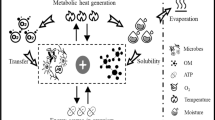
Abstract
Sewage sludge treatment and disposal remains a challenging problem. Composting of sewage sludges is gaining increasing attention due to its cost-effectiveness, operation convenience, advantages in lifecycle management, and low greenhouse gas emissions. Disadvantages, such as long reaction time, significant land area occupation requirement, potential risks of residual heavy metals, and emerging contaminants, have restricted wider application. Here we review applications of hyperthermophiles in composting , focusing on the unique improvements provided by hyperthermophiles in composing temperatures, product safety, nitrogen preservation and humification. Inoculation of hyperthermophiles allows temperature of composting to reach over 80°C. Specific metabolic strategies are critical in hyperthermophiles-inoculated composting. High-temperature resistance in the metabolism of hyperthermophiles and their roles in temperature rising during composting is often overlooked. This review discusses both aspects, allowing for a deeper understanding of the functions and influences of hyperthermophiles in sludge composting. Additionally, this review highlights the policy challenges associated with the hyperthermophiles-inoculated sludge composing technique and provides potential directions for future research in this field.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- DNA:
-
Deoxyribonucleic acid
- Mn:
-
Manganese
References
Alvarenga P, Mourinha C, Farto M et al (2015) Sewage sludge, compost and other representative organic wastes as agricultural soil amendments: benefits versus limiting factors. Waste Manag 40:44–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.01.027
Amo T, Paje ML, Inagaki A, Ezaki S, Atomi H, Imanaka T (2002) Pyrobaculum calidifontis sp. nov., a novel hyperthermophilic archaeon that grows in atmospheric air. Archaea 1(2):113–121. https://doi.org/10.1155/2002/616075
Awasthi MK, Awasthi SK, Wang Q et al (2018) Influence of biochar on volatile fatty acids accumulation and microbial community succession during biosolids composting. Bioresour Technol 251:158–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.12.037
Barik S (2020) Evolution of protein structure and stability in global warming. Int J Mol Sci 21(24):9662. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21249662
Bendia AG, Lemos LN, Mendes LW, Signori CN, Bohannan BJM, Pellizari VH (2021) Metabolic potential and survival strategies of microbial communities across extreme temperature gradients on deception Island volcano. Antarctica Environ Microbiol 23(7):4054–4073. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.15649
Białobrzewski I, Mikš-Krajnik M, Dach J, Markowski M, Czekała W, Głuchowska K (2015) Model of the sewage sludge-straw composting process integrating different heat generation capacities of mesophilic and thermophilic microorganisms. Waste Manag 43:72–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.05.036
Blöchl E, Burggraf S, Fiala G et al (1995) Isolation, taxonomy and phylogeny of hyperthermophilic microorganisms. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 11(1):9–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00339133
Blumer-Schuette SE, Kataeva I, Westpheling J, Adams MW, Kelly RM (2008) Extremely thermophilic microorganisms for biomass conversion: status and prospects. Curr Opin Biotechnol 19(3):210–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2008.04.007
Boldrin A, Hartling KR, Laugen M, Christensen TH (2010) Environmental inventory modelling of the use of compost and peat in growth media preparation. Resour Conserv Recycl 54(12):1250–1260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2010.04.003
Brock TD, Freeze H (1969) Thermus aquaticus gen. n. and sp. n., a nonsporulating extreme thermophile. J Bacteriol 98(1):289–297. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.98.1.289-297.1969
Bruins MR, Kapil S, Oehme FW (2000) Microbial resistance to metals in the environment. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 45(3):198–207. https://doi.org/10.1006/eesa.1999.1860
Bunsan S, Chen W-Y, Chen H-W, Chuang YH, Grisdanurak N (2013) Modeling the dioxin emission of a municipal solid waste incinerator using neural networks. Chemosphere 92(3):258–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.01.083
Caldwell SL, Liu Y, Ferrera I, Beveridge T, Reysenbach AL (2010) Thermocrinis minervae sp. nov., a hydrogen- and sulfur-oxidizing, thermophilic member of the Aquificales from a Costa Rican terrestrial hot spring. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:338–343. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.010496-0
Cao Y, Wang X, Zhang X, Misselbrook TH, Bai Z, Wang H, Ma L (2022) The effects of electric field assisted composting on ammonia and nitrous oxide emissions varied with different electrolytes. Bioresour Technol 344:126194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126194
