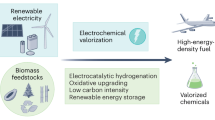
Abstract
The decrease in fossil fuel usage and the projected 28% increase in the global energy demand by 2040 are calling for advanced methods to convert modern biomass into fine chemicals. For instance, biomass-derived aldehydes appear as promising substitutes for the chemical and fuel industries. Here, we review electrochemical upgrading of furfural and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural with a focus on catalysis and selectivity mechanisms. We also present hybrid water electrolysis systems for production of hydrogen and chemicals. We discuss electrochemical oxidation or hydrogenation of furfural and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural using metal oxides, noble metals, transition metal nanoparticles and alloys, and nonoxides. We compare electrochemical processes with combustion, chemical, thermochemical, and biochemical processes for biomass conversion.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou Rjeily M, Gennequin C, Pron H, Abi-Aad E, Randrianalisoa JH (2021) Pyrolysis-catalytic upgrading of bio-oil and pyrolysis-catalytic steam reforming of biogas: a review. Environ Chem Lett 19(4):2825–2872. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-021-01190-2
Alamillo R, Tucker M, Chia M, Pagán-Torres Y, Dumesic J (2012) The selective hydrogenation of biomass-derived 5-hydroxymethylfurfural using heterogeneous catalysts. Green Chem 14(5):1413–1419
Albert WC, Lowy A (1939) The electrochemical reduction of furfural. Trans Electrochem Soc 75(1):367. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.3498392
Andrews E, Lopez-Ruiz JA, Egbert JD, Koh K, Sanyal U, Song M, Li D, Karkamkar AJ, Derewinski MA, Holladay J, Gutiérrez OY, Holladay JD (2020) Performance of base and noble metals for electrocatalytic hydrogenation of bio-oil-derived oxygenated compounds. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 8(11):4407–4418. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b07041
Antonetti C, Licursi D, Fulignati S, Valentini G, Raspolli Galletti AM (2016) New frontiers in the catalytic synthesis of levulinic acid: from sugars to raw and waste biomass as starting feedstock. Catalysts 6(12):196. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6120196
Balakrishnan M, Sacia ER, Bell AT (2012) Etherification and reductive etherification of 5-(hydroxymethyl)furfural: 5-(alkoxymethyl)furfurals and 2,5-bis(alkoxymethyl)furans as potential bio-diesel candidates. Green Chem 14(6):1626–1634. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2GC35102A
Barrett C, Chheda J, Huber G, Dumesic J (2006) Single-reactor process for sequential aldol-condensation and hydrogenation of biomass-derived compounds in water. Appl Catal B 66(1–2):111–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2006.03.001
Bi J, Ying H, Hao J, Li Z (2022) Application of metal chalcogenide-based anodic electrocatalyst toward substituting oxygen evolution reaction in water splitting. Curr Opin Electrochem 33:100963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coelec.2022.100963
Bridgwater AV, Meier D, Radlein D (1999) An overview of fast pyrolysis of biomass. Org Geochem 30(12):1479–1493. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0146-6380(99)00120-5
Buntara T, Noel S, Phua PH, Melián-Cabrera I, de Vries JG, Heeres HJ (2011) Caprolactam from renewable resources: catalytic conversion of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural into caprolactone. Angew Chem 123(31):7221–7225. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201102156
Cao B, Wang S, Hu Y, Abomohra AE-F, Qian L, He Z, Wang Q, Uzoejinwa BB, Esakkimuthu S (2019) Effect of washing with diluted acids on enteromorpha clathrata pyrolysis products: towards enhanced bio-oil from seaweeds. Renew Energy 138:29–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.01.084
Cao Y, Knijff J, Delparish A, d’Angelo MFN, Noёl T (2021) A Divergent paired electrochemical process for the conversion of furfural using a divided-cell flow microreactor. Chemsuschem 14(2):590–594. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.202002833
Chadderdon DJ, Xin L, Qi J, Qiu Y, Krishna P, More KL, Li W (2014) Electrocatalytic oxidation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural to 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid on supported Au and Pd bimetallic nanoparticles. Green Chem 16(8):3778–3786. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4GC00401A
Chang C, Chen W, Chen Y, Chen Y, Chen Y, Ding F, Fan C, Fan HJ, Fan Z, Gong C (2021) Recent progress on two-dimensional materials. Acta Phys-Chim Sin 37(12):2108017. https://doi.org/10.3866/PKU.WHXB202108017
Chen X, Sun W, Xiao N, Yan Y, Liu S (2007) Experimental study for liquid phase selective hydrogenation of furfuryl alcohol to tetrahydrofurfuryl alcohol on supported Ni catalysts. Chem Eng J 126(1):5–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2006.08.019
