Abstract
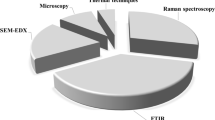
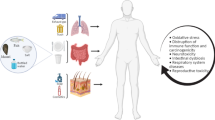
Microplastics have been recently detected in many environmental media and living organisms, yet their transfer and toxicity to humans are poorly known. Here, we review microplastic transfer in the food chain with focus on microplastic pollution sources, methods to analyze microplastics in food, health impact of food-related microplastic exposure, and remediation of microplastic pollution. Microplastic pollution sources include seafood, food additives, packaging materials, and agricultural and industrial products. Remediation techniques comprise the use of microbial enzymes and biofilms. Microplastic detection methods in food rely on separation and quantification by optical detection, scanning electron micrography, and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. Human health impact following microplastic ingestion include cancers, organ and respiration damage, and reproductive impairments. Overall, microplastic toxicity is mainly due to their ability to enter the metabolism, adsorption into the circulatory system for translocation, and difficulty, if not impossibility, of excretion.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analyzed in this study.
References
Abbasi S, Moore F, Keshavarzi B et al (2020) PET-microplastics as a vector for heavy metals in a simulated plant rhizosphere zone. Sci Total Environ 744:140984. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2020.140984
Abidli S, Lahbib Y, Trigui El Menif N (2019) Microplastics in commercial molluscs from the lagoon of Bizerte (Northern Tunisia). Mar Pollut Bull 142:243–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.03.048
Adıgüzel AO, Tunçer M (2017) Purification and characterization of cutinase from Bacillus sp. KY0701 isolated from plastic wastes. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 47:925–933. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826068.2017.1365245
Afrin S, Rahman MM, Hossain MN et al (2022) Are there plastic particles in my sugar? A pioneering study on the characterization of microplastics in commercial sugars and risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 837:155849. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2022.155849
Akan OD, Udofia GE, Okeke ES et al (2021) Plastic waste: Status, degradation and microbial management options for Africa. J Environ Manag 292:112758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112758
Akhbarizadeh R, Moore F, Keshavarzi B (2018) Investigating a probable relationship between microplastics and potentially toxic elements in fish muscles from northeast of Persian Gulf. Environ Pollut 232:154–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.09.028
Akhbarizadeh R, Dobaradaran S, Nabipour I et al (2020) Abundance, composition, and potential intake of microplastics in canned fish. Mar Pollut Bull 160:111633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111633
Akoueson F, Sheldon LM, Danopoulos E et al (2020) A preliminary analysis of microplastics in edible versus non-edible tissues from seafood samples. Environ Pollut 263:114452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114452
Al Mamun A, Prasetya TAE, Dewi IR, Ahmad M (2023) Microplastics in human food chains: Food becoming a threat to health safety. Sci Total Environ 858:159834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.159834
Alberghini L, Truant A, Santonicola S et al (2022) Microplastics in fish and fishery products and risks for human health: a review. Int J Environ Res Public Heal 20:789. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJERPH20010789
Ali W, Ali H, Souissi S, Zinck P (2023) Are bioplastics an ecofriendly alternative to fossil fuel plastics? Environ Chem Lett 21:1991–2002. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10311-023-01601-6/FIGURES/3
Alma AM, de Groot GS, Buteler M (2023) Microplastics incorporated by honeybees from food are transferred to honey, wax and larvae. Environ Pollut 320:121078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2023.121078
Anand U, Dey S, Bontempi E et al (2023) (2023) Biotechnological methods to remove microplastics: a review. Environ Chem Lett 213(21):1787–1810. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10311-022-01552-4
Anderson PJ, Warrack S, Langen V et al (2017) Microplastic contamination in Lake Winnipeg, Canada. Environ Pollut 225:223–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVPOL.2017.02.072
Asif MB, Hai FI, Singh L et al (2017) Degradation of pharmaceuticals and personal care products by white-rot fungi—a critical review. Curr Pollut Reports 3:88–103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40726-017-0049-5
Auguet T, Bertran L, Barrientos-Riosalido A et al (2022) Are ingested or inhaled microplastics involved in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease? Int J Environ Res Public Health. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192013495
Auta HS, Emenike CU, Fauziah SH (2017) Screening of Bacillus strains isolated from mangrove ecosystems in Peninsular Malaysia for microplastic degradation. Environ Pollut 231:1552–1559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.09.043
Auta HS, Emenike CU, Jayanthi B, Fauziah SH (2018) Growth kinetics and biodeterioration of polypropylene microplastics by Bacillus sp. and Rhodococcus sp. isolated from mangrove sediment. Mar Pollut Bull 127:15–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.11.036
Avio CG, Pittura L, D’Errico G et al (2020) Distribution and characterization of microplastic particles and textile microfibers in Adriatic food webs: general insights for biomonitoring strategies. Environ Pollut 258:113766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113766
Azeem I, Adeel M, Ahmad MA et al (2021) Uptake and accumulation of nano/microplastics in plants: a critical review. Nanomaterials 11:2935. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112935
Barboza LGA, Lopes C, Oliveira P et al (2020) Microplastics in wild fish from North East Atlantic Ocean and its potential for causing neurotoxic effects, lipid oxidative damage, and human health risks associated with ingestion exposure. Sci Total Environ 717:134625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134625
Bardají DKR, Furlan JPR, Stehling EG (2019) Isolation of a polyethylene degrading Paenibacillus sp. from a landfill in Brazil. Arch Microbiol 201:699–704. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-019-01637-9
Benson NU, Agboola OD, Fred-Ahmadu OH et al (2022) Micro(nano)plastics prevalence, food web interactions, and toxicity assessment in aquatic organisms: a review. Front Mar Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2022.851281
Bhatt P, Pathak VM, Bagheri AR, Bilal M (2021) Microplastic contaminants in the aqueous environment, fate, toxicity consequences, and remediation strategies. Environ Res 200:111762. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVRES.2021.111762
Birnstiel S, Soares-Gomes A, da Gama BAP (2019) Depuration reduces microplastic content in wild and farmed mussels. Mar Pollut Bull 140:241–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.01.044
Bollinger A, Thies S, Knieps-Grünhagen E et al (2020) A novel polyester hydrolase from the marine bacterium pseudomonas aestusnigri—structural and functional insights. Front Microbiol 11:510772. https://doi.org/10.3389/FMICB.2020.00114/BIBTEX
Bornscheuer UT (2016) Feeding on plastic. Science (80- ) 351:1154–1155. https://doi.org/10.1126/SCIENCE.AAF2853
Bour A, Avio CG, Gorbi S et al (2018) Presence of microplastics in benthic and epibenthic organisms: Influence of habitat, feeding mode and trophic level. Environ Pollut 243:1217–1225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.09.115
Bouwmeester H, Hollman PCH, Peters RJB (2015) Potential health impact of environmentally released micro- and nanoplastics in the human food production chain: experiences from nanotoxicology. Environ Sci Technol 49:8932–8947. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b01090
Brandon J, Goldstein M, Ohman MD (2016) Long-term aging and degradation of microplastic particles: comparing in situ oceanic and experimental weathering patterns. Mar Pollut Bull 110:299–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MARPOLBUL.2016.06.048