Cárdenas-Fernández M, Subrizi F, Dobrijevic D, Hailes HC, Ward JM (2021) Characterisation of a hyperthermophilic transketolase from Thermotoga maritima DSM3109 as a biocatalyst for 7-keto-octuronic acid synthesis. Org Biomol Chem 19:6493–6500. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1OB01237A
Cario A, Grossi V, Schaeffer P, Oger PM (2015) Membrane homeoviscous adaptation in the piezo-hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermococcus barophilus. Front Microbiol 6:1152. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.01152
Castán P, Zafra O, Moreno R et al (2002) The periplasmic space in Thermus thermophilus: evidence from a regulation-defective S-layer mutant overexpressing an alkaline phosphatase. Extremophiles 6(3):225–232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-001-0246-3
Chakraborty S, Jo BW, Jo JH, Baloch Z (2017) Effectiveness of sewage sludge ash combined with waste pozzolanic minerals in developing sustainable construction material: an alternative approach for waste management. J Cleaner Prod 153:253–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.03.059
Chan MT, Selvam A, Wong JWC (2016) Reducing nitrogen loss and salinity during ‘struvite’ food waste composting by zeolite amendment. Bioresour Technol 200:838–844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.10.093
Chang R, Guo Q, Chen Q, Bernal MP, Wang Q, Li Y (2019) Effect of initial material bulk density and easily-degraded organic matter content on temperature changes during composting of cucumber stalk. J Environ Sci 80:306–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2017.10.004
Chen H, Zhang M (2013) Occurrence and removal of antibiotic resistance genes in municipal wastewater and rural domestic sewage treatment systems in eastern China. Environ Int 55:9–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2013.01.019
Chen Z, Pan XH, Chen H, Guan X, Lin Z (2016) Biomineralization of Pb(II) into Pb-hydroxyapatite induced by Bacillus cereus 12–2 isolated from Lead-Zinc mine tailings. J Hazard Mater 301:531–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.09.023
Chen X, Zhao Y, Zhang C et al (2020) Speciation, toxicity mechanism and remediation ways of heavy metals during composting: a novel theoretical microbial remediation method is proposed. J Environ Manage 272:111109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111109
Chen Z, Xing R, Yang X, Zhao Z, Liao H, Zhou S (2021) Enhanced in situ Pb(II) passivation by biotransformation into chloropyromorphite during sludge composting. J Hazard Mater 408:124973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124973
Chen X, Du G, Wu C, Li Q, Zhou P, Shi J, Zhao Z (2022a) Effect of thermophilic microbial agents on nitrogen transformation, nitrogen functional genes, and bacterial communities during bean dregs composting. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 29:31846–31860. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17946-w
Chen XH, Huang YH, Lu H et al (2022b) Plant-scale hyperthermophilic composting of sewage sludge shifts bacterial community and promotes the removal of organic pollutants. Bioresour Technol 347:126702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.126702
Cheng Q, Zhang L, Wang D, Niu B (2021) Bioaugmentation mitigates ammonia and hydrogen sulfide emissions during the mixture compost of dewatered sewage sludge and reed straw. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:68487–68497. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15446-5
Collivignarelli MC, Abbà A, Carnevale Miino M, Torretta V (2019) What advanced treatments can be used to minimize the production of sewage sludge in WWTPs? Appl Sci 9(13):2650. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9132650
Cui P, Chen Z, Zhao Q, Yu Z, Yi Z, Liao H, Zhou S (2019a) Hyperthermophilic composting significantly decreases N2O emissions by regulating N2O-related functional genes. Bioresour Technol 272:433–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.10.044
Cui P, Liao H, Bai Y et al (2019b) Hyperthermophilic composting reduces nitrogen loss via inhibiting ammonifiers and enhancing nitrogenous humic substance formation. Sci Total Environ 692:98–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.239
Cusidó JA, Cremades LV (2012) Environmental effects of using clay bricks produced with sewage sludge: leachability and toxicity studies. Waste Manag 32(6):1202–1208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2011.12.024
Cyprowski M, Ławniczek-Wałczyk A, Gołofit-Szymczak M, Frączek K, Kozdrój J, Górny RL (2019) Bacterial aerosols in a municipal landfill environment. Sci Total Environ 660:288–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.356
Daniel RM, Cowan DA (2000) Biomolecular stability and life at high temperatures. Cell Mol Life Sci 57(2):250–264. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00000688
De Rosa M, Gambacorta A, Nicolaus B (1983) A new type of cell membrane, in thermophilic archaebacteria, based on bipolar ether lipids. J Membr Sci 16:287–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0376-7388(00)81316-2
Degli-Innocenti F (2021) Is composting of packaging real recycling? Waste Manage 130:61–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2021.05.017
