Abstract
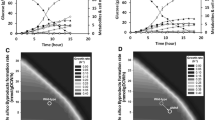
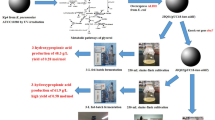
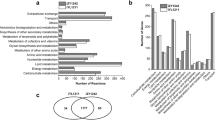
Klebsiella pneumoniae naturally produces relatively large amounts of 1,3-propanediol (1,3-PD) and 2,3-butanediol (2,3-BD) along with various byproducts using glycerol as a carbon source. The ldhA and mdh genes in K. pneumoniae were deleted based on its in silico gene knockout simulation with the criteria of maximizing 1,3-PD and 2,3-BD production and minimizing byproducts formation and cell growth retardation. In addition, the agitation speed, which is known to strongly affect 1,3-PD and 2,3-BD production in Klebsiella strains, was optimized. The K. pneumoniae ΔldhA Δmdh strain produced 125 g/L of diols (1,3-PD and 2,3-BD) with a productivity of 2.0 g/L/h in the lab-scale (5-L bioreactor) fed-batch fermentation using high-quality guaranteed reagent grade glycerol. To evaluate the industrial capacity of the constructed K. pneumoniae ΔldhA Δmdh strain, a pilot-scale (5000-L bioreactor) fed-batch fermentation was carried out using crude glycerol obtained from the industrial biodiesel plant. The pilot-scale fed-batch fermentation of the K. pneumoniae ΔldhA Δmdh strain produced 114 g/L of diols (70 g/L of 1,3-PD and 44 g/L of 2,3-BD), with a yield of 0.60 g diols per gram glycerol and a productivity of 2.2 g/L/h of diols, which should be suitable for the industrial co-production of 1,3-PD and 2,3-BD.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arasu MV, Kumar V, Ashok S, Hyohak S, Rathnasingh C, Lee HJ, Seung D, Park S (2011) Isolation and characterization of the new Klebsiella pneumoniae J2B strain showing improved growth characteristics with reduced lipopolysaccharide formation. Biotech Bioproc Eng 16:1134–1143
Biebl H, Zeng AP, Menzel K, Deckwer WD (1998) Fermentation of glycerol to 1,3-propanediol and 2,3-butanediol by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 50:24–29
Celińska E, Grajek W (2009) Biotechnological production of 2,3-butanediol—current state and prospects. Biotechnol Adv 27:715–725
Cui YL, Zhou JJ, Gao LR, Zhu CQ, Jiang X, Fu SL, Gong H (2014) Utilization of excess NADH in 2,3-butanediol-deficient Klebsiella pneumoniae for 1,3-propanediol production. J Appl Microbiol 117:690–698
da Silva GP, Mack M, Contiero J (2009) Glycerol: a promising and abundant carbon source for industrial microbiology. Biotechnol Adv 27:30–39
Durgapal M, Kumar V, Yang TH, Lee HJ, Seung D, Park S (2014) Production of 1,3-propanediol from glycerol using the newly isolated Klebsiella pneumoniae J2B. Bioresour Technol 159:223–231
Edwards JS, Ramakrishna R, Schilling CH, Palsson BO (1999) Metabolic flux balance analysis. In: Lee SY, Papoutsakis ET (eds) Metabolic engineering. Marcel Dekker, New York
Garg SK, Jain A (1995) Fermentative production of 2,3-butanediol: a review. Bioresour Technol 51:103–109
Gombert AK, Nielsen J (2000) Mathematical modelling of metabolism. Curr Opin Biotechnol 11:180–186
Guo X, Cao C, Wang Y, Li C, Wu M, Chen Y, Zhang C, Pei H, Xiao D (2014) Effect of the inactivation of lactate dehydrogenase, ethanol dehydrogenase, and phosphotransacetylase on 2,3-butanediol production in Klebsiella pneumoniae strain. Biotechnol Biofuels 7:44
Ji XJ, Huang H, Du J, Zhu JG, Ren LJ, Hu N, Li S (2009) Enhanced 2,3-butanediol production by Klebsiella oxytoca using a two-stage agitation speed control strategy. Bioresour Technol 100:3410–3414
Jung MY, Mazumdar S, Shin SH, Yang KS, Lee J, Oh MK (2014) Improvement of 2,3-butanediol yield in Klebsiella pneumoniae by deletion of the pyruvate formate-lyase gene. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:6195–6203
Kosaric N, Magee RJ, Blaszczyk R (1992) Redox potential measurement for monitoring glucose and xylose conversion by K. pneumoniae. Chem Biochem Eng Q 6:145–152
Kumar V, Durgapal M, Sankaranarayanan M, Somasundar A, Rathnasingh C, Song H, Seung D, Park S (2016) Effects of mutation of 2,3-butanediol formation pathway on glycerol metabolism and 1,3-propanediol production by Klebsiella pneumoniae J2B. Bioresour Technol 214:432–440
Lakshmanan M, Kim TY, Chung BK, Lee SY, Lee DY (2015) Flux-sum analysis identifies metabolite targets for strain improvement. BMC Syst Biol 9:73
Liao YC, Huang TW, Chen FC, Charusanti P, Hong JS, Chang HY, Tsai SF, Palsson BO, Hsiung CA (2011) An experimentally validated genome-scale metabolic reconstruction of Klebsiella pneumoniae MGH 78578, iYL1228. J Bacteriol 193:1710–1717
Lin J, Zhang Y, Xu D, Xiang G, Jia Z, Fu S, Gong H (2016) Deletion of poxB, pta, and ackA improves 1,3-propanediol production by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:2775–2784