Bubpachat T, Sombatsompop N, Prapagdee B (2018) Isolation and role of polylactic acid-degrading bacteria on degrading enzymes productions and PLA biodegradability at mesophilic conditions. Polym Degrad Stab 152:75–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2018.03.023
Carr Kinnear EJ, Miller KY, Tong AZ (2021) Impacts of brewing time, brewing temperature and brands on the leaching of phthalates and bisphenol A in dry tea. Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess 38:1755–1766. https://doi.org/10.1080/19440049.2021.1940307
Catarino AI, Thompson R, Sanderson W, Henry TB (2017) Development and optimization of a standard method for extraction of microplastics in mussels by enzyme digestion of soft tissues. Environ Toxicol Chem 36:947–951. https://doi.org/10.1002/ETC.3608
Chandrakanthan K, Fraser MP, Herckes P (2023) Airborne microplastics in a suburban location in the desert southwest: occurrence and identification challenges. Atmos Environ 298:119617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2023.119617
Chen X, Chen X, Zhao Y et al (2020) Effects of microplastic biofilms on nutrient cycling in simulated freshwater systems. Sci Total Environ 719:137276. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2020.137276
Chia RW, Lee JY, Kim H (2021) Jang J (2021) Microplastic pollution in soil and groundwater: a review. Environ Chem Lett 196(19):4211–4224. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10311-021-01297-6
Chia RW, Lee JY, Cha J, Rodríguez-Seijo A (2023) Methods of soil sampling for microplastic analysis: a review. Environ Chem Lett 1:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10311-023-01652-9/TABLES/2
Çıtar Dazıroğlu ME, Bilici S (2023) The hidden threat to food safety and human health: microplastics. Environ Dev Sustain. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-023-03565-7
Cole M, Webb H, Lindeque PK et al (2014) (2014) Isolation of microplastics in biota-rich seawater samples and marine organisms. Sci Rep 41(4):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep04528
Courtene-Jones W, Quinn B, Murphy F et al (2017) Optimisation of enzymatic digestion and validation of specimen preservation methods for the analysis of ingested microplastics. Anal Methods 9:1437–1445. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6AY02343F
Crossman J, Hurley RR, Futter M, Nizzetto L (2020) Transfer and transport of microplastics from biosolids to agricultural soils and the wider environment. Sci Total Environ 724:138334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138334
Cverenkárová K, Valachovičová M, Mackul’ak T et al (2021) Microplastics in the food chain. Life 11:1349. https://doi.org/10.3390/LIFE11121349
De Boer J, Garrigues P, Gu J-D et al (2011) The handbook of environmental chemistry
da Costa CHS, dos Santos AM, Alves CN et al (2021) Assessment of the PETase conformational changes induced by poly(ethylene terephthalate) binding. Proteins Struct Funct Bioinforma 89:1340–1352. https://doi.org/10.1002/PROT.26155
Dalmau-Soler J, Ballesteros-Cano R, Boleda MR et al (2021) Microplastics from headwaters to tap water: occurrence and removal in a drinking water treatment plant in Barcelona Metropolitan area (Catalonia, NE Spain). Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 28:59462–59472. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13220-1
Daniel DB, Ashraf PM, Thomas SN (2020) Abundance, characteristics and seasonal variation of microplastics in Indian white shrimps (Fenneropenaeus indicus) from coastal waters off Cochin, Kerala. India Sci Total Environ 737:139839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139839
Daniel DB, Ashraf PM, Thomas SN, Thomson KT (2021) Microplastics in the edible tissues of shellfishes sold for human consumption. Chemosphere 264:128554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128554
Danso D, Schmeisser C, Chow J et al (2018) New insights into the function and global distribution of polyethylene terephthalate (PET)-degrading bacteria and enzymes in marine and terrestrial metagenomes. Appl Environ Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02773-17/SUPPL_FILE/ZAM008188431S1.PDF
De Jesus R, Alkendi R (2022) A minireview on the bioremediative potential of microbial enzymes as solution to emerging microplastic pollution. Front Microbiol 13:1066133. https://doi.org/10.3389/FMICB.2022.1066133/BIBTEX
De Witte B, Devriese L, Bekaert K et al (2014) Quality assessment of the blue mussel (Mytilus edulis): comparison between commercial and wild types. Mar Pollut Bull 85:146–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.06.006
Dekiff JH, Remy D, Klasmeier J, Fries E (2014) Occurrence and spatial distribution of microplastics in sediments from Norderney. Environ Pollut 186:248–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVPOL.2013.11.019
De-la-Torre GE (2020) Microplastics: an emerging threat to food security and human health. J Food Sci Technol 57:1601–1608. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-04138-1
De-la-torre GE, De-la-torre GE (2020) Microplastics : an emerging threat to food security and human health. J Food Sci Technol 57:1601–1608. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-04138-1
Deme GG, Ewusi-Mensah D, Olagbaju OA et al (2022) Macro problems from microplastics: toward a sustainable policy framework for managing microplastic waste in Africa. Sci Total Environ 804:150170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150170
Dessì C, Okoffo ED, O’Brien JW et al (2021) Plastics contamination of store-bought rice. J Hazard Mater 416:125778. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2021.125778
Diaz-Basantes MF, Conesa JA, Fullana A (2020) Microplastics in honey, beer, milk and refreshments in ecuador as emerging contaminants. Sustain 12:5514. https://doi.org/10.3390/SU12145514
Diaz-Basantes MF, Nacimba-Aguirre D, Conesa JA, Fullana A (2022) Presence of microplastics in commercial canned tuna. Food Chem 385:132721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132721
Ding J, Li J, Sun C et al (2020) An examination of the occurrence and potential risks of microplastics across various shellfish. Sci Total Environ 739:139887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139887
Du F, Cai H, Zhang Q et al (2020) Microplastics in take-out food containers. J Hazard Mater 399:122969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122969
Duis K, Coors A (2016) Microplastics in the aquatic and terrestrial environment: sources (with a specific focus on personal care products), fate and effects. Environ Sci Eur 28:1–25. https://doi.org/10.1186/S12302-015-0069-Y
Dutta B, Bandopadhyay R (2022) Biotechnological potentials of halophilic microorganisms and their impact on mankind. Beni-Suef Univ J Basic Appl Sci. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43088-022-00252-w
EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (2016) Presence of microplastics and nanoplastics in food, with particular focus on seafood. EFSA J. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2016.4501
Enechi OC, Okeke ES, Awoh OE et al (2021) Inhibition of phospholipase A2, platelet aggregation and egg albumin induced rat paw oedema as anti-inflammatory effect of Peltophorun pterocarpus stem-bark. Clin Phytosci. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40816-021-00310-3
Erni-Cassola G, Gibson MI, Thompson RC, Christie-Oleza JA (2017) Lost, but found with nile red: a novel method for detecting and quantifying small microplastics (1 mm to 20 μm) in environmental samples. Environ Sci Technol 51:13641–13648. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.EST.7B04512/SUPPL_FILE/ES7B04512_SI_001.PDF
Fabbri D, Rombolà AG, Vassura I et al (2020) Off-line analytical pyrolysis GC–MS to study the accumulation of polystyrene microparticles in exposed mussels. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 149:104836. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JAAP.2020.104836
Fadare OO, Okoffo ED, Olasehinde EF (2021) Microparticles and microplastics contamination in African table salts. Mar Pollut Bull 164:112006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112006
Faheem M, Shabbir S, Zhao J et al (2020a) Multifunctional periphytic biofilms: polyethylene degradation and Cd2+ and Pb2+ bioremediation under high methane scenario. Int J Mol Sci 21:5331. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJMS21155331
