obviously changed, although the PTEN expression enhanced remarkably in comparison with the control.
Conclusion
Through its phosphatase activity, tumor suppressor gene PTEN can suppress the phosphorylation of FAK and Akt, and induce anoikis in human bladder transitional carcinoma cells BIU-87.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Frisch SM, Francis H. Disruption of epithelial cell-matrix interactions induces apoptosis. J Cell Biol, 1994, 124: 619–626.
Frisch SM, Vuori K, Ruoslahti E, et al. Control of adhesion-dependent cell survival by focal adhesion kinase. J Cell Biol, 1996, 134: 793–799.
Frisch SM, Screaton RA. Anoikis mechanisms. Curr Opin Cell Biol, 2001, 13: 555–562.
Yamada KM, Araki M. Tumor suppressor PTEN: modulator of cell signaling, growth, migration and apoptosis. J Cell Sci, 2001, 114, 2375–2382.
Iijima M, Huang YE, Luo HR, et al. Novel mechanism of PTEN regulation by its phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate binding motif is critical for chemotaxis. J Biol Chem, 2004, 279: 16606–16613.
Tamura M, Gu J, Takino T, et al. Tumor suppressor PTEN inhibition of cell invasion, migration, and growth: differential involvement of focal adhesion kinase and p130Cas. Cancer Res, 1999, 59: 442–449.
Grossmann J. Molecular mechanisms of “detachment-induced apoptosis — Anoikis“. Apoptosis, 2002, 7: 247–260.
Liotta LA, Kohn E. Anoikis: cancer and the homeless cell. Nature, 2004, 430: 973–974.
Rytomaa M, Lehmann K, Downward J. Matrix detachment induces caspase-dependent cytochrome c release from mitochondria: inhibition by PKB/Akt but not Raf signalling. Oncogene, 2000, 19: 4461–4468.
Simpson L, Parsons R. PTEN: life as a tumor suppressor. Exp Cell Res, 2001, 264: 29–41.
Li J, Simpson L, Takahashi M, et al. The PTEN/MMAC1 tumor suppressor induces cell death that is rescued by the AKT/protein kinase B oncogene. Cancer Res, 1998, 58: 5667–5672.
Gildea JJ, Herlevsen M, Harding MA, et al. PTEN can inhibit in vitro organotypic and in vivo orthotopic invasion of human bladder cancer cells even in the absence of its lipid phosphatase activity. Oncogene, 2004, 23: 6788–6797.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30271300).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Y., Zhang, X., Zhou, S. et al. PTEN induces anoikis through its phosphatase activity in human bladder transitional carcinoma cells BIU-87. Chinese German J Clin Oncol 6, 373–377 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10330-007-0018-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10330-007-0018-3