Abstract
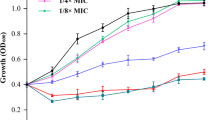
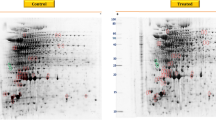
We previously demonstrated the effects of azo dyes and their reduction metabolites on bacterial cell growth and cell viability. In this report, the effects of Orange II and Sudan III on gene expression profiling in Staphylococcus aureus ATCC BAA 1556 were analyzed using microarray and quantitative RT-PCR technology. Upon exposure to 6 μg/ml Orange II for 18 h, 21 genes were found to be differently expressed. Among them, 8 and 13 genes were up- and down-regulated, respectively. Most proteins encoded by these differentially expressed genes involve stress response caused by drug metabolism, oxidation, and alkaline shock indicating that S. aureus could adapt to Orange II exposure through a balance between up and down regulated gene expression. Whereas, after exposure to 6 μg/ml Sudan III for 18 h, 57 genes were differentially expressed. In which, 51 genes were up-regulated and 6 were down-regulated. Most proteins encoded by these differentially expressed genes involve in cell wall/membrane biogenesis and biosynthesis, nutrient uptake, transport and metabolite, and stress response, suggesting that Sudan III damages the bacterial cell wall or/and membrane due to binding of the dye. Further analysis indicated that all differentially expressed genes encoded membrane proteins were up-regulated and most of them serve as transporters. The result suggested that these genes might contribute to survival, persistence and growth in the presence of Sudan III. Only one gene msrA, which plays an important role in oxidative stress resistance, was found to be down-regulated after exposure to both Orange II and Sudan III. The present results suggested that both these two azo dyes can cause stress in S. aureus and the response of the bacterium to the stress is mainly related to characteristics of the azo dyes.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Ajdić D, McShan WM, McLaughlin RE, Savić G, Chang J, Carson MB, Primeaux C, Tian R, Kenton S, Jia H (2002) Genome sequence of Streptococcus mutans UA159, a cariogenic dental pathogen. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99:14434–14439
An Y, Jiang L, Cao J, Geng C, Zhong L (2007) Sudan I induces genotoxic effects and oxidative DNA damage in HepG2 cells. Mut Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 627:164–170
Bedekar PA, Saratale RG, Saratale GD, Govindwar SP (2014) Oxidative stress response in dye degrading bacterium Lysinibacillus sp. RGS exposed to Reactive Orange 16, degradation of RO16 and evaluation of toxicity. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 21:11075–11085
Beenken KE, Dunman PM, McAleese F, Macapagal D, Murphy E, Projan SJ, Blevins JS, Smeltzer MS (2004) Global gene expression in Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. J Bacteriol 186:4665–4684
Bore E, Langsrud S, Langsrud Ø, Rode TM, Holck A (2007) Acid-shock responses in Staphylococcus aureus investigated by global gene expression analysis. Microbiology 153:2289–2303
Boschi-Muller S, Olry A, Antoine M, Branlant G (2005) The enzymology and biochemistry of methionine sulfoxide reductases. Biochim Biophys Acta 1703:231–238
Brechtel C, King S (1998) 4-Aminobutyrate (GABA) transporters from the amine-polyamine-choline superfamily: substrate specificity and ligand recognition profile of the 4-aminobutyrate permease from Bacillus subtilis. Biochem J 333:565–571
Cameron DR, Ward DV, Kostoulias X, Howden BP, Moellering RC, Eliopoulos GM, Peleg AY (2012) Serine/threonine phosphatase Stp1 contributes to reduced susceptibility to vancomycin and virulence in Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis 205:1677–1687
Chatterjee I, Schmitt S, Batzilla CF, Engelmann S, Keller A, Ring MW, Kautenburger R, Ziebuhr W, Hecker M, Preissner KT (2009) Staphylococcus aureus ClpC ATPase is a late growth phase effector of metabolism and persistence. Proteomics 9:1152–1176
Chen H, Hopper SL, Cerniglia CE (2005) Biochemical and molecular characterization of an azoreductase from Staphylococcus aureus, a tetrameric NADPH-dependent flavoprotein. Microbiology 151:1433–1441
Chen H (2006) Recent advances in azo dye degrading enzyme research. Curr Protein Pept Sci 7:101–111