Farrell P, Nelson K (2013) Trophic level transfer of microplastic: Mytilus edulis ( L.) to Carcinus maenas ( L.). Environ Pollut 177:1–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.01.046
Fauzi A, Hameed IH, Kadhim MJ (2017) A review: uses of gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS) technique for analysis of bioactive natural compounds of some plants forensic nursing view project biochemical analysis view project. Artic Int J Toxicol Pharmacol Res. https://doi.org/10.25258/ijtpr.v9i01.9042
Feng Z, Wang R, Zhang T et al (2020) Microplastics in specific tissues of wild sea urchins along the coastal areas of northern China. Sci Total Environ 728:138660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138660
Ferraz M, Bauer AL, Valiati VH, Schulz UH (2020) Microplastic concentrations in raw and drinking water in the sinos river, southern brazil. Water (switzerland) 12:1–10. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12113115
Fries E, Dekiff JH, Willmeyer J et al (2013) Identification of polymer types and additives in marine microplastic particles using pyrolysis-GC/MS and scanning electron microscopy. Environ Sci Process Impacts 15:1949–1956. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3EM00214D
Furukawa M, Kawakami N, Tomizawa A, Miyamoto K (2019) Efficient degradation of poly(ethylene terephthalate) with thermobifida fusca cutinase exhibiting improved catalytic activity generated using mutagenesis and additive-based approaches. Sci Rep 91(9):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-52379-z
Galafassi S, Sighicelli M, Pusceddu A et al (2021) Microplastic pollution in perch (Perca fluviatilis, Linnaeus 1758) from Italian south-alpine lakes. Environ Pollut 288:117782. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117782
Gambarini V, Pantos O, Kingsbury JM et al (2022) PlasticDB: a database of microorganisms and proteins linked to plastic biodegradation. Database 2022:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1093/DATABASE/BAAC008
Ganal-Vonarburg SC, Hornef MW, Macpherson AJ (2020) Microbial–host molecular exchange and its functional consequences in early mammalian life. Science (80- ) 368:604–607. https://doi.org/10.1126/SCIENCE.ABA0478/SUPPL_FILE/ABA0478_GANAL-VONARBURG_SM.PDF
Ganesan S, Ruendee T, Kimura SY et al (2022) Effect of biofilm formation on different types of plastic shopping bags: structural and physicochemical properties. Environ Res 206:112542. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVRES.2021.112542
Giorgetti L, Spanò C, Muccifora S et al (2020) Exploring the interaction between polystyrene nanoplastics and Allium cepa during germination: Internalization in root cells, induction of toxicity and oxidative stress. Plant Physiol Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.02.014
Grbic J, Nguyen B, Guo E et al (2019) Magnetic extraction of microplastics from environmental samples. Environ Sci Technol Lett 6:68–72. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.ESTLETT.8B00671/SUPPL_FILE/EZ8B00671_SI_001.PDF
Guerrera MC, Aragona M, Porcino C et al (2021) Micro and nano plastics distribution in fish as model organisms: Histopathology, blood response and bioaccumulation in different organs. Appl Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11135768
Guilhermino L, Martins A, Lopes C et al (2021) Microplastics in fishes from an estuary (Minho River) ending into the NE Atlantic Ocean. Mar Pollut Bull 173:113008. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MARPOLBUL.2021.113008
Gündoğdu S (2018) Contamination of table salts from Turkey with microplastics. Food Addit Contam Part A 35:1006–1014. https://doi.org/10.1080/19440049.2018.1447694
Habib RZ, Al KR, Al SF et al (2022) Microplastic contamination of chicken meat and fish through plastic cutting boards. Int J Environ Res Public Health. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192013442
Hadad D, Geresh S, Sivan A (2005) Biodegradation of polyethylene by the thermophilic bacterium Brevibacillus borstelensis. J Appl Microbiol 98:1093–1100. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1365-2672.2005.02553.X
Hantoro I, Löhr AJ, Van Belleghem FGAJ et al (2019) Microplastics in coastal areas and seafood: implications for food safety. Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess 36:674–711. https://doi.org/10.1080/19440049.2019.1585581
He D, Zhang Y, Gao W (2021a) ScienceDirect Micro (nano) plastic contaminations from soils to plants: human food risks Curr Opin Food Sci 116–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/.COFS.2021.04.001
He D, Zhang Y, Gao W (2021b) Micro(nano)plastic contaminations from soils to plants: human food risks. Curr Opin Food Sci 41:116–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cofs.2021.04.001
Henini M (2000) Scanning electron microscopy: an introduction. III-Vs Rev 13:40–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0961-1290(00)80006-X
Hermabessiere L, Paul-Pont I, Cassone AL et al (2019) Microplastic contamination and pollutant levels in mussels and cockles collected along the channel coasts. Environ Pollut 250:807–819. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVPOL.2019.04.051
Herrera A, Garrido-Amador P, Martínez I et al (2018) Novel methodology to isolate microplastics from vegetal-rich samples. Mar Pollut Bull 129:61–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MARPOLBUL.2018.02.015
Hidalgo-Ruz V, Gutow L, Thompson RC, Thiel M (2012) Microplastics in the marine environment: a review of the methods used for identification and quantification. Environ Sci Technol 46:3060–3075. https://doi.org/10.1021/ES2031505/ASSET/IMAGES/MEDIUM/ES-2011-031505_0006.GIF
Hidayaturrahman H, Lee TG (2019) A study on characteristics of microplastic in wastewater of South Korea: Identification, quantification, and fate of microplastics during treatment process. Mar Pollut Bull 146:696–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MARPOLBUL.2019.06.071
Horton AA, Svendsen C, Williams RJ et al (2017) Large microplastic particles in sediments of tributaries of the River Thames, UK—abundance, sources and methods for effective quantification. Mar Pollut Bull 114:218–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MARPOLBUL.2016.09.004
Hossain MS, Rahman MS, Uddin MN et al (2020) Microplastic contamination in Penaeid shrimp from the Northern Bay of Bengal. Chemosphere 238:124688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124688
Huang Z, Hu B, Wang H (2022) Analytical methods for microplastics in the environment: a review. Environ Chem Lett 211(21):383–401. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10311-022-01525-7
Huerta Lwanga E, Mendoza Vega J, Ku Quej V et al (2017) Field evidence for transfer of plastic debris along a terrestrial food chain. Sci Rep 7:14071. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-14588-2
Huerta Lwanga E, Thapa B, Yang X et al (2018) Decay of low-density polyethylene by bacteria extracted from earthworm’s guts: a potential for soil restoration. Sci Total Environ 624:753–757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.144
Hurley RR, Nizzetto L (2018) Fate and occurrence of micro(nano)plastics in soils: knowledge gaps and possible risks. Curr Opin Environ Sci Heal 1:6–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coesh.2017.10.006
Imhof HK, Laforsch C, Wiesheu AC et al (2016) Pigments and plastic in limnetic ecosystems: a qualitative and quantitative study on microparticles of different size classes. Water Res 98:64–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WATRES.2016.03.015
Jadhav EB, Singh M, Ahmad R, Bhagat DS (2021) Microplastics from food packaging: an overview of human consumption, health threats, and alternative solutions. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 16:100608
Jain K, Bhunia H, Reddy MS (2022) Degradation of polypropylene-poly-l-lactide blends by Bacillus isolates: a microcosm and field evaluation. Bioremediat J 26:64–75. https://doi.org/10.1080/10889868.2021.1886037
Jeon J-M, Park S-J, Choi T-R et al (2021) Biodegradation of polyethylene and polypropylene by Lysinibacillus species JJY0216 isolated from soil grove. Polym Degrad Stab 191:109662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2021.109662
Jiang X, Chen H, Liao Y et al (2019) Ecotoxicity and genotoxicity of polystyrene microplastics on higher plant Vicia faba. Environ Pollut 250:831–838. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVPOL.2019.04.055
