Abstract
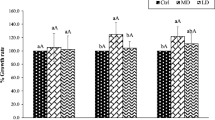
A field experiment was carried out to determine the effect of different land use systems such as continuous grass and agricultural crops rotation on the bioavailability of heavy metals in soils contaminated by former excessive sewage sludge application. The results show that Cd and Zn concentrations increased to 2 and 3.5 folds within 3 cuts of grass, respectively. Even 10 years after the end of excessive sewage sludge application the concentration of Cd in winter and summer wheat is 3.4 and 2.5 folds higher than the control, respectively. Zn concentration increased by two folds for both crops. In conclusion, the uptake depends on plant species and the degree of soil contamination. The availability of heavy metals was not changed with time.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Najar H, Schulz R, Roemheld V (2003) Plant availability of thallium in the rhizosphere of hyperaccumulator plants: a key factor for assessment of phytoextraction. Plant Soil 249:97–105
Barbera A (1987) Extraction and dosage of heavy metals from compost amended soils. In: compost production, quality and use. Appl. Sci. Publ. London 598–614
Berrow ML (1986) An overview of the soil contamination problems. In: Lester JM, Perry R, Sterritt RM (eds) Chemicals in the environment. Selper, London, pp 543–552
Chaney RL, Ryan JA (1993) Toxic metals and toxic organic pollutants in MSW-compost: Research results on phyto- availability, fate etc. In: Keener (ed) Science and engineering of composting: design, environmental, microbiological and utilization aspects. Renaissance Publ, Worthington, Ohio, pp 451–506
McBride MB (1995) Toxic metal accumulation from agricultural use of sewage sludge: are USEPA regulation protective J. Environ Qual 24:5–18
McGrath SP, Zhao FJ, Dunham SJ, Crosland AR, Coleman K (2000) Long term changes in the extractability and bioavailability of zinc and cadmium after sludge application. J Environ Qual 29:875–883
Petruzzelli G, Petronio GB, Gennaro M, Vanni A, Liberatori A (1994) Soil sorption of heavy metals as influenced by sewage sludge addition J. Environ Sci Health 29:31–50
Sanders JR, Adams TM (1987) The effect of pH and soil type on the concentration of zinc, copper and nickel extracted by calcium-chloride from sewage sludge soils. Environmental Pollution Series A 43:219–228
Schulz R, Roemheld V (1997) Recycling of municipal and industrial organic wastes in agriculture: benefits, limitations, and means of improvement. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr 43:1051–1056
Acknowledgement
The authors thank Mrs. Maria Ruckwied for ICP-MS measurements and Mr. Hans Bucher for managing the field work
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Najar, H., Schulz, R., Breuer, J. et al. Effect of cropping systems on the mobility and uptake of Cd and Zn. Environ Chem Lett 3, 13–17 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-005-0105-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-005-0105-z