Abstract
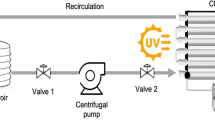
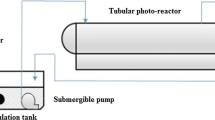
Titanium dioxide photocatalysis, using 200 mgl−1 of TiO2, and photo-Fenton, using 20 mg l−1 of iron, were applied to the treatment of dimethoate dissolved in water at 50 mg l−1. A heterogeneous photocatalysis test was performed in a 35-l solar pilot plant with Compound Parabolic Collectors (CPCs) under natural illumination. A homogeneous photocatalysis test was performed in a different solar pilot plant with four CPC units and a total volume of 75 l. In this work total disappearance of dimethoate and 90% of mineralization were attained in both solar treatments. Treatment time, hydrogen peroxide consumption and ferric phosphate precipitation during photo-Fenton treatment were discussed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bockelmann D, Dillert R, Dzengel J, Goslich R, Grob E, Higendorff M, Hufschmidt D, Memming R, Sagawe G, Schober M, Schuhmacher H-W, Selzer V, Siemon U, Vollmer S, Theurich J, Bahnemann D (2004) Photocatalysis. Solar Energy 77:445
Evgenidou E, Fytianos K, Poulios I (2005) Photocatalytic oxidation of dimethoate in aqueous solution. J Photochem Photobiol A: Chem 175:29–38
Gallo MA, Lawryk NJ (1988) In: Hayes WJ Jr, Laws ER Jr (eds), Handbook of pesticide toxicology. Academic Press, New York, p. 917
Gogate PR, Pandit AB (2004) A review of imperative technologies for wastewater treatment I: oxidations technologies at ambient conditions. Adv Environ Res 8:501–551
Konstantinou IK, Albanis TA (2003) Photocatalytic transformation of pesticides in aqueous titanium dioxide suspensions using artificial and solar light: intermediates and degradation pathways. Appl Catal B: Environ 42:319–335
Kositzi M, Poulios I, Malato S, Cáceres J, Campos A (2004) Solar photocatalytic treatment of synthetic municipal wastewater. Water Res 38:1147–1154
Malato Rodríguez S, Blanco Gálvez J, Maldonado Rubio MI, Fernández Ibáñez P, Alarcón Padilla D, Collares Pereira M, Farinha Mendes J, Correia de Oliveira J (2004) Engineering of solar photocatalytic collectors. Solar Energy 77:513–524
Occupational Health Services, Inc. (1991, Sept. 16) MSDS for dimethoate. OHS Inc., Secaucus, NJ
Ragnarsdottir KV (2000) Environmental fate and toxicology of organophosphate pesticides. J Geol Soc 157(18):859–876
The Water Framework Directive. Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Spanish Ministry of Education and Science for its financial assistance under the “Fotodetox” Project (PPQ 2003-07596-C03-01). They also thank Mrs. Deborah Fuldauer for correcting the English. Isabel Oller thanks the Ministry of Education and Science for her Ph.D research grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10311-006-0075-9
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oller, I., Gernjak, W., Maldonado, M.I. et al. Photocatalytic treatment of dimethoate by solar photocatalysis at pilot plant scale. Environ Chem Lett 3, 118–121 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-005-0013-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-005-0013-2