Abstract
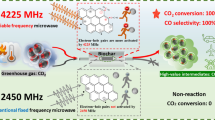
The conventional process for CO2 conversion requires high energy and expensive catalysts, and shows poor product selectivity. In this study, we address these challenges by investigating an environmentally friendly method for CO production through the variable frequency microwave-driven CO2 Boudouard reaction over biochar. We hypothesized that tuning the microwave frequency to align with the dielectric properties of biochar, and thereby induce a resonance effect, could significantly enhance reaction efficiency. Experiments were conducted to explore the effect of microwave frequency on CO2 conversion efficiency in the variable frequency microwave reactor operating within a frequency range of 2430–6000 MHz. Results reveal a significant resonance effect at 4225 MHz resulting in an outstanding CO2 conversion of 96.3%, in sharp contrast to the complete absence of conversion observed at the conventional 2450 MHz. The resonance frequency not only facilitated exceptional conversion but also remarkably improved energy efficiency, yielding a productivity of 1427.5 µmol/kJ of CO. This represents a remarkable 474-fold increase compared to electrical heating. Furthermore, continuous microwave irradiation at this optimized frequency demonstrated remarkable stability and induced substantial enhancements in the pore structure and surface area of biochar. This innovative approach provides promising insights into sustainable and efficient CO production processes.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balyan S, Jiang C, Caiola A, Hu J (2023) Microwave catalytic conversion of acetylene for co-production of hydrogen and carbon nanotubes. Chem Eng J 454:140115
Christiansen T, Robinson B, Caiola A, Jiang C, Hu J (2022) Improved efficiency of the microwave-enhanced catalytic pyrolysis of methane through supplemental thermal heating. Ind Eng Chem Res 61(43):15832–15841
Goyal H, Chen TY, Chen W, Vlachos DG (2022) A review of microwave-assisted process intensified multiphase reactors. Chem Eng J 430:133183
Jie X, Li W, Slocombe D, Gao Y, Banerjee I, Gonzalez-Cortes S, Yao B, AlMegren H, Alshihri S, Dilworth J, Thomas J, Xiao T, Edwards P (2020) Microwave-initiated catalytic deconstruction of plastic waste into hydrogen and high-value carbons. Nat Catal 3(11):902–912
Khattak HK, Bianucci P, Slepkov AD (2019) Linking plasma formation in grapes to microwave resonances of aqueous dimers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116(10):4000–4005
Kishimoto F, Yoshioka T, Ishibashi R, Yamada H, Muraoka K, Taniguchi H, Takanabe K (2023) Direct microwave energy input on a single cation for outstanding selective catalysis. Sci Adv 9(33):eadi1744
Lahijani P, Mohammadi M, Zainal ZA, Mohamed AR (2015) Improvement of biomass char-CO2 gasification reactivity using microwave irradiation and natural catalyst. Thermochim Acta 604:61–66
Miotk R, Hrycak B, Czylkowski D, Dors M, Jasinski M, Mizeraczyk J (2016) Liquid fuel reforming using microwave plasma at atmospheric pressure. Plasma Sourc Sci Technol 25(3):035022
Ren X, Ghazani MS, Zhu H, Ao W, Zhang H, Moreside E, Bi X (2022) Challenges and opportunities in microwave-assisted catalytic pyrolysis of biomass: a review. Appl Energ 315:118970
Suriapparao DV, Tanneru HK, Reddy BR (2022) A review on the role of susceptors in the recovery of valuable renewable carbon products from microwave-assisted pyrolysis of lignocellulosic and algal biomasses: Prospects and challenges. Environ Res 215(Pt 3):114378
Yao X, Hu X, Zhang W, Gong X, Wang X, Pillai SC, Wang D (2020) Mie resonance in hollow nanoshells of ternary TiO2-Au-CdS and enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Appl Catal B Environ 276:119153
Funding
The authors express their gratitude to the basic research in Chinese Academy of Forestry (No. CAFYBB2020ZF006), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52376195). AJR and XZM efforts were supported by The University of Tennessee, Knoxville.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XL contributed to Methodology, Investigation. JR contributed to Methodology, Investigation. MW contributed to Methodology, Investigation. XM contributed to Methodology, Resources. AJR contributed to Project administration, Writing—Review & Editing. JW contributed to Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Funding acquisition, Writing—Original draft preparation. JJ contributed to Conceptualization, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition, Writing—Review & Editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
La, X., Ren, J., Wen, M. et al. Microwave resonance enhanced CO2 reduction using biochar. Environ Chem Lett 22, 7–12 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-023-01670-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-023-01670-7