Jiang J-J, Hanun JN, Chen K-Y et al (2023) Current levels and composition profiles of microplastics in irrigation water. Environ Pollut 318:120858. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120858
Johnson AC, Ball H, Cross R et al (2020) Identification and quantification of microplastics in potable water and their sources within water treatment works in England and Wales. Environ Sci Technol 54:12326–12334. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.EST.0C03211/ASSET/IMAGES/LARGE/ES0C03211_0005.JPEG
Jung H-W, Yang M-K, Su R-C (2018) Purification, characterization, and gene cloning of an Aspergillus fumigatus polyhydroxybutyrate depolymerase used for degradation of polyhydroxybutyrate, polyethylene succinate, and polybutylene succinate. Polym Degrad Stab 154:186–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2018.06.002
Kallenbach EMF, Rødland ES, Buenaventura NT, Hurley R (2022) Microplastics in terrestrial and freshwater environments: Microplastic in the Environment: Pattern and Process 87–130. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-78627-4_4
Karami A, Golieskardi A, Bin HY et al (2017a) Microplastics in eviscerated flesh and excised organs of dried fish. Sci Rep 7:5473. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-05828-6
Karami A, Golieskardi A, Keong Choo C et al (2017b) The presence of microplastics in commercial salts from different countries. Sci Rep 71(7):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep46173
Karbalaei S, Golieskardi A, Watt DU et al (2020) Analysis and inorganic composition of microplastics in commercial Malaysian fish meals. Mar Pollut Bull 150:110687. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MARPOLBUL.2019.110687
Karlsson TM, Vethaak AD, Almroth BC et al (2017) Screening for microplastics in sediment, water, marine invertebrates and fish: Method development and microplastic accumulation. Mar Pollut Bull 122:403–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MARPOLBUL.2017.06.081
Kashiwada S (2006) Distribution of nanoparticles in the see-through medaka (Oryzias latipes). Environ Health Perspect 114:1697–1702. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.9209
Kedzierski M, Lechat B, Sire O et al (2020) Microplastic contamination of packaged meat: occurrence and associated risks. Food Packag Shelf Life 24:100489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fpsl.2020.100489
Keshavarzifard M, Vazirzadeh A, Sharifinia M (2021) Occurrence and characterization of microplastics in white shrimp, Metapenaeus affinis, living in a habitat highly affected by anthropogenic pressures, northwest Persian Gulf. Mar Pollut Bull 169:112581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112581
Kim J-S, Lee H-J, Kim S-K, Kim H-J (2018) Global pattern of microplastics (MPs) in commercial food-grade salts: sea salt as an indicator of seawater MP pollution. Environ Sci Technol 52:12819–12828. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b04180
Kirstein IV, Hensel F, Gomiero A et al (2021) Drinking plastics? Quantification and qualification of microplastics in drinking water distribution systems by µFTIR and Py-GCMS. Water Res 188:116519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.116519
Knott BC, Erickson E, Allen MD et al (2020) Characterization and engineering of a two-enzyme system for plastics depolymerization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 117:25476–25485. https://doi.org/10.1073/PNAS.2006753117/SUPPL_FILE/PNAS.2006753117.SM03.MP4
Kosuth M, Mason SA, Wattenberg EV (2018) Anthropogenic contamination of tap water, beer, and sea salt. PLoS ONE 13:e0194970. https://doi.org/10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0194970
Kusch P, Knupp G (2004) Headspace-SPME-GC-MS identification of volatile organic compounds released from expanded polystyrene. J Polym Environ 12:83–87. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JOOE.0000010053.20382.D7/METRICS
Kutralam-Muniasamy G, Pérez-Guevara F, Elizalde-Martínez I, Shruti VC (2020) Branded milks—are they immune from microplastics contamination? Sci Total Environ 714:136823. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2020.136823
Kuttykattil A, Raju S, Vanka KS et al (2023) Consuming microplastics? Investigation of commercial salts as a source of microplastics (MPs) in diet. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:930–942. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22101-0
La Nasa J, Biale G, Fabbri D, Modugno F (2020) A review on challenges and developments of analytical pyrolysis and other thermoanalytical techniques for the quali-quantitative determination of microplastics. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 149:104841. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JAAP.2020.104841
Lee CW, Hsu LF, Wu IL et al (2022) Exposure to polystyrene microplastics impairs hippocampus-dependent learning and memory in mice. J Hazard Mater 430:128431. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2022.128431
Levin IW, Bhargava R (2004) Fourier transform infrared vibrational spectroscopic imaging: integrating microscopy and molecular recognition*. 56:429–474. https://doi.org/10.1146/ANNUREV.PHYSCHEM.56.092503.141205
Li J, Green C, Reynolds A et al (2018a) Microplastics in mussels sampled from coastal waters and supermarkets in the United Kingdom. Environ Pollut 241:35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVPOL.2018.05.038
Li J, Liu H, Paul Chen J (2018b) Microplastics in freshwater systems: a review on occurrence, environmental effects, and methods for microplastics detection. Water Res 137:362–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WATRES.2017.12.056
Li J, Lusher AL, Rotchell JM et al (2019) Using mussel as a global bioindicator of coastal microplastic pollution. Environ Pollut 244:522–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.10.032
Li B, Ding Y, Cheng X et al (2020a) Polyethylene microplastics affect the distribution of gut microbiota and inflammation development in mice. Chemosphere 244:125492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125492
Li D, Shi Y, Yang L et al (2020b) Microplastic release from the degradation of polypropylene feeding bottles during infant formula preparation. Nat Food 1:746–754. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43016-020-00171-y
Li Q, Feng Z, Zhang T et al (2020c) Microplastics in the commercial seaweed nori. J Hazard Mater 388:122060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122060
Li C, Gao Y, He S et al (2021a) Quantification of nanoplastic uptake in cucumber plants by pyrolysis gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Environ Sci Technol Lett 8:633–638. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.estlett.1c00369
Li H, Lu X, Wang S et al (2021b) Vertical migration of microplastics along soil profile under different crop root systems. Environ Pollut 278:116833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116833
Li Z, Li Q, Li R et al (2021c) The distribution and impact of polystyrene nanoplastics on cucumber plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 28:16042–16053. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11702-2
Li Y, Wang Z, Guan B (2022) Separation and identification of nanoplastics in tap water. Environ Res 204:112134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.112134
Liebezeit G, Dubaish F (2012) Microplastics in beaches of the East Frisian Islands Spiekeroog and Kachelotplate. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 89:213–217. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00128-012-0642-7/TABLES/1
Liu G, Wang J, Wang M et al (2022a) Disposable plastic materials release microplastics and harmful substances in hot water. Sci Total Environ 818:151685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151685
Liu Z, Zhuan Q, Zhang L et al (2022b) Polystyrene microplastics induced female reproductive toxicity in mice. J Hazard Mater 424:127629. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2021.127629
Löder MGJ, Gerdts G (2015) Methodology used for the detection and identification of microplastics—a critical appraisal. Mar Anthropog Litter. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-16510-3_8/FIGURES/7
Logemann J, Oveland E, Bjorøy Ø et al (2018) Pyrolysis-GC-Orbitrap MS—a powerful analytical tool for identification and quantification of microplastics in a biological matrix