Ma BB, Xu XL, Zhang GL, Wang LW, Wu M, Li C (2009) Microbial production of 1,3-propanediol by Klebsiella pneumoniae XJPD-Li under different aeration strategies. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 152:127–134
Mahadevan R, Schilling CH (2003) The effects of alternate optimal solutions in constraint-based genome-scale metabolic models. Metab Eng 5:264–276
Oh BR, Seo JW, Heo SY, Hong WK, Luo LH, Kim S, Park DH, Kim CH (2012) Optimization of culture conditions for 1,3-propanediol production from glycerol using a mutant strain of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 166:127–137
Orth JD, Conrad TM, Na J, Lerman JA, Nam H, Feist AM, Palsson BO (2011) A comprehensive genome-scale reconstruction of Escherichia coli metabolism—2011. Mol Syst Biol 7:535
Park JM, Kim TY, Lee SY (2009) Constraints-based genome-scale metabolic simulation for systems metabolic engineering. Biotechnol Adv 27:979–988
Park JM, Kim TY, Lee SY (2010) Prediction of metabolic fluxes by incorporating genomic context and flux-converging pattern analyses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:14931–14936
Park JM, Song H, Lee HJ, Seung D (2013) Genome-scale reconstruction and in silico analysis of Klebsiella oxytoca for 2,3-butanediol production. Microb Cell Fact 12:20
Park JM, Song H, Lee HJ, Seung D (2013) In silico aided metabolic engineering of Klebsiella oxytoca and fermentation optimization for enhanced 2,3-butanediol production. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 40:1057–1066
Rathnasingh C, Kim DK, Song H, Lee HJ, Seung D, Park S (2012) Isolation and characterization of a new mucoid-free Klebsiella pneumoniae strain for 2,3-butanediol production. Afr J Biotechnol 11:11252–11261
Rathnasingh C, Park JM, Kim DK, Song H, Chang YK (2016) Metabolic engineering of Klebsiella pneumoniae and in silico investigation for enhanced 2,3-butanediol production. Biotechnol Lett 38:975–982
Ryu CM, Farag MA, Hu CH, Reddy MS, Kloepper JW, Paré PW (2004) Bacterial volatiles induce systemic resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 134:1017–1026
Ryu CM, Farag MA, Hu CH, Reddy MS, Wei HX, Paré PW, Kloepper JW (2003) Bacterial volatiles promote growth in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:4927–4932
Saxena RK, Anand P, Saran S, Isar J (2009) Microbial production of 1,3-propanediol: recent developments and emerging opportunities. Biotechnol Adv 27:895–913
Schuetz R, Kuepfer L, Sauer U (2007) Systematic evaluation of objective functions for predicting intracellular fluxes in Escherichia coli. Mol Syst Biol 3:119
Varma A, Palsson BO (1994) Metabolic flux balancing: basic concepts, scientific and practical use. Biotechnology 12:994–998
Wang Y, Teng H, Xiu Z (2011) Effect of aeration strategy on the metabolic flux of Klebsiella pneumoniae producing 1,3-propanediol in continuous cultures at different glycerol concentrations. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 38:705–715
Williamson JR, Jones EA (1964) Inhibition of glycolysis by pyruvate in relation to the accumulation of citric acid cycle intermediates in the perfused rat heart. Nature 203:1171–1173
Xu YZ, Guo NN, Zheng ZM, Ou XJ, Liu HJ, Liu DH (2009) Metabolism in 1,3-propanediol fed-batch fermentation by a d-lactate deficient mutant of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Biotechnol Bioeng 104:965–972
Yen HW, Li FT, Chang JS (2014) The effects of dissolved oxygen level on the distribution of 1,3-propanediol and 2,3-butanediol produced from glycerol by an isolated indigenous Klebsiella sp. Ana-WS5. Bioresour Technol 153:374–378
Zeng AP, Sabra W (2011) Microbial production of diols as platform chemicals: recent progresses. Curr Opin Biotechnol 22:749–757
Zhu C, Jiang X, Zhang Y, Lin J, Fu S, Gong H (2015) Improvement of 1,3-propanediol production in Klebsiella pneumoniae by moderate expression of puuC (encoding an aldehyde dehydrogenase). Biotechnol Lett 37:1783–1790
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Industrial Strategic Technology Development Program (No. 10050407) funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (MOTIE, Korea).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, J.M., Rathnasingh, C. & Song, H. Metabolic engineering of Klebsiella pneumoniae based on in silico analysis and its pilot-scale application for 1,3-propanediol and 2,3-butanediol co-production. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 44, 431–441 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-016-1898-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-016-1898-4