DeLong EF (2001) A phylogenetic perspective on hyperthermophilic microorganisms. Methods Enzymol 330:3–11
DiGiacomo J, McKay C, Davila A (2022) ThermoBase: a database of the phylogeny and physiology of thermophilic and hyperthermophilic organisms. PLoS ONE 17(5):e0268253. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0268253
Dio V, Maione A, Guida M, Dec O, Liguori R, Carraturo F, Galdiero E (2021) Screening and isolation of microbes from a mud community of Ischia Island thermal springs: preliminary analysis of a bioactive compound. J Prev Med Hyg 62(2):E479-e488. https://doi.org/10.15167/2421-4248/jpmh2021.62.2.1792
Dodsworth JA, Ong JC, Williams AJ, Dohnalkova AC, Hedlund BP (2015) Thermocrinis jamiesonii sp. nov., a thiosulfate-oxidizing, autotropic thermophile isolated from a geothermal spring. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65(12):4769–4775. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.000647
Du J, Zhang Y, Qu M et al (2019) Effects of biochar on the microbial activity and community structure during sewage sludge composting. Bioresour Technol 272:171–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.10.020
Eder W, Huber R (2002) New isolates and physiological properties of the Aquificales and description of Thermocrinis albus sp. nov. Extremophiles 6(4):309–318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-001-0259-y
Elleuche S, Schäfers C, Blank S, Schröder C, Antranikian G (2015) Exploration of extremophiles for high temperature biotechnological processes. Curr Opin Microbiol 25:113–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2015.05.011
Fang B, Yu J, Chen Z et al (2023) Artificial intelligence for waste management in smart cities: a review. Environ Chem Lett 21(4):1959–1989. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-023-01604-3
Fijalkowski K, Rorat A, Grobelak A, Kacprzak MJ (2017) The presence of contaminations in sewage sludge: the current situation. J Environ Manage 203:1126–1136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.05.068
Flores PA, Amenábar MJ, Blamey JM (2013) Hot environments from Antarctica: source of thermophiles and hyperthermophiles, with potential biotechnological applications. Thermophilic microbes in environmental and industrial biotechnology: biotechnology of thermophiles. Springer, Netherlands, Dordrecht, pp 99–118
Forterre P (2002) A hot story from comparative genomics: reverse gyrase is the only hyperthermophile-specific protein. Trends Genet 18(5):236–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9525(02)02650-1
Gambacorta A, Trincone A, Nicolaus B, Lama L, De Rosa M (1993) Unique features of lipids of archaea. Syst Appl Microbiol 16(4):518–527. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0723-2020(11)80321-8
Ghanem A, Dubroca J, Chaplain V, Mougin C (2006) Fate of herbicides and nonylphenol in soil–plant–water systems amended with contaminated sewage sludge. Environ Chem Lett 4(2):63–67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-006-0034-5
Gioia C, Giacobazzi G, Vannini M et al (2021) End of life of biodegradable plastics: composting vs. re/upcycling. Chemsuschem 14:4167. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.202101226
Glyakina AV, Garbuzynskiy SO, Lobanov MY, Galzitskaya OV (2007) Different packing of external residues can explain differences in the thermostability of proteins from thermophilic and mesophilic organisms. Bioinformatics 23(17):2231–2238. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm345
Goñi FM (2014) The basic structure and dynamics of cell membranes: an update of the Singer-Nicolson model. Biochim Biophys Acta 1838(6):1467–1476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2014.01.006
González-Faune P, Sánchez-Arévalo I, Sarkar S et al (2021) Computational study on temperature driven structure-function relationship of polysaccharide producing bacterial glycosyl transferase enzyme. Polymers 13(11):1771. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111771
Graham JE, Clark ME, Nadler DC et al (2011) Identification and characterization of a multidomain hyperthermophilic cellulase from an archaeal enrichment. Nat Commun 2(1):375. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms1373
Gromiha MM, Pathak MC, Saraboji K, Ortlund EA, Gaucher EA (2013) Hydrophobic environment is a key factor for the stability of thermophilic proteins. Proteins Struct Funct Bioinform 81(4):715–721. https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.24232
Guiral M, Giudici-Orticoni M-T (2021) Microbe profile: Aquifex aeolicus: an extreme heat-loving bacterium that feeds on gases and inorganic chemicals. Microbiology 167(1):001010. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.001010
Guo H-n, Wu S-b, Tian Y-j, Zhang J, Liu H-t (2021) Application of machine learning methods for the prediction of organic solid waste treatment and recycling processes: a review. Bioresour Technol 319:124114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.124114