Lopes C, Raimundo J, Caetano M, Garrido S (2020) Microplastic ingestion and diet composition of planktivorous fish. Limnol Oceanogr Lett 5:103–112. https://doi.org/10.1002/lol2.10144
Lu L, Luo T, Zhao Y et al (2019) Interaction between microplastics and microorganism as well as gut microbiota: A consideration on environmental animal and human health. Sci Total Environ 667:94–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2019.02.380
Luissint AC, Parkos CA, Nusrat A (2016) Inflammation and the intestinal barrier: leukocyte-epithelial cell interactions, cell junction remodeling, and mucosal repair. Gastroenterology 151:616–632. https://doi.org/10.1053/J.GASTRO.2016.07.008
Luo Q, Liu ZH, Yin H et al (2018) Migration and potential risk of trace phthalates in bottled water: a global situation. Water Res 147:362–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WATRES.2018.10.002
Lusher AL, Welden NA, Sobral P, Cole M (2020) Sampling, isolating and identifying microplastics ingested by fish and invertebrates*. Anal Nanoplast Microplast Food. https://doi.org/10.1201/9780429469596-8
Lwanga EH, Beriot N, Corradini F et al (2022) Review of microplastic sources, transport pathways and correlations with other soil stressors: a journey from agricultural sites into the environment. Chem Biol Technol Agric 9:20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40538-021-00278-9
Ma J, Niu X, Zhang D et al (2020) High levels of microplastic pollution in aquaculture water of fish ponds in the Pearl River Estuary of Guangzhou. China Sci Total Environ 744:140679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140679
Makhdoumi P, Amin AA, Karimi H et al (2021) Occurrence of microplastic particles in the most popular Iranian bottled mineral water brands and an assessment of human exposure. J Water Process Eng 39:101708. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JWPE.2020.101708
Markic A, Niemand C, Bridson JH et al (2018) Double trouble in the South Pacific subtropical gyre: Increased plastic ingestion by fish in the oceanic accumulation zone. Mar Pollut Bull 136:547–564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.09.031
Martinelli JC, Phan S, Luscombe CK, Padilla-Gamiño JL (2020a) Low incidence of microplastic contaminants in Pacific oysters (Crassostrea gigas Thunberg) from the Salish Sea, USA. Sci Total Environ 715:136826. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2020.136826
Mason SA, Garneau D, Sutton R et al (2016) Microplastic pollution is widely detected in US municipal wastewater treatment plant effluent. Environ Pollut 218:1045–1054. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVPOL.2016.08.056
Mason SA, Welch VG, Neratko J (2018) Synthetic polymer contamination in bottled water. Front Chem 6:389699. https://doi.org/10.3389/FCHEM.2018.00407/BIBTEX
Meng X, Yang L, Liu H et al (2021) Protein engineering of stable IsPETase for PET plastic degradation by Premuse. Int J Biol Macromol 180:667–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJBIOMAC.2021.03.058
Métais I, Latchere O, Roman C et al (2023) Continuum from microplastics to nanoplastics: effects of size and source on the estuarine bivalve Scrobicularia plana. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25588-3
Miller JD, Young SL (2023) Water security and nutrition. In: Fourth E (ed) Caballero BBT-E of HN. Academic Press, Oxford, pp 706–716
Milojevic N, Cydzik-Kwiatkowska A (2021) Agricultural use of sewage sludge as a threat of microplastic (MP) spread in the environment and the role of governance. Energies 14:6293. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14196293
Mintenig SM, Löder MGJ, Primpke S, Gerdts G (2019) Low numbers of microplastics detected in drinking water from ground water sources. Sci Total Environ 648:631–635. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2018.08.178
Mohanan N, Wong CH, Budisa N, Levin DB (2022) Characterization of polymer degrading lipases, LIP1 and LIP2 from pseudomonas chlororaphis PA23. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 10:854298. https://doi.org/10.3389/FBIOE.2022.854298/BIBTEX
Moog D, Schmitt J, Senger J et al (2019) Using a marine microalga as a chassis for polyethylene terephthalate (PET) degradation. Microb Cell Fact 18:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/S12934-019-1220-Z/FIGURES/5
Muhib MI, Uddin MK, Rahman MM, Malafaia G (2023) Occurrence of microplastics in tap and bottled water, and food packaging: a narrative review on current knowledge. Sci Total Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.161274
Muroi F, Tachibana Y, Soulenthone P et al (2017) Characterization of a poly(butylene adipate-co -terephthalate) hydrolase from the aerobic mesophilic bacterium Bacillus pumilus. Polym Degrad Stab 137:11–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2017.01.006
Myszka R, Enfrin M, Giustozzi F (2023) Microplastics in road dust: a practical guide for identification and characterisation. Chemosphere 315:137757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.137757
Nakamura Y, Watanabe H, Tanaka A et al (2020) Effect of increased daily water intake and hydration on health in japanese adults. Nutrients. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12041191
Nalbone L, Cincotta F, Giarratana F et al (2021) Microplastics in fresh and processed mussels sampled from fish shops and large retail chains in Italy. Food Control 125:108003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2021.108003
Nematollahi MJ, Keshavarzi B, Moore F et al (2021) Microplastic fibers in the gut of highly consumed fish species from the southern Caspian Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 168:112461. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MARPOLBUL.2021.112461
Neto JGB, Rodrigues FL, Ortega I et al (2020) Ingestion of plastic debris by commercially important marine fish in southeast-south Brazil. Environ Pollut 267:115508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115508
Neves D, Sobral P, Ferreira JL, Pereira T (2015) Ingestion of microplastics by commercial fish off the Portuguese coast. Mar Pollut Bull 101:119–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.11.008
Nguyen B, Claveau-Mallet D, Hernandez LM et al (2019a) Separation and Analysis of microplastics and nanoplastics in complex environmental samples. Acc Chem Res 52:858–866. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.ACCOUNTS.8B00602/ASSET/IMAGES/LARGE/AR-2018-00602E_0004.JPEG
Nishimoto N, Terao K, Mima T et al (2008) Mechanisms and pathologic significances in increase in serum interleukin-6 (IL-6) and soluble IL-6 receptor after administration of an anti-IL-6 receptor antibody, tocilizumab, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and Castleman disease. Blood 112:3959–3964. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2008-05-155846
Nithin A, Sundaramanickam A, Surya P et al (2021) Microplastic contamination in salt pans and commercial salts—a baseline study on the salt pans of Marakkanam and Parangipettai, Tamil Nadu. India Mar Pollut Bull 165:112101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112101
Novotna K, Cermakova L, Pivokonska L et al (2019) Microplastics in drinking water treatment—current knowledge and research needs. Sci Total Environ 667:730–740. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2019.02.431
Okeke ES, Atinuke O, Okoye OC et al (2022a) Microplastic burden in Africa: a review of occurrence, impacts, and sustainability potential of bioplastics. Chem Eng J Adv 12:100402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceja.2022.100402
Okeke ES, Okoye CO, Atakpa EO et al (2022b) Microplastics in agroecosystems-impacts on ecosystem functions and food chain. Resour Conserv Recycl 177:105961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.105961
Okeke ES, Prince T, Ezeorba C et al (2022c) Ecotoxicological and health implications of microplastic—associated biofilms: a recent review and prospect for turning the hazards into benefits. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22612-w
Okeke ES, Ikechukwu K, Izuma C et al (2023a) Micro and nanoplastics ravaging our agroecosystem: a review of occurrence, fate, ecological impacts, detection, remediation, and prospects. Heliyon 9:e13296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13296
Okeke ES, Nweze EJ, Ezike TC et al (2023b) Silicon-based nanoparticles for mitigating the effect of potentially toxic elements and plant stress in agroecosystems: a sustainable pathway towards food security. Sci Total Environ 898:165446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.165446
