Abstract
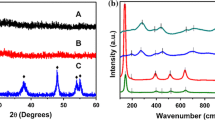
Photocatalysis is a cost-effective method to degrade and remove pollutants, using semiconductor catalysts such as titanium dioxide. The brookite form of titanium dioxide could be as efficient or more efficient compared to the anatase and rutile forms, yet the synthesis of brookite titanium dioxide is actually arduous. Here, we synthesized brookite titanium dioxide nanosquares using a mixture of titanium(IV) bis(ammonium lactato) dihydroxide and titanium oxychloride at low temperature. We observed pure brookite TiO2 nanosquares with a mean edge length of 51 nm. Brookite nanosquares exhibit better photoactivity for the decomposition of rhodamine B under ultraviolet, compared to common titanium dioxide. The synthetic method is simple and does not need any template, organic additive, or organic solvent. This is the first work addressing the synthesis of brookite nanosquare simultaneously using two kinds of water-soluble titanium precursors.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahamad T, Naushad M, Al-Shahrani T, Al-hokbany N, Alshehri SM (2020) Preparation of chitosan based magnetic nanocomposite for tetracycline adsorption: kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Int J Biol Macromol 147:258–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.01.025
Buonsanti R, Grillo V, Carlino E, Giannini C, Kipp T, Cingolani R, Cozzoli PD (2008) Nonhydrolytic synthesis of high-quality anisotropically shaped Brookite TiO2 nanocrystals. J Am Chem Soc 130:11223–11233. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja803559b
Chen X, Mao SS (2007) Titanium dioxide nanomaterials: synthesis, properties, modifications, and applications. Chem Rev 107:2891–2959. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr0500535
Choi M, Yong K (2014) A facile strategy to fabricate high-quality single crystalline brookite TiO2 nanoarrays and their photoelectrochemical properties. Nanoscale 6:13900–13909. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NR04735D
Choi M, Lim J, Choi W, Kim W, Yong K (2017) Investigating the unrevealed photocatalytic activity and stability of nanostructured Brookite TiO2 film as an environmental photocatalyst. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 19:16252–16260. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b03481
Chowdhary P, Raj PA, Bharagava RN (2018) Environmental pollution and health hazards from distillery wastewater and treatment approaches to combat the environmental threats: a review. Chemosphere 194:229–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.11.163
Eddy DR, Permana MD, Sakti LK, Sheha GAN, Solihudin HS, Takei T, Kumada N, Rahayu I (2023) Heterophase polymorph of tio2 (anatase, rutile, brookite, TiO2 (B)) for efficient photocatalyst: fabrication and activity. Nanomaterials 13:704. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13040704
Han J, He S, Lichtfouse E (2023) Waves of pharmaceutical waste. Environ Chem Lett 21:1251–1255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-022-01491-0
Hu WB, Li LP, Li GS, Tang CL, Sun L (2009) High-quality brookite TiO2 flowers: synthesis, characterization, and dielectric performance. Cryst Growth Des 9:3676–3682. https://doi.org/10.1021/cg9004032
Jiang L, Wang Y, Feng C (2012) Application of photocatalytic technology in environmental safety. Procedia Engin 45:993–997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2012.08.271
Johari ND, Rosli ZM, Juoi JM (2022) Effect of heat treatment temperature on the structural, morphological, optical and water contact angle properties of brookite TiO2 thin film deposited via green sol-gel route for photocatalytic activity. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 33:15143–15155. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08433-0
Kandiel TA, Feldhoff A, Robben L, Dillert R, Bahnemann DW (2010) Tailored titanium dioxide nanomaterials: anatase nanoparticles and brookite nanorods as highly active photocatalysts. Chem Mater 22:2050–2060. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm903472p
Kinsinger NM, Wong A, Li D, Villalobos F, Kisailus D (2010) Nucleation and crystal growth of nanocrystalline anatase and rutile phase TiO2 from a water-soluble precursor. Cryst Growth Des 10(12):5254–5261. https://doi.org/10.1021/cg101105t
Kobayashi M, Petrykin VV, Kakihana M (2007) One-step synthesis of TiO2(B) nanoparticles from a water-soluble titanium complex. Chem Mater 19:5373–5376. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm071370q
Li GH, Gray KA (2007) Preparation of mixed-phase titanium dioxide nanocomposites via solvothermal processing. Chem Mater 19:1143–1146. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm061817f