Hemati A, Aliasgharzad N, Khakvar R, Khoshmanzar E, Asgari Lajayer B, van Hullebusch ED (2021) Role of lignin and thermophilic lignocellulolytic bacteria in the evolution of humification indices and enzymatic activities during compost production. Waste Manag 119:122–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2020.09.042
Hemmat A, Aghilinategh N, Rezainejad Y, Sadeghi M (2010) Long-term impacts of municipal solid waste compost, sewage sludge and farmyard manure application on organic carbon, bulk density and consistency limits of a calcareous soil in central Iran. Soil Tillage Res 108(1):43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2010.03.007
Hendriksen RS, Munk P, Njage P et al (2019) Global monitoring of antimicrobial resistance based on metagenomics analyses of urban sewage. Nat Commun 10(1):1124. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-08853-3
Hiroshi N, Satoshi F, Ken N (2003) Compositional changes in RNA, DNA and proteins for bacterial adaptation to higher and lower temperatures. J Biochem 133(4):507–513. https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvg067
Hoppert M, Valdez M, Enseleit M et al (2012) Structure–functional analysis of the Dictyoglomus cell envelope. Syst Appl Microbiol 35(5):279–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.syapm.2012.06.004
Huang W, Li Y, Liu X, Wang W, Wen P, Yu Z, Zhou S (2021) Linking the electron transfer capacity with the compositional characteristics of dissolved organic matter during hyperthermophilic composting. Sci Total Environ 755:142687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142687
Huber R, Eder W, Heldwein S, Wanner G, Huber H, Rachel R, Stetter KO (1998) Thermocrinis ruber gen. nov., sp. nov., A pink-filament-forming hyperthermophilic bacterium isolated from yellowstone national park. Appl Environ Microbiol 64(10):3576–3583. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.64.10.3576-3583.1998
Hudcová H, Vymazal J, Rozkošný M (2019) Present restrictions of sewage sludge application in agriculture within the European Union. Soil Water Res 14(2):104–120. https://doi.org/10.17221/36/2018-swr
Itoh T, Iino T (2013) Phylogeny and biological features of thermophiles. Thermophilic microbes in environmental and industrial biotechnology: biotechnology of thermophiles. Springer, Netherlands, Dordrecht, pp 249–270
Jia R, Wan X, Geng X, Xue D, Xie Z, Chen C (2021) Microbial L-asparaginase for application in acrylamide mitigation from food: current research status and future perspectives. Microorganisms 9(8):1659. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9081659
Kanazawa S, Ishikawa Y, Tomita-Yokotani K et al (2008) Space agriculture for habitation on Mars with hyper-thermophilic aerobic composting bacteria. Adv Space Res 41(5):696–700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2007.09.040
Karlstrom M, Steen IH, Madern D, Fedoy AE, Birkeland NK, Ladenstein R (2006) The crystal structure of a hyperthermostable subfamily II isocitrate dehydrogenase from Thermotoga maritima. FEBS J 273(13):2851–2868. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2006.05298.x
Ke GR, Lai CM, Liu YY, Yang SS (2010) Inoculation of food waste with the thermo-tolerant lipolytic actinomycete Thermoactinomyces vulgaris A31 and maturity evaluation of the compost. Bioresour Technol 101(19):7424–7431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.04.051
Kissling GE, Grogan DW, Drake JW (2013) Confounders of mutation-rate estimators: selection and phenotypic lag in Thermus thermophilus. Mutat Res 749(1–2):16–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2013.07.006
Knapik K, Becerra M, González-Siso M-I (2019) Microbial diversity analysis and screening for novel xylanase enzymes from the sediment of the Lobios hot spring in Spain. Sci Rep 9(1):11195. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-47637-z
Ko HJ, Kim KY, Kim HT, Kim CN, Umeda M (2008) Evaluation of maturity parameters and heavy metal contents in composts made from animal manure. Waste Manag 28(5):813–820. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2007.05.010
Koko MYF, Mu W, Hassanin HAM et al (2020) Archaeal hyperthermostable mannitol dehydrogenases: a promising industrial enzymes for d-mannitol synthesis. Food Res Int 137:109638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109638
Kong Z, Wang X, Wang M, Chai L, Wang X, Liu D, Shen Q (2020) Bacterial ecosystem functioning in organic matter biodegradation of different composting at the thermophilic phase. Bioresour Technol 317:123990. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123990
Kristjánsson JK, Hreggvidsson GO (1995) Ecology and habitats of extremophiles. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 11(1):17–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00339134
Krska D, Mazurkewich S, Brown HA et al (2021) Structural and functional analysis of a multimodular hyperthermostable xylanase-glucuronoyl esterase from Caldicellulosiruptor kristjansonii. Biochemistry 60:2206–2220. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.1c00305
Kupper T, Bürge D, Bachmann HJ, Güsewell S, Mayer J (2014) Heavy metals in source-separated compost and digestates. Waste Manage 34(5):867–874. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2014.02.007