Okoye CO, Addey CI, Oderinde O et al (2022a) Toxic chemicals and persistent organic pollutants associated with micro-and nanoplastics pollution. Chem Eng J Adv 11:100310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceja.2022.100310
Okoye CO, Okeke ES, Okoye KC et al (2022b) Occurrence and fate of pharmaceuticals, personal care products (PPCPs) and pesticides in African water systems: a need for timely intervention. Heliyon 8:e09143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09143
Oliveri Conti G, Ferrante M, Banni M et al (2020) Micro- and nano-plastics in edible fruit and vegetables. The first diet risks assessment for the general population. Environ Res 187:109677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109677
Osman AI, Hosny M, Eltaweil AS et al (2023) Microplastic sources, formation, toxicity and remediation: a review. Environ Chem Lett 214(21):2129–2169. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10311-023-01593-3
Oßmann BE, Sarau G, Holtmannspötter H et al (2018) Small-sized microplastics and pigmented particles in bottled mineral water. Water Res 141:307–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WATRES.2018.05.027
Othman AR, Hasan HA, Muhamad MH et al (2021) Microbial degradation of microplastics by enzymatic processes: a review. Environ Chem Lett 194(19):3057–3073. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10311-021-01197-9
Padervand M (2017) Reusable porous Na(SiAl)O6·xH2O/NiFe2O4 structure for selective removal of heavy metals from waste waters. U.S. Patent 11,014,082, 25 May 2021
Padervand M, Lichtfouse E, Robert D, Wang C (2020) Removal of microplastics from the environment. A review. Environ Chem Lett 183(18):807–828. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10311-020-00983-1
Panel E, Chain F (2016) Presence of microplastics and nanoplastics in food, with particular focus on seafood EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (CONTAM). https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2016.4501
Park SY, Kim CG (2019) Biodegradation of micro-polyethylene particles by bacterial colonization of a mixed microbial consortium isolated from a landfill site. Chemosphere 222:527–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2019.01.159
Pereira R, Rodrigues SM, Silva D et al (2023) Microplastic contamination in large migratory fishes collected in the open Atlantic Ocean. Mar Pollut Bull 186:114454. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MARPOLBUL.2022.114454
Periyasamy AP, Tehrani-Bagha A (2022) A review on microplastic emission from textile materials and its reduction techniques. Polym Degrad Stab 199:109901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2022.109901
Pham DT, Kim J, Lee S-H et al (2023) Analysis of microplastics in various foods and assessment of aggregate human exposure via food consumption in Korea. Environ Pollut 322:121153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2023.121153
Phillips MB, Bonner TH (2015) Occurrence and amount of microplastic ingested by fishes in watersheds of the Gulf of Mexico. Mar Pollut Bull 100:264–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.08.041
Phuong NN, Zalouk-Vergnoux A, Kamari A et al (2018) Quantification and characterization of microplastics in blue mussels (Mytilus edulis): protocol setup and preliminary data on the contamination of the French Atlantic coast. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:6135–6144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8862-3
Pironti C, Ricciardi M, Motta O et al (2021) Microplastics in the environment: intake through the food web, human exposure and toxicological effects. Toxics. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9090224
Pittura L, Avio CG, Giuliani ME et al (2018) Microplastics as vehicles of environmental PAHs to marine organisms: Combined chemical and physical hazards to the mediterranean mussels. Mytilus Galloprovincialis Front Mar Sci 5:351215. https://doi.org/10.3389/FMARS.2018.00103/BIBTEX
Piyawardhana N, Weerathunga V, Sen CH et al (2022) Occurrence of microplastics in commercial marine dried fish in Asian countries. J Hazard Mater 423:127093. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2021.127093
Prata JC (2018) Airborne microplastics: consequences to human health? Environ Pollut 234:115–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVPOL.2017.11.043
Prata JC, da Costa JP, Lopes I et al (2020) Environmental exposure to microplastics: an overview on possible human health effects. Sci Total Environ 702:134455. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2019.134455
Praveena SM, Shamsul Ariffin NI, Nafisyah AL (2022) Microplastics in Malaysian bottled water brands: Occurrence and potential human exposure. Environ Pollut 315:120494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120494
Primpke S, Christiansen SH, Christiansen SH et al (2020a) Critical assessment of analytical methods for the harmonized and cost-efficient analysis of microplastics. Appl Spectrosc 74:1012–1047
Primpke S, Godejohann M, Gerdts G (2020b) Rapid Identification and quantification of microplastics in the environment by quantum cascade laser-based hyperspectral infrared chemical imaging. Environ Sci Technol 54:15893–15903. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c05722
Prüst M, Meijer J, Westerink RHS (2020) The plastic brain: neurotoxicity of micro- and nanoplastics. Part Fibre Toxicol 17:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12989-020-00358-y
Qi Y, Beriot N, Gort G et al (2020) Impact of plastic mulch film debris on soil physicochemical and hydrological properties. Environ Pollut 266:115097. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115097
Rasmussen LA, Lykkemark J, Andersen TR, Vollertsen J (2023) Permeable pavements: a possible sink for tyre wear particles and other microplastics? Sci Total Environ 869:161770. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.161770
Reinold S, Herrera A, Saliu F et al (2021) Evidence of microplastic ingestion by cultured European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Mar Pollut Bull. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112450
Renner G, Schmidt TC, Schram J (2018) Analytical methodologies for monitoring micro(nano)plastics: which are fit for purpose? Curr Opin Environ Sci Heal 1:55–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COESH.2017.11.001
Renzi M, Blašković A (2018) Litter & microplastics features in table salts from marine origin: Italian versus Croatian brands. Mar Pollut Bull 135:62–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.06.065
Ribeiro F, Okoffo ED, O’Brien JW et al (2021) Out of sight but not out of mind: size fractionation of plastics bioaccumulated by field deployed oysters. J Hazard Mater Lett 2:100021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hazl.2021.100021
Richard H, Carpenter EJ, Komada T et al (2019) Biofilm facilitates metal accumulation onto microplastics in estuarine waters. Sci Total Environ 683:600–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2019.04.331
Ru J, Huo Y, Yang Y (2020) Microbial degradation and valorization of plastic wastes. Front Microbiol 11:507487. https://doi.org/10.3389/FMICB.2020.00442/BIBTEX
Rummel CD, Jahnke A, Gorokhova E et al (2017) Impacts of biofilm formation on the fate and potential effects of microplastic in the aquatic environment. Environ Sci Technol Lett 4:258–267. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.ESTLETT.7B00164
Saad D, Chauke P, Cukrowska E et al (2022) First biomonitoring of microplastic pollution in the Vaal river using Carp fish (Cyprinus carpio) “as a bio-indicator.” Sci Total Environ 836:155623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155623
Samandra S, Mescall OJ, Plaisted K et al (2022) Assessing exposure of the Australian population to microplastics through bottled water consumption. Sci Total Environ 837:155329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155329
Sarmah P, Rout J (2018) Efficient biodegradation of low-density polyethylene by cyanobacteria isolated from submerged polyethylene surface in domestic sewage water. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:33508–33520. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3079-7
