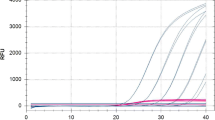
Abstract
We developed real-time PCR assays using TaqMan probes to detect and quantify Rosellinia necatrix, the causal agent of white root rot in many plant species. Two sets of PCR primers and TaqMan probe indicated that their detection limits could be as low as 1 fg of template DNA. Using the real-time PCR assays with the TaqMan probes, we were able to quantify R. necatrix DNA in naturally diseased roots of Japanese pear and in artificially infested soil samples. Although the new assays were inadequate for use with naturally infested soil samples, nested PCR procedures improved the detectability of the new assays.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bridge P, Spooner B (2001) Soil fungi: diversity and detection. Plant Soil 232:147–154
Cullen DW, Hirsch PR (1998) Simple and rapid method for direct extraction of microbial DNA from soil for PCR. Soil Biol Biochem 30:983–993
Eguchi N, Kondo K, Yamagishi N (2009) Bait twig method for soil detection of Rosellinia necatrix, causal agent of white root rot of Japanese pear and apple, at an early stage of tree infection. J Gen Plant Pathol 75:325–330
Glass NL, Donaldson GC (1995) Development of primer sets designed for use with the PCR to amplify conserved genes from filamentous ascomycetes. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:1323–1330
Heid CA, Stevens J, Livak KJ, Williams PM (1996) Real-time quantitative PCR. Genome Res 6:986–994
Josefsen MH, Löfström C, Sommer HM, Hoorfar J (2009) Diagnostic PCR: comparative sensitivity of four probe chemistries. Mol Cell Probes 23:201–203
Klerks MM, Zijlstra C, van Bruggen AHC (2004) Comparison of real-time PCR methods for detection of Salmonella enterica and Escherichia coli O157:H7, and introduction of a general internal amplification control. J Microbiol Methods 59:337–349
Nakamura H, Uetake Y, Arakawa M, Okabe I, Matsumoto N (2000) Observations on the teleomorph of the white root rot fungus, Rosellinia necatrix, and a related fungus, Rosellinia aquila. Mycoscience 41:503–507
Pérez-Jiménez RM (2006) A review of the biology and pathogenicity of Rosellinia necatrix—The cause of white root rot disease of fruit trees and other plants. J Phytopathol 154:257–266
Schena L, Ippolito A (2003) Rapid and sensitive detection of Rosellinia necatrix in roots and soils by real time Scorpion-PCR. J Plant Pathol 85:15–25
Schena L, Nigro F, Ippolito A (2002) Identification and detection of Rosellinia necatrix by conventional and real-time Scorpion-PCR. Eur J Plant Pathol 108:355–366
Schena L, Nigro F, Ippolito A, Gallitelli D (2004) Real-time quantitative PCR: a new technology to detect and study phytopathogenic and antagonistic fungi. Eur J Plant Pathol 110:893–908
Shishido M, Yoshida N, Usami T, Shinozaki T, Kobayashi M, Takeuchi T (2006) Black root rot of cucurbits caused by Phomopsis sclerotioides in Japan and phylogenetic grouping of the pathogen. J Gen Plant Pathol 72:220–227
Takemoto S, Nakamura H, Sasaki A, Shimane T (2009) Rosellinia compacta, a new species similar to the white root rot fungus Rosellinia necatrix. Mycologia 101:84–94
Takemoto S, Nakamura H, Sasaki A, Shimane T (2011) Species-specific PCRs differentiate Rosellinia necatrix from R. compacta as the prevalent cause of white root rot in Japan. J Gen Plant Pathol 77:107–111
van Gent-Pelzer MPE, Krijger M, Bonants PJM (2010) Improved real-time PCR assay for detection of the quarantine potato pathogen, Synchytrium endobioticum, in zonal centrifuge extracts from soil and in plants. Eur J Plant Pathol 126:129–133
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. T. Usami and K. Ohkawa for valuable comments. This study was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (21580052) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shishido, M., Kubota, I. & Nakamura, H. Development of real-time PCR assay using TaqMan probe for detection and quantification of Rosellinia necatrix in plant and soil. J Gen Plant Pathol 78, 115–120 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10327-012-0366-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10327-012-0366-x