Lee DW, Hong YH, Choe EA et al (2005) A thermodynamic study of mesophilic, thermophilic, and hyperthermophilic L-arabinose isomerases: the effects of divalent metal ions on protein stability at elevated temperatures. FEBS Lett 579(5):1261–1266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2005.01.027
Li G, Zhou X, Li Z et al (2021a) Significantly improving the thermostability of a hyperthermophilic GH10 family xylanase XynAF1 by semi-rational design. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105:4561–4576. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11340-9
Li Y, Sun B, Deng T, Lian P, Chen J, Peng X (2021b) Safety and efficiency of sewage sludge and garden waste compost as a soil amendment based on the field application in woodland. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 222:112497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112497
Liao H, Lu X, Rensing C et al (2018) Hyperthermophilic composting accelerates the removal of antibiotic resistance genes and mobile genetic elements in sewage sludge. Environ Sci Technol 52(1):266–276. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b04483
Liu B, Wei Q, Zhang B, Bi J (2013) Life cycle GHG emissions of sewage sludge treatment and disposal options in Tai Lake Watershed, China. Sci Total Environ 447:361–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.01.019
Liu X, Wang Y, Wang W, Huang W, Yu Z, Zhou S (2021) Protein-derived structures determines the redox capacity of humic acids formed during hyperthermophilic composting. Waste Manage 126:810–820. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2021.04.016
Liu Z, Wang X, Li S, Bai Z, Ma L (2022) Advanced composting technologies promotes environmental benefits and eco-efficiency: a life cycle assessment. Bioresour Technol 346:126576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126576
Lopez MJ, Jurado MM, Lopez-Gonzalez JA, Estrella-Gonzalez MJ, Martinez-Gallardo MR, Toribio A, Suarez-Estrella F (2021) Characterization of thermophilic lignocellulolytic microorganisms in composting. Front Microbiol 12:697480. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.697480
Lopez-Gonzalez JA, Estrella-Gonzalez MJ, Lerma-Moliz R, Jurado MM, Suarez-Estrella F, Lopez MJ (2021) Industrial composting of sewage sludge: study of the bacteriome, sanitation, and antibiotic-resistant strains. Front Microbiol 12:784071. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.784071
Lora Grando R, de Souza Antune AM, da Fonseca FV, Sánchez A, Barrena R, Font X (2017) Technology overview of biogas production in anaerobic digestion plants: a European evaluation of research and development. Renew Sust Energ Rev 80:44–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.05.079
Lü H, Chen X-H, Mo C-H et al (2021) Occurrence and dissipation mechanism of organic pollutants during the composting of sewage sludge: a critical review. Bioresour Technol 328:124847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.124847
Lv B, Xing M, Yang J (2016) Speciation and transformation of heavy metals during vermicomposting of animal manure. Bioresour Technol 209:397–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.03.015
Makarichi L, Jutidamrongphan W, Techato K-a (2018) The evolution of waste-to-energy incineration: a review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 91:812–821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.04.088
Marchioretto MM, Bruning H, Rulkens W (2005) Heavy metals precipitation in sewage sludge. Sep Sci Technol 40(16):3393–3405. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496390500423748
Miller-Coleman RL, Dodsworth JA, Ross CA et al (2012) Korarchaeota diversity, biogeography, and abundance in Yellowstone and Great Basin hot springs and ecological niche modeling based on machine learning. PLoS ONE 7(5):e35964. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0035964
Miretzky P, Fernandez-Cirelli A (2008) Phosphates for Pb immobilization in soils: a review. Environ Chem Lett 6(3):121–133. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-007-0133-y
Mondini C, Dell’Abate MT, Leita L, Benedetti A (2003) An integrated chemical, thermal, and microbiological approach to compost stability evaluation. J Environ Qual 32(6):2379–2386. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2003.2379
Moreno J, López-González JA, Arcos-Nievas MA, Suárez-Estrella F, Jurado MM, Estrella-González MJ, López MJ (2021) Revisiting the succession of microbial populations throughout composting: a matter of thermotolerance. Sci Total Environ 773:145587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145587
Moriya T, Hikota T, Yumoto I, Ito T, Terui Y, Yamagishi A, Oshima T (2011) Calditerricola satsumensis gen. nov., sp. nov. and Calditerricola yamamurae sp. nov., extreme thermophiles isolated from a high-temperature compost. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61(3):631–636. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.018416-0