Chen B, Li X, Rui P, Ye Y, Ye T, Zhou R, Li D, Carter JH, Hutchings GJ (2022a) The reaction pathways of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural conversion in a continuous flow reactor using copper catalysts. Catal Sci Technol 12(9):3016–3027. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CY02197D
Chen C, Zhou Z, Liu J, Zhu B, Hu H, Yang Y, Chen G, Gao M, Zhang J (2022b) Sustainable biomass upgrading coupled with H2 generation over in-situ oxidized Co3O4 electrocatalysts. Appl Catal B 307:121209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2022b.121209
Chum HL, Overend RP (2001) Biomass and renewable fuels. Fuel Process Technol 71(1):187–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-3820(01)00146-1
Coq B, Figuéras F, Moreau C, Moreau P, Warawdekar M (1993) Hydrogenation of substituted acrolein over alumina supported ruthenium catalysts. Catal Lett 22(3):189–195. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00810365
De S, Burange AS, Luque R (2022) Conversion of biomass-derived feedstocks into value-added chemicals over single-atom catalysts. Green Chem 24(6):2267–2286. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1GC04285H
de Luna GS, Sacco A, Hernandez S, Ospitali F, Albonetti S, Fornasari G, Benito P (2022) Insights into the electrochemical reduction of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural at high current densities. Chemsuschem 15(13):e202102504. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.202102504
Deng X, Kang X, Li M, Xiang K, Wang C, Guo Z, Zhang J, Fu X-Z, Luo J-L (2020a) Coupling efficient biomass upgrading with H2 production via bifunctional CuxS@NiCo-LDH core–shell nanoarray electrocatalysts. J Mater Chem 8(3):1138–1146. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9TA06917H
Deng X, Li M, Fan Y, Wang L, Fu X-Z, Luo J-L (2020b) Constructing multifunctional ‘Nanoplatelet-on-Nanoarray’ electrocatalyst with unprecedented activity towards novel selective organic oxidation reactions to boost hydrogen production. Appl Catal B 278:119339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2020b.119339
Deng X, Xu G-Y, Zhang Y-J, Wang L, Zhang J, Li J-F, Fu X-Z, Luo J-L (2021) Understanding the roles of electrogenerated Co3+ and Co4+ in selectivity-tuned 5-hydroxymethylfurfural oxidation. Angew Chem Int Ed 60(37):20535–20542. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202108955
Dhawan MS, Yadav GD, Calabrese Barton S (2021) Zinc-electrocatalyzed hydrogenation of furfural in near-neutral electrolytes. Sustain Energy Fuels 5(11):2972–2984. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1SE00221J
Dick GR, Frankhouser AD, Banerjee A, Kanan MW (2017) A scalable carboxylation route to furan-2,5-dicarboxylic acid. Green Chem 19(13):2966–2972. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7GC01059A
Dixit RJ, Bhattacharyya K, Ramani VK, Basu S (2021) Electrocatalytic hydrogenation of furfural using non-noble-metal electrocatalysts in alkaline medium. Green Chem 23(11):4201–4212. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1GC00579K
Du L, Sun Y, You B (2021) Hybrid water electrolysis: replacing oxygen evolution reaction for energy-efficient hydrogen production and beyond. Mater Rep Energy 1(1):100004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matre.2020.12.001
Ebhodaghe SO, Imanah OE, Ndibe H (2022) Biofuels from microalgae biomass: a review of conversion processes and procedures. Arab J Chem 15(2):103591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2021.103591
Fu Z, Wang Z, Lin W, Song W, Li S (2017) High efficient conversion of furfural to 2-methylfuran over Ni-Cu/Al2O3 catalyst with formic acid as a hydrogen donor. Appl Catal Gen 547:248–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2017.09.011
Gao L, Liu Z, Ma J, Zhong L, Song Z, Xu J, Gan S, Han D, Niu L (2020) NiSe@NiOx core-shell nanowires as a non-precious electrocatalyst for upgrading 5-hydroxymethylfurfural into 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid. Appl Catal Environ 261:118235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118235
Ge R, Wang Y, Li Z, Xu M, Xu S-M, Zhou H, Ji K, Chen F, Zhou J, Duan H (2022) Selective electrooxidation of biomass-derived alcohols to aldehydes in a neutral medium: promoted water dissociation over a nickel-oxide-supported ruthenium single-atom catalyst. Angew Chem Int Ed 61(19):e202200211. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202200211
Gharbi-Benarous J, Morales-Rios MS, Dana G (1984) Rearrangement of ethylenic. alpha.-diols (3-butene-1, 2-diols) to ethylenic. alpha.-diols (1-butene-3, 4-diols). J Org Chem 49(11):2039–2040. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo00185a050
Giudicianni P, Gargiulo V, Grottola CM, Alfè M, Ragucci R (2018) Effect of alkali metal ions presence on the products of xylan steam assisted slow pyrolysis. Fuel 216:36–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2017.11.150