Chen KC, Huang WT, Wu JY, Houng JY (1999) Microbial decolorization of azo dyes by Proteus mirabilis. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 23:686–690
Chen PR, Nishida S, Poor CB, Cheng A, Bae T, Kuechenmeister L, Dunman PM, Missiakas D, He C (2009) A new oxidative sensing and regulation pathway mediated by the MgrA homologue SarZ in Staphylococcus aureus. Mol Microbiol 71:198–211
Chengalroyen M, Dabbs E (2013) The microbial degradation of azo dyes: minireview. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 29:389–399
Cohen SP, Hächler H, Levy S (1993) Genetic and functional analysis of the multiple antibiotic resistance (mar) locus in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 175:1484–1492
Davidson AL, Chen J (2004) ATP-binding cassette transporters in bacteria. Ann Rev Biochem 73:241–268
den Hengst CD, Groeneveld M, Kuipers OP, Kok J (2006) Identification and functional characterization of the Lactococcus lactis CodY-regulated branched-chain amino acid permease BcaP (CtrA). J Bacteriol 188:3280–3289
Diep BA, Gill SR, Chang RF, Phan TH, Chen JH, Davidson MG, Lin F, Lin J, Carleton HA, Mongodin EF, Sensabaugh GF, Perdreau-Remington F (2006) Complete genome sequence of USA300, an epidemic clone of community-acquired meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet 367:731–739
Dillon D, Combes R, Zeiger E (1994) Activation by caecal reduction of the azo dye D & C red no. 9 to a bacterial mutagen. Mutagenesis 9:295–299
Dyda F, Klein DC, Hickman AB (2000) GCN5-related N-acetyltransferases: a structural overview. Ann Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 29:81–103
El Hassouni M, Chambost JP, Expert D, Van Gijsegem F, Barras F (1999) The minimal gene set member msrA, encoding peptide methionine sulfoxide reductase, is a virulence determinant of the plant pathogen Erwinia chrysanthemi. Proc Natl Acad Sci 96:887–892
El Omari K, Dhaliwal B, Lockyer M, Charles I, Hawkins AR, Stammers DK (2006) Structure of Staphylococcus aureus guanylate monophosphate kinase. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 62:949–953
Feng J, Heinze M, Xu H, Cerniglia E, Chen H (2010) Evidence for significantly enhancing reduction of azo dyes in Escherichia coli by expressed cytoplasmic Azoreductase (AzoA) of enterococcus faecalis. Protein Pept Lett 17:578–584
Feng J, Cerniglia CE, Chen H (2012) Toxicological significance of azo dye metabolism by human intestinal microbiota. Front Biosci 4:568–586
Ferson AE, Wray LV Jr, Fisher SH (1996) Expression of the Bacillus subtilis gabP gene is regulated independently in response to nitrogen and amino acid availability. Mol Microbiol 22:693–701
Foster TJ, Geoghegan JA, Ganesh VK, Höök M (2014) Adhesion, invasion and evasion: the many functions of the surface proteins of Staphylococcus aureus. Nat Rev Microbiol 12:49–62
Frederick JR, Elkins JG, Bollinger N, Hassett DJ, McDermott TR (2001) Factors affecting catalase expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms and planktonic cells. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:1375–1379
Fuller TE, Kennedy MJ, Lowery DE (2000) Identification of Pasteurella multocida virulence genes in a septicemic mouse model using signature-tagged mutagenesis. Microb Pathog 29:25–38
Geckil H, Gencer S, Kahraman H, Erenler SO (2003) Genetic engineering of Enterobacter aerogenes with the Vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene: cell growth, survival, and antioxidant enzyme status under oxidative stress. Res Microbiol 154:425–431
Greenberg JT, Monach P, Chou JH, Josephy PD, Demple B (1990) Positive control of a global antioxidant defense regulon activated by superoxide-generating agents in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci 87:6181–6185
Grice EA, Kong HH, Renaud G, Young AC, Bouffard GG, Blakesley RW, Wolfsberg TG, Turner ML, Segre JA (2008) A diversity profile of the human skin microbiota. Genome Res 18:1043–1050
Grundy FJ, Waters DA, Takova TY, Henkin TM (1993) Identification of genes involved in utilization of acetate and acetoin in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol 10:259–271
Hiramatsu T, Kodama K, Kuroda T, Mizushima T, Tsuchiya T (1998) A putative multisubunit Na+/H+ antiporter from Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol 180:6642–6648