Musto H, Naya H, Zavala A, Romero H, Alvarez-Valin F, Bernardi G (2005) The correlation between genomic G+C and optimal growth temperature of prokaryotes is robust: a reply to Marashi and Ghalanbor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 330(2):357–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.02.133
Nakagawa S, Takai K, Horikoshi K, Sako Y (2004) Aeropyrum camini sp. nov., a strictly aerobic, hyperthermophilic archaeon from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent chimney. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54(2):329–335. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.02826-0
Nanda S, Berruti F (2021) Municipal solid waste management and landfilling technologies: a review. Environ Chem Lett 19(2):1433–1456. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-01100-y
Nguyen C, Yearwood LM, McCully ME (2022) Thermostabilization mechanisms in thermophilic versus mesophilic three-helix bundle proteins. J Comput Chem 43(3):197–205. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.26782
Nishio Y, Nakamura Y, Kawarabayasi Y et al (2003) Comparative complete genome sequence analysis of the amino acid replacements responsible for the thermostability of Corynebacterium efficiens. Genome Res 13(7):1572–1579. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.1285603
Oshima T, Imahori K (1974) Description of Thermus thermophilus (Yoshida and Oshima) comb. Nov., a nonsporulating thermophilic bacterium from a Japanese thermal spa. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 24(1):102–112. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-24-1-102
Oshima T, Moriya T (2008) A preliminary analysis of microbial and biochemical properties of high-temperature compost. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1125:338–344. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1419.012
Osińska A, Korzeniewska E, Harnisz M et al (2020) Small-scale wastewater treatment plants as a source of the dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes in the aquatic environment. J Hazard Mater 381:121221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121221
Osman AI, Farghali M, Ihara I et al (2023) Materials, fuels, upgrading, economy, and life cycle assessment of the pyrolysis of algal and lignocellulosic biomass: a review. Environ Chem Lett 21(3):1419–1476. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-023-01573-7
Pan XH, Wang YH, Chen Z et al (2013) Investigation of antibacterial activity and related mechanism of a series of nano-Mg(OH)(2). Acs Appl Mater Inter 5(3):1137–1142. https://doi.org/10.1021/am302910q
Pan C, Zhao Y, Zhao L et al (2021) Modified montmorillonite and illite adjusted the preference of biotic and abiotic pathways of humus formation during chicken manure composting. Bioresour Technol 319:124121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.124121
Pandit NR, Schmidt HP, Mulder J, Hale SE, Husson O, Cornelissen G (2020) Nutrient effect of various composting methods with and without biochar on soil fertility and maize growth. Arch Agron Soil Sci 66(2):250–265. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2019.1610168
Peng X, Jiang Y, Chen Z, Osman AI, Farghali M, Rooney DW, Yap P-S (2023) Recycling municipal, agricultural and industrial waste into energy, fertilizers, food and construction materials, and economic feasibility: a review. Environ Chem Lett 21(2):765–801. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-022-01551-5
Qian MY, Li RH, Li J, Wedwitschka H, Nelles M, Stinner W, Zhou HJ (2016) Industrial scale garage-type dry fermentation of municipal solid waste to biogas. Bioresour Technol 217:82–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.02.076
Quax TEF, Claassens NJ, Soll D, van der Oost J (2015) Codon bias as a means to fine-tune gene expression. Mol Cell 59(2):149–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2015.05.035
Rastogi G, Bhalla A, Adhikari A, Bischoff KM, Hughes SR, Christopher LP, Sani RK (2010) Characterization of thermostable cellulases produced by Bacillus and Geobacillus strains. Bioresour Technol 101(22):8798–8806. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.06.001
Rawat S, Johri BN (2013) Role of thermophilic microflora in composting. Thermophilic microbes in environmental and industrial biotechnology: biotechnology of thermophiles. Springer, Netherlands, Dordrecht, pp 137–169
Rawoof SAA, Kumar PS, Vo D-VN, Subramanian S (2021) Sequential production of hydrogen and methane by anaerobic digestion of organic wastes: a review. Environ Chem Lett 19(2):1043–1063. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-01122-6
Salvador-Castell M, Golub M, Erwin N et al (2021) Characterisation of a synthetic Archeal membrane reveals a possible new adaptation route to extreme conditions. Commun Biol 4(1):653. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-021-02178-y
Samolada MC, Zabaniotou AA (2014) Comparative assessment of municipal sewage sludge incineration, gasification and pyrolysis for a sustainable sludge-to-energy management in Greece. Waste Manage 34(2):411–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2013.11.003
