Abstract
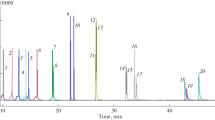
Pyrolysis coupled with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (Py–GC–MS) has been previously proved to be an appropriate tool for the screening of organic contaminants in sediments. In this work the double-shoot pyrolysis technique has been applied to assess the contamination degree of sediment samples from Castro Marim Natural Park (South Portugal) and the Ria of Huelva (SW Spain). Compounds released both by thermodesorption at sub-pyrolysis temperatures (250–280°C) and subsequent pyrolysis (300–500°C) revealed information on the origin of the sedimentary organic matter and the occurrence of organic contamination in the sediments. Thermal desorption was found to be effective in releasing organic contaminants from spiked samples. However, in real sediments samples, higher pyrolysis temperatures (>300°C) were necessary to detect the occurrence of organic contaminants. Particularly polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and linear alkylbenzenes (LABs) were detected in variable proportions in most sediment samples.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Derenne S, Largeau C, Casadevall E, Berkaloff C, Rousseau B (1991) Chemical evidence of Kerogen fromation in souce rocks and oil shales via selective preservation of thin resistant outer walls of microalgae: origin of ultralaminae. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 55:1041–1050. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(91)90162-X
Faure P, Vilmin F, Michels R, Jarde E, Mansuy L, Elie M et al (2002) Application of thermodesorption and pyrolysis-GC-AED to the analysis of river sediments and sewage sludges for environmental purpose. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 62:297–318. doi:10.1016/S0165-2370(01)00127-9
Galleti GC (1991) Py-GC-ion trap detection of sorghum grain polyphenols (syn vegetable tannius): preliminary results. Fuel Chem Div ACS 36:691–702
Gonzalez-Perez JA, de Andres JR, Clemente L, Martín JA, González-Vila FJ (2008) Organic carbon and environmental quality of riverine and off-shore sediments from the Gulf of Cadiz, Spain. Environ Chem Lett 6:41–46. doi:10.1007/s10311-007-0107-0
González-Vila FJ, Polvillo O, Boski T, Moura D, de Andrés JR (2003) Biomarker patterns in a time-resolved holocene/terminal pleistocene sedimentary sequence from the Guadiana river estuarine area (SW Portugal/Spain border). Org Geochem 34:1601–1613. doi:10.1016/j.orggeochem.2003.08.006
Kronimus A, Schwarbauer J, Ricking M (2006) Analysis of non-extractable DDT-related compounds in riverine sediments of the Teltow canal Berlin, by pyrolysis and thermochemolysis. Environ Sci Technol 40:5882–5890. doi:10.1021/es0605568
Kruge MA, Mukhopadhyay PK, Lewis CFM (1998) A molecular evaluation of contaminants and natural organic matter in bottom sediments from western Lake Ontario. Org Geochem 29:1797–1812. doi:10.1016/S0146-6380(98)00105-3
Medina-Vera M (1996) Pyrolysis-gas chromatography/mass spectrometry used for screening aromatic hydrocarbons by desorption from sediment. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 36:27–33. doi:10.1016/0165-2370(95)00924-8
Meyers PA, Zsolnay A, Eadie BJ (1995) Pyrolysis-mass spectrometry of sediment trap organic matter from Lake Michigan. Chem Spec Bioavail 7:33–37
Peulvé S, de Leeuw JW, Sicre MA, Bass M, Saliot A (1996) Characterization of macromolecular organic matter in sediment traps from the northwestern Mediterranean sea. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 60:1239–1259. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(95)00442-4
Saiz Jimenez C, de Lew JW (1986) Lignin pyrolysis products: their structures and their significance as biomarkers. Org Geochem 10:869–876. doi:10.1016/S0146-6380(86)80024-9
Sharma RK, Hajaligol MR (2003) Effect of pyrolysis conditions on the formation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) from polyphenolic compounds. J Anal Pyrolysis 66:123–144. doi:10.1016/S0165-2370(02)00109-2
Sicre MA, Peulve A, Saliot A, De Leeu JW, Baas M (1994) Molecular characterization of the organic fraction of suspended matter in the surface wates and bottom nepheloid layer of the Rhone delta using analytical pyrolysis. Org Geochem 21:11–26. doi:10.1016/0146-6380(94)90084-1
Takada H, Eganhouse R (1998) Molecular markers of anthropogenic waste. In: Meyers RA (ed) Encyclopedia of environmental analysis and remediation. John Wiley and Sons, Inc, pp 2883–2940
Tsuge S, Matsubara H (1985) High-resolution pyrolysis-gas chromatography of proteins and related materials. J Anal Appl Pyrol 8:49–64. doi:10.1016/0165-2370(85)80014-0
van Bergen PF, Collinson ME, Sinninhge Damsté JS, de Leeuw JW (1994) Chemical and microscopial characterisation of inner seed coast of fossil water plants. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 58:231–239. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(94)90460-X
Van Smeerdijk DG, Boon JJ (1987) Characterisation of subfossil Sphagnum leaves, rootlets of Ericaceae and peat by pyrolysis-high resolution gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 11:377–402. doi:10.1016/0165-2370(87)85043-X
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Terán, A., Gonzalez-Vila, F.J. & Gonzalez-Perez, J.A. Detection of organic contamination in sediments by double-shoot pyrolysis–GC/MS. Environ Chem Lett 7, 301–308 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-008-0169-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-008-0169-7