Schwaminger SP, Fehn S, Steegmüller T et al (2021) Immobilization of PETase enzymes on magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for the decomposition of microplastic PET. Nanoscale Adv 3:4395–4399. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1NA00243K
Schymanski D, Goldbeck C, Humpf HU, Fürst P (2018) Analysis of microplastics in water by micro-Raman spectroscopy: release of plastic particles from different packaging into mineral water. Water Res 129:154–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WATRES.2017.11.011
Sewwandi M, Wijesekara H, Upamali A (2023) Microplastics and plastics-associated contaminants in food and beverages: global trends, concentrations, and human exposure. Environ Pollut 317:120747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120747
Shabbir S, Faheem M, Ali N et al (2020) Periphytic biofilm: an innovative approach for biodegradation of microplastics. Sci Total Environ 717:137064. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2020.137064
Sharma VK, Ma X, Lichtfouse E, Robert D (2023) Nanoplastics are potentially more dangerous than microplastics. Environ Chem Lett 21:1933–1936. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10311-022-01539-1/TABLES/1
Sheik S, Chandrashekar KR, Swaroop K, Somashekarappa HM (2015) Biodegradation of gamma irradiated low density polyethylene and polypropylene by endophytic fungi. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 105:21–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2015.08.006
Shi Y, Yi L, Du G et al (2023) Visual characterization of microplastics in corn flour by near field molecular spectral imaging and data mining. Sci Total Environ 862:160714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160714
Shruti VC, Pérez-Guevara F, Elizalde-Martínez I, Kutralam-Muniasamy G (2020) First study of its kind on the microplastic contamination of soft drinks, cold tea and energy drinks—future research and environmental considerations. Sci Total Environ 726:138580. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2020.138580
Simon M, van Alst N, Vollertsen J (2018) Quantification of microplastic mass and removal rates at wastewater treatment plants applying Focal Plane Array (FPA)-based Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) imaging. Water Res 142:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WATRES.2018.05.019
Skariyachan S, Taskeen N, Kishore AP et al (2021) Novel consortia of enterobacter and pseudomonas formulated from cow dung exhibited enhanced biodegradation of polyethylene and polypropylene. J Environ Manag 284:112030. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112030
Sobhani Z, Lei Y, Tang Y et al (2020) Microplastics generated when opening plastic packaging. Sci Rep 10:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-61146-4
Son HF, Joo S, Seo H et al (2020) Structural bioinformatics-based protein engineering of thermo-stable PETase from Ideonella sakaiensis. Enzyme Microb Technol 141:109656. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENZMICTEC.2020.109656
Sowmya HV, Ramalingappa KM, Thippeswamy B (2015) Degradation of polyethylene by Penicillium simplicissimum isolated from local dumpsite of Shivamogga district. Environ Dev Sustain 17:731–745. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-014-9571-4
Sridhar A, Ponnuchamy M, Kumar PS et al (2021) (2021) Techniques and modeling of polyphenol extraction from food: a review. Environ Chem Lett 194(19):3409–3443. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10311-021-01217-8
Sridhar A, Kannan D, Kapoor A, Prabhakar S (2022) Extraction and detection methods of microplastics in food and marine systems: a critical review. Chemosphere 286:131653
Stabnikova O, Stabnikov V, Marinin A et al (2022) The role of microplastics biofilm in accumulation of trace metals in aquatic environments. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 387(38):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11274-022-03293-6
Stavila E, Arsyi RZ, Petrovic DM, Loos K (2013) Fusarium solani pisi cutinase-catalyzed synthesis of polyamides. Eur Polym J 49:834–842. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EURPOLYMJ.2012.12.010
Sun Q, Ren SY, Ni HG (2020a) Incidence of microplastics in personal care products: an appreciable part of plastic pollution. Sci Total Environ 742:140218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140218
Sun X, Yuan X, Jia Y et al (2020b) Differentially charged nanoplastics demonstrate distinct accumulation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Nanotechnol 15:755–760. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-020-0707-4
Šunta U, Trebše P, Kralj MB (2021) Simply applicable method for microplastics determination in environmental samples. Molecules 26:1840. https://doi.org/10.3390/MOLECULES26071840
Taniguchi I, Yoshida S, Hiraga K et al (2019) Biodegradation of PET: current status and application aspects. ACS Catal 9:4089–4105. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSCATAL.8B05171/ASSET/IMAGES/MEDIUM/CS-2018-05171U_0012.GIF
Teng J, Wang Q, Ran W et al (2019) Microplastic in cultured oysters from different coastal areas of China. Sci Total Environ 653:1282–1292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.057
Ter Halle A, Ladirat L, Gendre X et al (2016) Understanding the fragmentation pattern of marine plastic debris. Environ Sci Technol 50:5668–5675. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.EST.6B00594/SUPPL_FILE/ES6B00594_SI_001.PDF
Tirkey A, Upadhyay LSB (2021) Microplastics: An overview on separation, identification and characterization of microplastics. Mar Pollut Bull 170:112604. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MARPOLBUL.2021.112604
Tong H, Jiang Q, Hu X, Zhong X (2020) Occurrence and identification of microplastics in tap water from China. Chemosphere 252:126493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126493
Udovicki B, Andjelkovic M, Cirkovic-Velickovic T, Rajkovic A (2022) Microplastics in food: scoping review on health effects, occurrence, and human exposure. Int J Food Contam 9:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40550-022-00093-6
Uurasjärvi E, Sainio E, Setälä O et al (2021) Validation of an imaging FTIR spectroscopic method for analyzing microplastics ingestion by Finnish lake fish (Perca fluviatilis and Coregonus albula). Environ Pollut 288:117780. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVPOL.2021.117780
Van Cauwenberghe L, Janssen CR (2014) Microplastics in bivalves cultured for human consumption. Environ Pollut 193:65–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVPOL.2014.06.010
Van Cauwenberghe L, Devriese L, Galgani F et al (2015) Microplastics in sediments: a review of techniques, occurrence and effects. Mar Environ Res 111:5–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MARENVRES.2015.06.007
Vickers NJ (2017) Animal communication: when I’m calling you, will you answer too? Curr Biol 27:R713–R715. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CUB.2017.05.064
Vitali C, Peters RJB, Janssen H, Nielen MWF (2023) Trends in analytical chemistry microplastics and nanoplastics in food, water, and beverages; part I. Occurrence. Trends Anal Chem 159:116670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2022.116670
Waddell EN, Lascelles N, Conkle JL (2020) Microplastic contamination in Corpus Christi Bay blue crabs, Callinectes sapidus. Limnol Oceanogr Lett 5:92–102. https://doi.org/10.1002/LOL2.10142
Wagner J, Wang ZM, Ghosal S et al (2017) Novel method for the extraction and identification of microplastics in ocean trawl and fish gut matrices. Anal Methods 9:1479–1490. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6AY02396G
Wagner J, Wang ZM, Ghosal S et al (2019) Nonestructive extraction an ientification of microplastics from freshwater sport fish stomachs. Environ Sci Technol 53:14496–14506. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.EST.9B05072/SUPPL_FILE/ES9B05072_SI_001.PDF
Wahl A, Le Juge C, Davranche M et al (2021) Nanoplastic occurrence in a soil amended with plastic debris. Chemosphere 262:127784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127784
Walkinshaw C, Lindeque PK, Thompson R et al (2020) Microplastics and seafood: lower trophic organisms at highest risk of contamination. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 190:110066. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECOENV.2019.110066