Gupta K, Rai RK, Singh SK (2018) Metal catalysts for the efficient transformation of biomass-derived hmf and furfural to value added chemicals. ChemCatChem 10(11):2326–2349. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201701754
Hidalgo-Carrillo J, Marinas A, Urbano FJ (2018) Chemistry of furfural and furanic derivatives. Furfural. https://doi.org/10.1142/9781786344878_0001
Hronec M, Fulajtarová K (2012) Selective transformation of furfural to cyclopentanone. Catal Commun 24:100–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2012.03.020
Hu X, Gholizadeh M (2019) Biomass pyrolysis: a review of the process development and challenges from initial researches up to the commercialisation stage. J Energy Chem 39:109–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jechem.2019.01.024
Hu K, Zhang M, Liu B, Yang Z, Li R, Yan K (2021) Efficient electrochemical oxidation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural to 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid using the facilely synthesized 3D porous WO3/Ni electrode. Mol Catal 504:111459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcat.2021.111459
Huang W, Li H, Zhu B, Feng Y, Wang S, Zhang S (2007) Selective hydrogenation of furfural to furfuryl alcohol over catalysts prepared via sonochemistry. Ultrason Sonochem 14(1):67–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2006.03.002
Isahak WNRW, Hisham MW, Yarmo MA, T-yY H (2012) A review on bio-oil production from biomass by using pyrolysis method. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 16(8):5910–5923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2012.05.039
Jiang N, You B, Boonstra R, Terrero Rodriguez IM, Sun Y (2016) Integrating electrocatalytic 5-hydroxymethylfurfural oxidation and hydrogen production via Co–P-derived electrocatalysts. ACS Energy Lett 1(2):386–390. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsenergylett.6b00214
Jung S, Biddinger EJ (2018) Controlling competitive side reactions in the electrochemical upgrading of furfural to biofuel. Energy Technol 6(7):1370–1379. https://doi.org/10.1002/ente.201800216
Kan T, Strezov V, Evans TJ (2016) Lignocellulosic biomass pyrolysis: a review of product properties and effects of pyrolysis parameters. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 57:1126–1140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.12.185
Kar S, Zhou Q-Q, Ben-David Y, Milstein D (2022) Catalytic furfural/5-hydroxymethyl furfural oxidation to furoic acid/furan-2,5-dicarboxylic Acid with H2 production using alkaline water as the formal oxidant. J Am Chem Soc 144(3):1288–1295. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.1c10908
Khairi S, Hara T, Ichikuni N, Shimazu S (2012) Highly efficient and selective hydrogenation of unsaturated carbonyl compounds using Ni–Sn alloy catalysts. Catal Sci Technol 2(10):2139–2145. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CY20216F
Kijeński J, Winiarek P, Paryjczak T, Lewicki A, Mikołajska A (2002) Platinum deposited on monolayer supports in selective hydrogenation of furfural to furfuryl alcohol. Appl Catal A 233(1–2):171–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-860X(02)00140-0
Kim JE, Choi S, Balamurugan M, Jang JH, Nam KT (2020) Electrochemical C–N Bond formation for sustainable amine synthesis. Trends Chem 2(11):1004–1019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trechm.2020.09.003
Kloth R, Vasilyev DV, Mayrhofer KJJ, Katsounaros I (2021) Electroreductive 5-hydroxymethylfurfural dimerization on carbon electrodes. Chemsuschem 14(23):5245–5253. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.202101575
Kong Q-S, Li X-L, Xu H-J, Fu Y (2020) Conversion of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural to chemicals: a review of catalytic routes and product applications. Fuel Process Technol 209:106528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2020.106528
Kubota SR, Choi K-S (2018) Electrochemical valorization of furfural to maleic acid. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6(8):9596–9600. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b02698
Lan X, Wang T (2020) Highly selective catalysts for the hydrogenation of unsaturated aldehydes: a review. ACS Catal 10(4):2764–2790. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.9b04331
Li K, Sun Y (2018) Electrocatalytic upgrading of biomass-derived intermediate compounds to value-added products. Chem Eur J 24(69):18258–18270. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201803319
Li X, Jia P, Wang T (2016) Furfural: a promising platform compound for sustainable production of C4 and C5 chemicals. ACS Catal 6(11):7621–7640. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.6b01838
Li Y, Dang Z, Gao P (2021) High-efficiency electrolysis of biomass and its derivatives: advances in anodic oxidation reaction mechanism and transition metal-based electrocatalysts. Nano Sel 2(5):847–864. https://doi.org/10.1002/nano.202000227