Li WK, Gong XQ, Lu G, Selloni A (2008) Different reactivities of TiO2 polymorphs: comparative DFT calculations of water and formic acid adsorption at anatase and brookite TiO2 surfaces. J Phys Chem C 112:6594–6596. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp802335h
Morales BA, Novaro O, Lopez T, Sanchez E, Gomez R (1995) Effect of hydrolysis catalyst on the Ti deficiency and crystallite size of sol-gel-TiO2 crystalline phases. J Mater Res 10:2788–2796. https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.1995.2788
Ochiai T, Fujishima A (2012) Photoelectrochemical properties of TiO2 photocatalyst and its applications for environmental purification. J Photochem Photobio C Photochem 4:247–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochemrev.2012.07.001
Paola AD, Bellardita M, Palmisano L (2013) Brookite, the least known TiO2 photocatalyst. Catal 3:36–73. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal3010036
Pigeot-Rémy S, Gregori D, Hazime R, Hérissan A, Guillard C, Ferronato C, Cassaignon S, Colbeau-Justin C, Durupthy O (2019) Size and shape effect on the photocatalytic efficiency of TiO2 brookite. J Mater Sci 54:1213–1225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2924-x
Pottier A, Chane C, Tronc E, Mazerollesb L, Jolivet JP (2001) Synthesis of brookite TiO2 nanoparticles by thermolysis of TiCl4 in strongly acidic aqueous media. J Mater Chem 11:1116–1121. https://doi.org/10.1039/B100435M
Reyes-Coronado D, Rodríguez-Gattorno G, Espinosa-Pesqueira ME, Cab C, de Coss R, Oskam G (2008) Phase-pure TiO2 nanoparticles: anatase, brookite and rutile. Nanotech 19:145605. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/19/14/145605
Rodriguez MM, Peng X, Liu L, Li Y, Andino JM (2012) A Density functional theory and experimental study of co2 interaction with brookite TiO2. J Phys Chem C 116:19755–19764. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp302342t
Tomita K, Petrykin V, Kobayashi M, Shiro M, Yoshimura M, Kakihana M (2006) A water-soluble titanium complex for the selective synthesis of nanocrystalline brookite, rutile, and anatase by a hydrothermal method. Angew Chem Int Edit 45:2378–2381. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200503565
Tompsett GA, Bowmaker GA, Cooney RP, Metson JB, Rodgers KA, Seakins JM (1995) The Raman spectrum of brookite, TiO2 (Pbca, Z = 8). J Raman Spectrosc 26:57–62. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrs.1250260110
Tran HTT, Kosslick H, Ibad MF, Fischer C, Bentrup U, Vuong TH, Nguyen LQ, Schulz A (2017) Photocatalytic performance of highly active brookite in the degradation of hazardous organic compounds compared to anatase and rutile. Appl Catal B Environ 200:647–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.07.017
Tran TTH, Bui TTH, Nguyen TL, Man HN, Tran TKC (2019) Phase-pure brookite TiO2 as a highly active photocatalyst for the degradation of pharmaceutical pollutants. J Elec Materi 48:7846–7861. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-019-07602-y
Vequizo JJM, Matsunaga H, Ishiku T, Kamimura S, Ohno T, Yamakata A (2017) Trapping-induced enhancement of photocatalytic activity on brookite TiO2 powders: comparison with anatase and rutile TiO2 powders. ACS Catal 7:2644–2651. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.7b00131
Wu ZG, Ren ZM, Li LL, LvLC CZP (2020) Hydrothermal synthesis of TiO2 quantum dots with mixed titanium precursors. Sep Purif Technol 251:117328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117328
Xu J, Wu S, Jin J, Peng T (2016) Preparation of brookite TiO2 nanoparticles with small sizes and the improved photovoltaic performance of brookite-based dye-sensitized solar cells. Nanoscale 8:18771–18781. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6NR07185F
Yang MH, Chen PC, Tsai MC, Chen TT, Chang IC, Chiu HT, Lee CY (2014) Anatase and brookite TiO2 with various morphologies and their proposed building block. Cryst Eng Comm 16:441–447. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CE41750F
Zhong L, Haghighat F (2015) Photocatalytic air cleaners and materials technologies-abilities and limitations. Build Environ 9(1):191–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2015.01.033
Funding
The authors have not get any founding or financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by WZ, WL, WY and ZA. The first draft of the manuscript was written by WZ, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Z., Wang, L., Wang, Y. et al. A novel hydrothermal method to synthesize brookite titanium dioxide nanosquares for efficient pollutant degradation. Environ Chem Lett 21, 3071–3076 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-023-01628-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-023-01628-9