Wang Z, Taylor SE, Sharma P, Flury M (2018) Poor extraction efficiencies of polystyrene nano- and microplastics from biosolids and soil. PLoS ONE 13:e0208009. https://doi.org/10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0208009
Wang F, Wang B, Duan L et al (2020) Occurrence and distribution of microplastics in domestic, industrial, agricultural and aquacultural wastewater sources: a case study in Changzhou, China. Water Res 182:115956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.115956
Wang J, Guo X, Xue J (2021a) Biofilm-developed microplastics as vectors of pollutants in aquatic environments. Environ Sci Technol 55:12780–12790. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.EST.1C04466/SUPPL_FILE/ES1C04466_SI_001.PDF
Wang K, Li J, Zhao L et al (2021b) Gut microbiota protects honey bees (Apis mellifera L.) against polystyrene microplastics exposure risks. J Hazard Mater 402:123828. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2020.123828
Watteau F, Dignac MF, Bouchard A et al (2018) Microplastic detection in soil amended with municipal solid waste composts as revealed by transmission electronic microscopy and pyrolysis/GC/MS. Front Sustain Food Syst 2:407866. https://doi.org/10.3389/FSUFS.2018.00081/BIBTEX
Wei R, Breite D, Song C et al (2019) Biocatalytic degradation efficiency of postconsumer polyethylene terephthalate packaging determined by their polymer microstructures. Adv Sci 6:1900491. https://doi.org/10.1002/ADVS.201900491
Wen S, Zhao Y, Wang M et al (2022) Micro (nano) plastics in food system: potential health impacts on human intestinal system. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2022.2116559
Winkler A, Santo N, Ortenzi MA et al (2019) Does mechanical stress cause microplastic release from plastic water bottles? Water Res 166:115082. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.115082
Wootton N, Reis-Santos P, Dowsett N et al (2021) Low abundance of microplastics in commercially caught fish across southern Australia. Environ Pollut 290:118030. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118030
Wu M, Liu W, Liang Y (2019) Probing size characteristics of disinfection by-products precursors during the bioavailability study of soluble microbial products using ultrafiltration fractionation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 175:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECOENV.2019.02.077
Wu RT, Cai YF, Chen YX et al (2021) Occurrence of microplastic in livestock and poultry manure in South China. Environ Pollut 277:116790. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVPOL.2021.116790
Wu P, Lin S, Cao G et al (2022) Absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion and toxicity of microplastics in the human body and health implications. J Hazard Mater 437:129361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129361
Xu JL, Thomas KV, Luo Z, Gowen AA (2019a) FTIR and Raman imaging for microplastics analysis: State of the art, challenges and prospects. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 119:115629. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TRAC.2019.115629
Xu M, Halimu G, Zhang Q et al (2019b) Internalization and toxicity: a preliminary study of effects of nanoplastic particles on human lung epithelial cell. Sci Total Environ 694:133794. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2019.133794
Xu X, Wong CY, Tam NFY et al (2020) Microplastics in invertebrates on soft shores in Hong Kong: Influence of habitat, taxa and feeding mode. Sci Total Environ 715:136999. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2020.136999
Yan M, Li W, Chen X et al (2021) A preliminary study of the association between colonization of microorganism on microplastics and intestinal microbiota in shrimp under natural conditions. J Hazard Mater 408:124882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124882
Yan Z, Liu Y, Zhang T et al (2022) Analysis of microplastics in human feces reveals a correlation between fecal microplastics and inflammatory bowel disease status. Environ Sci Technol 56:414–421. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.1c03924
Yu L, Di ZJ, Liu Y et al (2021) Distribution characteristics of microplastics in agricultural soils from the largest vegetable production base in China. Sci Total Environ 756:143860. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2020.143860
Zabel F, Delzeit R, Schneider JM et al (2019) Global impacts of future cropland expansion and intensification on agricultural markets and biodiversity. Nat Commun 10:2844. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10775-z
Zhang J, Tian K, Lei C, Min S (2018) Identification and quantification of microplastics in table sea salts using micro-NIR imaging methods. Anal Methods 10:2881–2887. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8AY00125A
Zhang F, Wang X, Xu J et al (2019a) Food-web transfer of microplastics between wild caught fish and crustaceans in East China Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 146:173–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MARPOLBUL.2019.05.061
Zhang J, Wang L, Kannan K (2019b) Polyethylene terephthalate and polycarbonate microplastics in pet food and feces from the United States. Environ Sci Technol 53:12035–12042. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.EST.9B03912/SUPPL_FILE/ES9B03912_SI_001.PDF
Zhang T, Sun Y, Song K et al (2021) Microplastics in different tissues of wild crabs at three important fishing grounds in China. Chemosphere 271:129479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129479
Zhang Q, Du F, Liang W et al (2022) Microfiber fallout during dining and potential human intake. J Hazard Mater 430:128477. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2022.128477
Zhao K, Wei Y, Dong J et al (2022) Separation and characterization of microplastic and nanoplastic particles in marine environment. Environ Pollut 297:118773. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVPOL.2021.118773
Zhu J, Wang C (2020) Recent advances in the analysis methodologies for microplastics in aquatic organisms: current knowledge and research challenges. Anal Methods 12:2944–2957. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0AY00143K
Zhu N, Liu J, Yang J et al (2016) Comparative analysis of the secretomes of Schizophyllum commune and other wood-decay basidiomycetes during solid-state fermentation reveals its unique lignocellulose-degrading enzyme system. Biotechnol Biofuels 9:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1186/S13068-016-0461-X/TABLES/8
Ziani K, Ioniță-Mîndrican CB, Mititelu M et al (2023) Microplastics: a real global threat for environment and food safety: a state of the art review. Nutrients. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15030617
Zitouni N, Cappello T, Missawi O et al (2022) Metabolomic disorders unveil hepatotoxicity of environmental microplastics in wild fish Serranus scriba (Linnaeus 1758). Sci Total Environ 838:155872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155872
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to their respective departments/institutes/universities for providing space and other necessary facilities, which helped draft this manuscript.
Funding
This article did not receive any form of funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors researched data for the article and contributed to the literature survey, manuscript writing, writing—review and editing. Emmanuel Sunday Okeke conceptualized the study, and Chidiebele Emmanuel Nwankwo significantly contributed to the study idea and review structure. Chukwuebuka Gabriel Eze, Chidiebele Emmanuel Nwankwo, Satarupa Dey, Suresh Sundaramurthy, and Emmanuel Sunday Okeke were contributed to investigation, methodology, project administration, resources, and software. The revision and modification of the article were done by Emmanuel Sunday Okeke and Chidiebele Emmanuel Nwankwo. All authors contributed substantially to the discussion of the content, figures, and tables. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have influenced the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Eze, C.G., Nwankwo, C.E., Dey, S. et al. Food chain microplastics contamination and impact on human health: a review. Environ Chem Lett (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-024-01734-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-024-01734-2