Li X, Tong Z, Zhu S, Deng Q, Chen S, Wang J, Zeng Z, Zhang Y, Zou J-J, Deng S (2022) Water-mediated hydrogen spillover accelerates hydrogenative ring-rearrangement of furfurals to cyclic compounds. J Catal 405:363–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2021.12.010
Liang S, Pan L, Thomas T, Zhu B, Chen C, Zhang J, Shen H, Liu J, Yang M (2021) Ni3N-V2O3 enables highly efficient 5-(Hydroxymethyl) furfural oxidation enabling membrane free hydrogen production. Chem Eng J 415:128864. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.128864
Lin C, Zhou J, Zheng Z, Chen J (2022) An efficient approach to biomass-based tertiary amines by direct and consecutive reductive amination of furfural. J Catal 410:164–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2022.04.016
Liñares GEG, Nudelman NS (2003) Reactions of lithiated aromatic heterocycles with carbon monoxide. J Phys Org Chem 16(8):569–576. https://doi.org/10.1002/poc.661
Liu D, Chen EYX (2013) Diesel and alkane fuels from biomass by organocatalysis and metal-acid tandem catalysis. Chemsuschem 6(12):2236–2239. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201300476
Liu S, Amada Y, Tamura M, Nakagawa Y, Tomishige K (2014) One-pot selective conversion of furfural into 1, 5-pentanediol over a Pd-added Ir–ReO x/SiO2 bifunctional catalyst. Green Chem 16(2):617–626. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3GC41335G
Liu L, Liu H, Huang W, He Y, Zhang W, Wang C, Lin H (2017) Mechanism and kinetics of the electrocatalytic hydrogenation of furfural to furfuryl alcohol. J Electr Chem 804:248–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2017.09.021
Liu H, Lee T-H, Chen Y, Cochran EW, Li W (2021) Paired electrolysis of 5-(hydroxymethyl)furfural in flow cells with a high-performance oxide-derived silver cathode. Green Chem 23(14):5056–5063. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1GC00988E
Lu Y, Liu T, Huang Y-C, Zhou L, Li Y, Chen W, Yang L, Zhou B, Wu Y, Kong Z, Huang Z, Li Y, Dong C-L, Wang S, Zou Y (2022) Integrated catalytic sites for highly efficient electrochemical oxidation of the aldehyde and hydroxyl groups in 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. ACS Catal 12(7):4242–4251. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.2c00174
Malolan R, Gopinath KP, Vo D-VN, Jayaraman RS, Adithya S, Ajay PS, Arun J (2021) Green ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents for desulphurization, denitrification, biomass, biodiesel, bioethanol and hydrogen fuels: a review. Environ Chem Lett 19(2):1001–1023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-01113-7
Mariscal R, Maireles-Torres P, Ojeda M, Sádaba I, López Granados M (2016) Furfural: a renewable and versatile platform molecule for the synthesis of chemicals and fuels. Energy Environ Sci 9(4):1144–1189. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5EE02666K
Mathew AK, Parameshwaran B, Sukumaran RK, Pandey A (2016) An evaluation of dilute acid and ammonia fiber explosion pretreatment for cellulosic ethanol production. Biores Technol 199:13–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.08.121
Maxwell I (1987) Zeolite catalysis in hydroprocessing technology. Catal Today 1(4):385–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/0920-5861(87)80006-8
May AS, Biddinger EJ (2020) Strategies to control electrochemical hydrogenation and hydrogenolysis of furfural and minimize undesired side reactions. ACS Catal 10(5):3212–3221. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.9b05531
Merlo AB, Vetere V, Ruggera JF, Casella ML (2009) Bimetallic PtSn catalyst for the selective hydrogenation of furfural to furfuryl alcohol in liquid-phase. Catal Commun 10(13):1665–1669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2009.05.005
Mitsudome T, Mikami Y, Matoba M, Mizugaki T, Jitsukawa K, Kaneda K (2012) Design of a silver–cerium dioxide core–shell nanocomposite catalyst for chemoselective reduction reactions. Angew Chem Int Ed 51(1):136–139. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201106244
Muir M, Molina DL, Islam A, Abdel-Rahman MK, Trenary M (2020) Selective hydrogenation of acrolein on a Pd/Ag(111) single-atom alloy surface. J Phys Chem C 124(44):24271–24278. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c08094
Musella E, Gualandi I, Scavetta E, Rivalta A, Venuti E, Christian M, Morandi V, Mullaliu A, Giorgetti M, Tonelli D (2019) Newly developed electrochemical synthesis of Co-based layered double hydroxides: toward noble metal-free electro-catalysis. J Mater Chem A 7(18):11241–11249. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TA11812D
Nagaraja B, Padmasri A, Raju BD, Rao KR (2007) Vapor phase selective hydrogenation of furfural to furfuryl alcohol over Cu–MgO coprecipitated catalysts. J Mol Catal Chem 265(1–2):90–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2006.09.037