Sar P, Kazy SK, Paul D, Sarkar A (2013) Metal bioremediation by thermophilic microorganisms. Thermophilic microbes in environmental and industrial biotechnology: biotechnology of thermophiles. Springer, Netherlands, Dordrecht, pp 171–201
Sardarmehni M, Levis JW, Barlaz MA (2021) What is the best end use for compost derived from the organic fraction of municipal solid waste? Environ Sci Technol 55(1):73–81. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c04997
Schönheit P, Schäfer T (1995) Metabolism of hyperthermophiles. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 11(1):26–57. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00339135
Schröder C, Eixenberger D, Suleiman M, Schäfers C, Antranikian G (2019) Characterization of an extremely thermo-active archaeal β-glucosidase and its activity towards glucan and mannan in concert with an endoglucanase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103(23):9505–9514. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10218-1
Seo G-Y, Lee H-S, Kim H, Cho S, Na J-G, Yeon YJ, Lee J (2021) A novel hyperthermophilic methylglyoxal synthase: molecular dynamic analysis on the regional fluctuations. Sci Rep 11(1):2538. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-82078-7
Shinoda W, Shinoda K, Baba T, Mikami M (2005) Molecular dynamics study of bipolar tetraether lipid membranes. Biophys J 89(5):3195–3202. https://doi.org/10.1529/biophysj.105.060962
Silva J, Bernardo F, Jesus M, Faria T, Alves A, Ratola N, Homem V (2021) Levels of volatile methylsiloxanes in urban wastewater sludges at various steps of treatment. Environ Chem Lett 19(3):2723–2732. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-021-01191-1
Stetter Karl O (2013) A brief history of the discovery of hyperthermophilic life. Biochem Soc Trans 41(1):416–420. https://doi.org/10.1042/bst20120284
Suleiman M, Krüger A, Antranikian G (2020) Biomass-degrading glycoside hydrolases of archaeal origin. Biotechnol Biofuels 13(1):153. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-020-01792-y
Szilágyi A, Závodszky P (2000) Structural differences between mesophilic, moderately thermophilic and extremely thermophilic protein subunits: results of a comprehensive survey. Structure 8(5):493–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00133-7
Takami H, Takaki Y, Chee G-J et al (2004) Thermoadaptation trait revealed by the genome sequence of thermophilic Geobacillus kaustophilus. Nucleic Acids Res 32(21):6292–6303. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh970
Tan Z, Zhu H, He X et al (2022) Effect of ventilation quantity on electron transfer capacity and spectral characteristics of humic substances during sludge composting. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 29(46):70269–70284. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20808-8
Tanaka Y, Tsumoto K, Yasutake Y et al (2004) How oligomerization contributes to the thermostability of an archaeon protein. Protein L-isoaspartyl-O-methyltransferase from Sulfolobus tokodaii. J Biol Chem 279(31):32957–32967. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M404405200
Tashiro Y, Tabata H, Itahara A, Shimizu N, Tashiro K, Sakai K (2016) Unique hyper-thermal composting process in Kagoshima City forms distinct bacterial community structures. J Biosci Bioeng 122(5):606–612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2016.04.006
Thomas SC, Payne D, Tamadonfar KO et al (2021) Genomics, exometabolomics, and metabolic probing reveal conserved proteolytic metabolism of thermoflexus hugenholtzii and three candidate species from China and Japan. Front Microbiol 12:632731–632731. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.632731
Tourte M, Schaeffer P, Grossi V, Oger PM (2022) Membrane adaptation in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus relies upon a novel strategy involving glycerol monoalkyl glycerol tetraether lipids. Environ Microbiol 24(4):2029–2046. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.15923
Turner P, Mamo G, Karlsson EN (2007) Potential and utilization of thermophiles and thermostable enzymes in biorefining. Microb Cell Fact 6:9. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-6-9
Vanden Nest T, Amery F, Fryda L, Boogaerts C, Bilbao J, Vandecasteele B (2021) Renewable P sources: P use efficiency of digestate, processed animal manure, compost, biochar and struvite. Sci Total Environ 750:141699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141699
Varjani S, Shah AV, Vyas S, Srivastava VK (2021) Processes and prospects on valorizing solid waste for the production of valuable products employing bio-routes: a systematic review. Chemosphere 282:130954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130954
Vieille C, Zeikus GJ (2001) Hyperthermophilic enzymes: sources, uses, and molecular mechanisms for thermostability. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 65(1):1–43. https://doi.org/10.1128/MMBR.65.1.1-43.2001
Vinnerås B, Björklund A, Jönsson H (2003) Thermal composting of faecal matter as treatment and possible disinfection method––laboratory-scale and pilot-scale studies. Bioresour Technol 88(1):47–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(02)00268-7
