Abstract
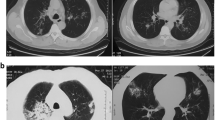
By now there are a few reports describing a case of pulmonary inflammatory pseudotumor, presenting multiple nodules in bilateral lungs and a pseudotumor caused by fungus infection is also a very rare disease. Here we report a rare case of pulmonary inflammatory pseudotumor with confirmed cause by Cryptococcus infection presenting multiple nodules in bilateral lungs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dorman JP, Arom KV. Pulmonary pseudotumor caused by actinomycosis. Tex Med, 1976, 72: 65–67.
Luhr H, Svane S. Pulmonary pseudotumor caused by Cryptococcus neoformans. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen, 1991, 111: 3288–3290.
Priebe-Richter C, Ivanyi P, Buer J, et al. Inflammatory pseudotumor of the lung following invasive aspergillosis in a patient with chronic graft-vs.-host disease. Eur J Haematol, 2005, 75: 68–72.
Zhi XY, Liu BD, Xu QS, et al. Clinical value of computed tomography and fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron remission tomography in diagnosis of mediastinal metastasis of non small cell lung cancer. Natl Med J Chin (Chinese), 2005, 85: 2026–2029.
Port JL, Andrade RS, Levin MA, et al. Positron emission tomographic scanning in the diagnosis and staging of non-small cell lung cancer 2 cm in size or less. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 2005, 130: 1611–1615.
Perrotin C, Lemeunier P, Grahek D, et al. Results of FDG-PET scanning in the pre-operative staging of broncho-pulmonary tumours. Rev Mal Respir, 2005, 22: 579–585.
Rohren EM, Lowe VJ. Update in PET imaging of nonsmall cell lung cancer. Semin Nucl Med, 2004, 34: 134–153.
Zhao J, Lin XT, Guan YH, et al. Dual time point 18F-FDG PET imaging for differentiating malignant from benign lung nodules. Chin J Nucl Med (Chinese), 2003, 23: 8–10.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, L., Pan, T., Wei, X. et al. Pulmonary inflammatory pseudotumor caused by Cryptococcus presenting multiple nodules in bilateral lungs. Chinese German J Clin Oncol 5, 460–462 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10330-006-0504-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10330-006-0504-z