Naik SN, Goud VV, Rout PK, Dalai AK (2010) Production of first and second generation biofuels: a comprehensive review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 14(2):578–597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2009.10.003
Nakagawa Y, Tomishige K (2010) Total hydrogenation of furan derivatives over silica-supported Ni–Pd alloy catalyst. Catal Commun 12(3):154–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2010.09.003
Nakagawa Y, Tomishige K (2012) Production of 1,5-pentanediol from biomass via furfural and tetrahydrofurfuryl alcohol. Catal Today 195(1):136–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2012.04.048
Nakagawa Y, Tamura M, Tomishige K (2013) Catalytic reduction of biomass-derived furanic compounds with hydrogen. ACS Catal 3(12):2655–2668. https://doi.org/10.1021/cs400616p
Nakagawa Y, Takada K, Tamura M, Tomishige K (2014) Total hydrogenation of furfural and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural over supported Pd–Ir alloy catalyst. ACS Catal 4(8):2718–2726. https://doi.org/10.1021/cs500620b
Nam D-H, Taitt BJ, Choi K-S (2018) Copper-based catalytic anodes to produce 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid, a biomass-derived alternative to terephthalic acid. ACS Catal 8(2):1197–1206. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.7b03152
Niu H, Luo J, Li C, Wang B, Liang C (2019) Transfer Hydrogenation of biomass-derived furfural to 2-methylfuran over CuZnAl catalysts. Ind Eng Chem Res 58(16):6298–6308. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.9b00408
Ohyama J, Sato T, Yamamoto Y, Arai S, Satsuma A (2013) Size specifically high activity of Ru nanoparticles for hydrogen oxidation reaction in alkaline electrolyte. J Am Chem Soc 135(21):8016–8021. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja4021638
Ordomsky VV, Schouten J, Van der Schaaf J, Nijhuis T (2013) Biphasic single-reactor process for dehydration of xylose and hydrogenation of produced furfural. Appl Catal A 451:6–13
Osman AI, Mehta N, Elgarahy AM, Al-Hinai A, AaH A-M, Rooney DW (2021) Conversion of biomass to biofuels and life cycle assessment: a review. Environ Chem Lett 19(6):4075–4118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-021-01273-0
Pang X, Bai H, Zhao H, Fan W, Shi W (2022) Efficient electrocatalytic oxidation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural coupled with 4-nitrophenol hydrogenation in a water system. ACS Catal 12(2):1545–1557. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.1c04880
Parpot P, Bettencourt AP, Chamoulaud G, Kokoh KB, Belgsir EM (2004) Electrochemical investigations of the oxidation–reduction of furfural in aqueous medium: application to electrosynthesis. Electrochim Acta 49(3):397–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2003.08.021
Paudel SR, Banjara SP, Choi OK, Park KY, Kim YM, Lee JW (2017) Pretreatment of agricultural biomass for anaerobic digestion: current state and challenges. Bioresour Technol 245:1194–1205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.08.182
Prasad RK, Chatterjee S, Mazumder PB, Gupta SK, Sharma S, Vairale MG, Datta S, Dwivedi SK, Gupta DK (2019) Bioethanol production from waste lignocelluloses: a review on microbial degradation potential. Chemosphere 231:588–606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.05.142
Qin Q, Heil T, Schmidt J, Schmallegger M, Gescheidt G, Antonietti M, Oschatz M (2019) Electrochemical fixation of nitrogen and its coupling with biomass valorization with a strongly adsorbing and defect optimized boron–carbon–nitrogen catalyst. ACS Appl Energy Mater 2(11):8359–8365. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.9b01852
Rao RS, Baker RTK, Vannice MA (1999) Furfural hydrogenation over carbon-supported copper. Catal Lett 60(1):51–57. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019090520407
Reza MT, Lynam JG, Uddin MH, Coronella CJ (2013) Hydrothermal carbonization: fate of inorganics. Biomass Bioenerg 49:86–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2012.12.004
Román-Leshkov Y, Barrett CJ, Liu ZY, Dumesic JA (2007) Production of dimethylfuran for liquid fuels from biomass-derived carbohydrates. Nature 447(7147):982–985. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05923
Roylance JJ, Kim TW, Choi K-S (2016) Efficient and selective electrochemical and photoelectrochemical reduction of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural to 2,5-bis(hydroxymethyl)furan using water as the hydrogen source. ACS Catal 6(3):1840–1847. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.5b02586
Ruiz JA, Juárez M, Morales M, Muñoz P, Mendívil M (2013) Biomass gasification for electricity generation: review of current technology barriers. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 18:174–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2012.10.021
