Abstract
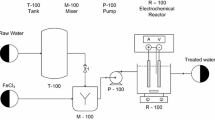
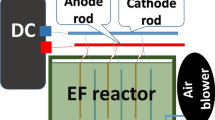
The electrocoagulation studies of distillery spentwash using copper anodes were utilized to demonstrate the usefulness of Box–Behnken experimental design of response surface analysis to derive a statistical model and the optimum parameters for color removal. The current intensity (1.5 A), dilution (10%) and time of electrolysis (5 h) had been found to be the optimum conditions for maximum 77.11% color removal. The actual color removal at optimized conditions was found to be 78.26%, which is to the predicted response using response surface methodology. The energy consumption and current efficiency were determined from reduction in chemical oxygen demand.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal CS, Pandey GS (1994) Soil pollution by spentwash discharge: depletion of manganese (II) and impairment of its oxidation. J Environ Biol 15:49–53
Annadurai G, Sheeja RY, Mathalai balan, Murugesan T, Srinivasamoorthy VR (1999) Factorial design of experiments in the determination of adsorption equilibrium constants for basic methylene blue using biopolymer. Bioprocess Eng 20:37–43. doi:10.1007/s004490050557
Box GEP, Behnken DW (1960) Some new three level design for the study of quantitative variables. Technometrics 2:455–475. doi:10.2307/1266454
Daewan P, Dowan C, Jeh BL (2001) Design parameters for an electrochemical cell with porous electrode to treat metal ion solution. Water Res 35(1):57–68. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00253-0
Ferreira SLC, Bruns RE, Ferreira HS, Matos GD, David JM, Brandao GC, Silva EGP, Portugal LA, Dos Reis PS, Souza AS, Dos Santos WNL (2007) Box–Behnken design: an alternative for the optimization of analytical methods. Anal Chim Acta 597:179–186. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2007.07.011
FitzGibbon FJ, Nigam P, Singh D, Marchant R (1995) Biological treatment of distillery waste for pollution remediation. J Basic Microbiol 35:293–301. doi:10.1002/jobm.3620350504
Kannabiran B, Prakasam A (1993) Effect of distillery effluent on seed germination, seedling growth and pigment content of Bigna Mungo Hepper (C.V.T.9). Geobios-Lyon 20:108–112
Kumar V, Wati L, Nigam P, Banat IM, Yadav BS, Singh D, Marchant R (1998) Decolorization and biodegradation of anaerobically digested sugarcane molasses spent was effluent from biomethanation plants by white rot fungi. Process Biochem 33(1):83–88. doi:10.1016/S0032-9592(97)00047-2
Lin SH, Peng CF (1994) Treatment of textile wastewater by electro chemical method. Water Res 28(2):277–282. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(94)90264-X
Ofir E, Oren Y, Adin A (2007) Comparing pretreatment by iron of electro-flocculation and chemical flocculation. Desalination 204:87–93. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2006.01.037
Piyaareetham P, Shenchunthichai K, Hunsom M (2006) Application of electro-oxidation processes for treating concentrated wastewater from distillery industry with a voluminous electrode. Water Res 40(15):2857–2864. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2006.05.025
Ravikumar K, Krishnan S, Ramalingam S, Balu K (2007) Optimization of process variables by application of response surface methodology for dye removal using a novel adsorbent. Dyes Pigments 72(1):66–74. doi:10.1016/j.dyepig.2005.07.018
Tennakone K, Tilakaratne CTK, Kottegoda IRM (1995) Photo catalytic degradation of organic contaminants in water with TiO2 supported on polythene films. J Photochem Photobiol 87:177–179. doi:10.1016/1010-6030(94)03980-9
Wilcock A, Brewster M, Tincher W (1992) Using electrochemical technology to treat textile wastewater: three case studies. American Dyestuff Reporter, pp 15–22
Zor S, Yazici B, Erbil M, Galip H (1998) The electro chemical degradation of linear alkyl benzene sulfonate on platinum electrode. Water Res 32(3):579–586. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(97)00305-9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krishna Prasad, R. Degradation of biopolymeric pigments in distillery spentwash by electrocoagulation using copper anodes: statistical and canonical analysis. Environ Chem Lett 8, 149–155 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-009-0202-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-009-0202-5