Wang S, Wu Y (2021) Hyperthermophilic composting technology for organic solid waste treatment: recent research advances and trends. Processes 9(4):675. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9040675
Wang Q, Cen Z, Zhao J (2015) The survival mechanisms of thermophiles at high temperatures: an angle of omics. Physiology 30(2):97–106. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiol.00066.2013
Wang M, Miao J, Wang X, Li T, Zhu H, Liu D, Shen Q (2020) Genomic and transcriptome analyses of a thermophilic bacterium Geobacillus stearothermophilus B5 isolated from compost reveal its enzymatic basis for lignocellulose degradation. Microorganisms 8(9):1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091357
Wang Y, Tang Y, Li M, Yuan Z (2021) Aeration rate improves the compost quality of food waste and promotes the decomposition of toxic materials in leachate by changing the bacterial community. Bioresour Technol 340:125716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125716
Wang K, Du M, Wang Z, Liu H, Zhao Y, Wu C, Tian Y (2022) Effects of bulking agents on greenhouse gases and related genes in sludge composting. Bioresour Technol 344:126270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126270
Wei L, Zhu F, Li Q et al (2020) Development, current state and future trends of sludge management in China: Based on exploratory data and CO2-equivaient emissions analysis. Environ Int 144:106093. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.106093
Welte CU, de Graaf R, Dalcin Martins P, Jansen RS, Jetten MSM, Kurth JM (2021) A novel methoxydotrophic metabolism discovered in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Archaeoglobus fulgidus. Environ Microbiol 23(7):4017–4033. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.15546
Wirth R, Sikorski J, Brambilla E et al (2010) Complete genome sequence of Thermocrinis albus type strain (HI 11/12T). Stand Genomic Sci 2(2):194–203. https://doi.org/10.4056/sigs.761490
Yamada T, Miyauchi K, Ueda H, Ueda Y, Sugawara H, Nakai Y, Endo G (2007) Composting cattle dung wastes by using a hyperthermophilic pre-treatment process: characterization by physicochemical and molecular biological analysis. J Biosci Bioeng 104(5):408–415. https://doi.org/10.1263/jbb.104.408
Yamada T, Suzuki A, Ueda H, Ueda Y, Miyauchi K, Endo G (2008) Successions of bacterial community in composting cow dung wastes with or without hyperthermophilic pre-treatment. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 81(4):771–781. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1736-3
Yang Y, Wang G, Li G, Ma R, Kong Y, Yuan J (2021) Selection of sensitive seeds for evaluation of compost maturity with the seed germination index. Waste Manag 136:238–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2021.09.037
Yoshii T, Moriya T, Oshima T (2013) Bacterial and biochemical properties of newly invented aerobic, high-temperature compost. Thermophilic microbes in environmental and industrial biotechnology: biotechnology of thermophiles. Springer, Netherlands, Dordrecht, pp 119–135
Yu Z, Tang J, Liao H et al (2018) The distinctive microbial community improves composting efficiency in a full-scale hyperthermophilic composting plant. Bioresour Technol 265:146–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.06.011
Zeller V, Lavigne C, D’Ans P, Towa E, Achten WMJ (2020) Assessing the environmental performance for more local and more circular biowaste management options at city-region level. Sci Total Environ 745:140690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140690
Zhang Z, Li X, Hu X et al (2021) Downward aeration promotes static composting by affecting mineralization and humification. Bioresour Technol 338:125592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125592
Zhao Y, Zhao Y, Zhang Z et al (2017) Effect of thermo-tolerant actinomycetes inoculation on cellulose degradation and the formation of humic substances during composting. Waste Manag 68:64–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.06.022
Zhao Y, Li W, Chen L, Meng L, Zheng Z (2020) Effect of enriched thermotolerant nitrifying bacteria inoculation on reducing nitrogen loss during sewage sludge composting. Bioresour Technol 311:123461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123461
Zhu N, Gao J, Liang D, Zhu Y, Li B, Jin H (2021) Thermal pretreatment enhances the degradation and humification of lignocellulose by stimulating thermophilic bacteria during dairy manure composting. Bioresour Technol 319:124149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.124149
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Numbers 52270119).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RY had the idea for the article; SC performed the literature search and data analysis, and drafted the work; JG and SZ critically revised the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, S., Gu, J., Zhang, S. et al. Application of hyperthermophiles in sludge composting: a review. Environ Chem Lett 22, 445–460 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-023-01657-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-023-01657-4