Sarwer A, Hamed SM, Osman AI, Jamil F, AaH A-M, Alhajeri NS, Rooney DW (2022) Algal biomass valorization for biofuel production and carbon sequestration: a review. Environ Chem Lett 20(5):2797–2851. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-022-01458-1
Seo G, Chon H (1981) Hydrogenation of furfural over copper-containing catalysts. J Catal 67(2):424–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9517(81)90302-X
Shao Y, Hu X, Zhang Z, Sun K, Gao G, Wei T, Zhang S, Hu S, Xiang J, Wang Y (2019) Direct conversion of furfural to levulinic acid/ester in dimethoxymethane: understanding the mechanism for polymerization. Green Energy Environ 4(4):400–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gee.2018.10.002
Sheng H, Lobo RF (2016) Iron-promotion of silica-supported copper catalysts for furfural hydrodeoxygenation. ChemCatChem 8(21):3402–3408. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201600540
Sitthisa S, An W, Resasco DE (2011a) Selective conversion of furfural to methylfuran over silica-supported NiFe bimetallic catalysts. J Catal 284(1):90–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2011.09.005
Sitthisa S, Pham T, Prasomsri T, Sooknoi T, Mallinson RG, Resasco DE (2011b) Conversion of furfural and 2-methylpentanal on Pd/SiO2 and Pd–Cu/SiO2 catalysts. J Catal 280(1):17–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2011.02.006
Slak J, Pomeroy B, Kostyniuk A, Grilc M, Likozar B (2022) A review of bio-refining process intensification in catalytic conversion reactions, separations and purifications of hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) and furfural. Chem Eng J 429:132325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.132325
Song Y, Li Z, Fan K, Ren Z, Xie W, Yang Y, Shao M, Wei M (2021) Ultrathin layered double hydroxides nanosheets array towards efficient electrooxidation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural coupled with hydrogen generation. Appl Catal B Environ 299:120669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.120669
Sovacool BK, Heffron RJ, McCauley D, Goldthau A (2016) Energy decisions reframed as justice and ethical concerns. Nat Energy 1(5):16024. https://doi.org/10.1038/nenergy.2016.24
Stirling RJ, Snape CE, Meredith W (2018) The impact of hydrothermal carbonisation on the char reactivity of biomass. Fuel Process Technol 177:152–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2018.04.023
Sun C, Zhang D, Zhao Y, Song C, Wang D (2022a) In-suit growth of NiS quantum dots embedded in ultra-thin N, O, S-tri-doped carbon porous nanosheets on carbon cloth for high-efficient HMF oxidation coupling hydrogen evolution. Colloids Surf A 650:129597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022a.129597
Sun H, Kim H, Song S, Jung W (2022b) Copper foam-derived electrodes as efficient electrocatalysts for conventional and hybrid water electrolysis. Mater Rep Energy 2(2):100092. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matre.2022b.100092
Sundaram V, Muthukumarappan K, Kamireddy SR (2015) Effect of ammonia fiber expansion (AFEX™) pretreatment on compression behavior of corn stover, prairie cord grass and switchgrass. Ind Crops Prod 74:45–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.04.027
Taitt BJ, Nam D-H, Choi K-S (2019) A comparative study of nickel, cobalt, and iron oxyhydroxide anodes for the electrochemical oxidation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural to 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid. ACS Catal 9(1):660–670. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.8b04003
Tamura M, Tokonami K, Nakagawa Y, Tomishige K (2013) Rapid synthesis of unsaturated alcohols under mild conditions by highly selective hydrogenation. Chem Commun 49(63):7034–7036. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CC41526K
Tan J, Zhang W, Shu Y, Lu H, Tang Y, Gao Q (2021) Interlayer engineering of molybdenum disulfide toward efficient electrocatalytic hydrogenation. Sci Bull 66(10):1003–1012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2020.11.002
Theerthagiri J, Park J, Das HT, Rahamathulla N, Cardoso ESF, Murthy AP, Maia G, Vo DVN, Choi MY (2022) Electrocatalytic conversion of nitrate waste into ammonia: a review. Environ Chem Lett 20(5):2929–2949. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-022-01469-y
Tuokko S, Pihko PM, Honkala K (2016) First principles calculations for hydrogenation of acrolein on pd and pt: chemoselectivity depends on steric effects on the surface. Angew Chem Int Ed 55(5):1670–1674. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201507631
van Putten R-J, van der Waal JC, de Jong E, Rasrendra CB, Heeres HJ, de Vries JG (2013) Hydroxymethylfurfural, a versatile platform chemical made from renewable resources. Chem Rev 113(3):1499–1597. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr300182k
Vasco-Correa J, Ge X, Li Y (2016) Biological pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. Biomass Fract Technol Lignocellul Feedstock Based Biorefinery. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-802323-5.00024-4
Wang A, Zhang T (2013) One-pot conversion of cellulose to ethylene glycol with multifunctional tungsten-based catalysts. Acc Chem Res 46(7):1377–1386. https://doi.org/10.1021/ar3002156
Wang D, Osmundsen CM, Taarning E, Dumesic JA (2013) Selective production of aromatics from alkylfurans over solid acid catalysts. ChemCatChem 5(7):2044–2050. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201200757
Wang G, Dai Y, Yang H, Xiong Q, Wang K, Zhou J, Li Y, Wang S (2020) A review of recent advances in biomass pyrolysis. Energy Fuels 34(12):15557–15578. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.0c03107
Wang C, Bongard H-J, Weidenthaler C, Wu Y, Schüth F (2022) Design and application of a high-surface-area mesoporous δ-MnO2 electrocatalyst for biomass oxidative valorization. Chem Mater 34(7):3123–3132. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.1c04223
Wegenhart BL, Liu S, Thom M, Stanley D, Abu-Omar MM (2012) Solvent-free methods for making acetals derived from glycerol and furfural and their use as a biodiesel fuel component. ACS Catal 2(12):2524–2530. https://doi.org/10.1021/cs300562e
West RM, Liu ZY, Peter M, Dumesic JA (2008) Liquid alkanes with targeted molecular weights from biomass-derived carbohydrates. Chemsuschem 1(5):417–424. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.200800001
Woo J, Moon BC, Lee U, Oh H-S, Chae KH, Jun Y, Min BK, Lee DK (2022) Collaborative electrochemical oxidation of the alcohol and aldehyde groups of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural by NiOOH and Cu(OH)2 for superior 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid production. ACS Catal 12(7):4078–4091. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.1c05341
Wu J, Shen Y, Liu C, Wang H, Geng C, Zhang Z (2005) Vapor phase hydrogenation of furfural to furfuryl alcohol over environmentally friendly Cu–Ca/SiO2 catalyst. Catal Commun 6(9):633–637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2005.06.009
Wu L, Moteki T, Gokhale Amit A, Flaherty David W, Toste FD (2016) Production of fuels and chemicals from biomass: condensation reactions and beyond. Chem 1(1):32–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chempr.2016.05.002
Wu H, Song J, Liu H, Xie Z, Xie C, Hu Y, Huang X, Hua M, Han B (2019) An electrocatalytic route for transformation of biomass-derived furfural into 5-hydroxy-2(5H)-furanone. Chem Sci 10(17):4692–4698. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9SC00322C
Xia H, Xu S, Hu H, An J, Li C (2018) Efficient conversion of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural to high-value chemicals by chemo- and bio-catalysis. RSC Adv 8(54):30875–30886. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA05308A
Xia D, Yu H, Li H, Huang P, Li Q, Wang Y (2022) Carbon-based and carbon-supported nanomaterials for the catalytic conversion of biomass: a review. Environ Chem Lett 20(3):1719–1744. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-022-01402-3
Xie Y, Zhou Z, Yang N, Zhao G (2021) An overall reaction integrated with highly selective oxidation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural and efficient hydrogen evolution. Adv Funct Mater 31(34):2102886. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202102886
Xinghua Z, Tiejun W, Longlong M, Chuangzhi W (2010) Aqueous-phase catalytic process for production of pentane from furfural over nickel-based catalysts. Fuel 89(10):2697–2702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2010.05.043
Xu Y, Zhang B (2019) Recent advances in electrochemical hydrogen production from water assisted by alternative oxidation reactions. ChemElectroChem 6(13):3214–3226. https://doi.org/10.1002/celc.201900675
Xu C, Paone E, Rodríguez-Padrón D, Luque R, Mauriello F (2020) Recent catalytic routes for the preparation and the upgrading of biomass derived furfural and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. Chem Soc Rev 49(13):4273–4306. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CS00041H
Yang G, Jiao Y, Yan H, Xie Y, Wu A, Dong X, Guo D, Tian C, Fu H (2020) Interfacial engineering of MoO2-FeP heterojunction for highly efficient hydrogen evolution coupled with biomass electrooxidation. Adv Mater 32(17):2000455. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202000455
Yang C, Wang C, Zhou L, Duan W, Song Y, Zhang F, Zhen Y, Zhang J, Bao W, Lu Y, Wang D, Fu F (2021) Refining d-band center in Ni0.85Se by Mo doping: a strategy for boosting hydrogen generation via coupling electrocatalytic oxidation 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. Chem Eng J 422:130125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.130125
Yang Z, Chou X, Kan H, Xiao Z, Ding Y (2022) Nanoporous copper catalysts for the fluidized electrocatalytic hydrogenation of furfural to furfuryl alcohol. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 10(22):7418–7425. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.2c02360
You B, Sun Y (2018) Innovative strategies for electrocatalytic water splitting. Acc Chem Res 51(7):1571–1580. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.accounts.8b00002
You B, Liu X, Jiang N, Sun Y (2016) A general strategy for decoupled hydrogen production from water splitting by integrating oxidative biomass valorization. J Am Chem Soc 138(41):13639–13646. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.6b07127
Yuan X, Lee K, Bender MT, Schmidt JR, Choi K-S (2022) Mechanistic differences between electrochemical hydrogenation and hydrogenolysis of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural and their pH dependence. Chemsuschem 15(17):e202200952. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.202200952
Zang H, Wang K, Zhang M, Xie R, Wang L, Chen EYX (2018) Catalytic coupling of biomass-derived aldehydes into intermediates for biofuels and materials. Catal Sci Technol 8(7):1777–1798. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CY02221B
Zhang Y, Kornienko N (2022) Conductive metal-organic frameworks bearing M−O4 active sites as highly active biomass valorization electrocatalysts. Chemsuschem 15(13):e202101587. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.202101587
Zhang Z, Bi P, Jiang P, Fan M, Deng S, Zhai Q, Li Q (2015) Production of gasoline fraction from bio-oil under atmospheric conditions by an integrated catalytic transformation process. Energy 90:1922–1930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2015.07.009
Zhang N, Zou Y, Tao L, Chen W, Zhou L, Liu Z, Zhou B, Huang G, Lin H, Wang S (2019a) Electrochemical oxidation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural on nickel nitride/carbon nanosheets: reaction pathway determined by in situ sum frequency generation vibrational spectroscopy. Angew Chem Int Ed 58(44):15895–15903. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.2019a08722
Zhang Y-R, Wang B-X, Qin L, Li Q, Fan Y-M (2019b) A non-noble bimetallic alloy in the highly selective electrochemical synthesis of the biofuel 2,5-dimethylfuran from 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. Green Chem 21(5):1108–1113. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8GC03689F
Zheng H-Y, Zhu Y-L, Teng B-T, Bai Z-Q, Zhang C-H, Xiang H-W, Li Y-W (2006) Towards understanding the reaction pathway in vapour phase hydrogenation of furfural to 2-methylfuran. J Mol Catal A Chem 246(1–2):18–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2005.10.003
Zheng R, Zhao C, Xiong J, Teng X, Chen W, Hu Z, Chen Z (2021) Construction of a hierarchically structured, NiCo–Cu-based trifunctional electrocatalyst for efficient overall water splitting and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural oxidation. Sustain Energy Fuels 5(16):4023–4031. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1SE00697E
Zhou Z, Xie Y-n, Sun L, Wang Z, Wang W, Jiang L, Tao X, Li L, Li X-H, Zhao G (2022) Strain-induced in situ formation of NiOOH species on CoCo bond for selective electrooxidation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural and efficient hydrogen production. Appl Catal B Environ 305:121072. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2022.121072
Zhu Y, Shi J, Li Y, Lu Y, Zhou B, Wang S, Zou Y (2022) Understanding the surface segregation behavior of bimetallic CoCu toward HMF oxidation reaction. J Energy Chem 74:85–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jechem.2022.05.041
Zhuang X, Liu J, Zhong S, Ma L (2022) Selective catalysis for the reductive amination of furfural toward furfurylamine by graphene-co-shelled cobalt nanoparticles. Green Chem 24(1):271–284. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1GC03578A
Zou H, Chen J (2022) Efficient and selective approach to biomass-based amine by reductive amination of furfural using Ru catalyst. Appl Catal B Environ 309:121262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2022.121262
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Korea Basic Science Institute (National Research Facilities and Equipment Center) grant funded by the Ministry of Education (No. 2019R1A6C1010042, 2021R1A6C103A427). The authors acknowledge the financial support from the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), (2022R1A2C2010686, 2022R1A4A3033528, 2019H1D3A1A01071209, 2021R1I1A1A01060380). Prof. G.M acknowledges the Brazilian foundations Fundect-MS (71/027.195/2022 and #71/039.199/2022) and CAPES-PrInt (88881.311799/2018-01) and Dr. A.P.M acknowledge Department of Science and Technology, India (SERB No. CRG/2022/005972).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Theerthagiri, J., Karuppasamy, K., Park, J. et al. Electrochemical conversion of biomass-derived aldehydes into fine chemicals and hydrogen: A review. Environ Chem Lett 21, 1555–1583 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-022-01543-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-022-01543-5