Kavanaugh JS, Thoendel M, Horswill AR (2007) A role for type I signal peptidase in Staphylococcus aureus quorum sensing. Mol Microbiol 65:780–798
Kazakov AE, Vassieva O, Gelfand MS, Osterman A, Overbeek R (2003) Bioinformatics classification and functional analysis of PhoH homologs. In silico Biol 3:3–15
Keating DH, Carey MR, Cronan JE (1995) The unmodified (apo) form of Escherichia coli acyl carrier protein is a potent inhibitor of cell growth. J Biol Chem 270:22229–22235
Khan MF, Wu X, Kaphalia BS, Boor PJ, Ansari GAS (1997) Acute hematopoietic toxicity of aniline in rats. Toxicol Lett 92:31–37
Kisker C, Schindelin H, Rees DC (1997) Molybdenum-cofactor-containing enzymes: structure and mechanism. Ann Rev Biochem 66:233–267
Kleiger G, Eisenberg D (2002) GXXXG and GXXXA motifs stabilize FAD and NAD(P)-binding Rossmann folds through C(alpha)-H… O hydrogen bonds and van der waals interactions. J Mol Biol 323:69–76
Kobayashi H, Miyamoto T, Hashimoto Y, Kiriki M, Motomatsu A, Honjoh K, Iio M (2005) Identification of factors involved in recovery of heat-injured Salmonella Enteritidis. J Food Prot 68:932–941
Kuhn ML, Majorek KA, Minor W, Anderson WF (2013) Broad-substrate screen as a tool to identify substrates for bacterial Gcn5-related N-acetyltransferases with unknown substrate specificity. Protein Sci 22:222–230
Kuroda M, Ohta T, Hayashi H (1995) Isolation and the gene cloning of an alkaline shock protein in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 207:978–984
Li L, Gao HW, Ren JR, Chen L, Li YC, Zhao JF, Zhao HP, Yuan Y (2007) Binding of Sudan II and IV to lecithin liposomes and E. coli membranes: insights into the toxicity of hydrophobic azo dyes. BMC Struct Biol 7:16
Lindgren V (1978) Mapping of a genetic locus that affects glycerol 3-phosphate transport in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 133:667–670
Lo M, Bulach DM, Powell DR, Haake DA, Matsunaga J, Paustian ML, Zuerner RL, Adler B (2006) Effects of temperature on gene expression patterns in Leptospira interrogans serovar Lai as assessed by whole-genome microarrays. Infect Immun 74:5848–5859
Loefdahl S, Guss B, Uhlen M, Philipson L, Lindberg M (1983) Gene for staphylococcal protein A. Proc Natl Acad Sci 80:697–701
Lundberg BE, Wolf RE, Dinauer MC, Xu Y, Fang FC (1999) Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase is required for Salmonella typhimurium virulence and resistance to reactive oxygen and nitrogen intermediates. Infect Immun 67:436–438
Ma J-F, Hager PW, Howell ML, Phibbs PV, Hassett DJ (1998) Cloning and characterization of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa zwf gene encoding glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, an enzyme important in resistance to methyl viologen (paraquat). J Bacteriol 180:1741–1749
Marmion DM (1991) Handbook of US colorants: foods, drugs, cosmetics, and medical devices. Wiley, New York
Martin RG, Rosner JL (1995) Binding of purified multiple antibiotic-resistance repressor protein (MarR) to mar operator sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci 92:5456–5460
McCallum N, Spehar G, Bischoff M, Berger-Bachi B (2006) Strain dependence of the cell wall-damage induced stimulon in Staphylococcus aureus. Biochim Biophys Acta 1760:1475–1481
Mendel RR, Bittner F (2006) Cell biology of molybdenum. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1763:621–635
Moch C, Schrögel O, Allmansberger R (2000) Transcription of the nfrA-ywcH operon from Bacillus subtilis is specifically induced in response to heat. J Bacteriol 182:4384–4393
Mostertz J, Scharf C, Hecker M, Homuth G (2004) Transcriptome and proteome analysis of Bacillus subtilis gene expression in response to superoxide and peroxide stress. Microbiology 150:497–512
Myslak ZW, Bolt HM (1998) Occupational exposure to azo dyes and risk of bladder cancer. Zbl Arbeitsmed 38:310–321
Novick RP, Geisinger E (2008) Quorum sensing in staphylococci. Ann Rev Genet 42:541–564
Pan H, Feng J, Cerniglia CE, Chen H (2011) Effects of Orange II and Sudan III azo dyes and their metabolites on Staphylococcus aureus. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 38:1729–1738
Pan H, Feng J, He GX, Cerniglia CE, Chen H (2012) Evaluation of impact of exposure of Sudan azo dyes and their metabolites on human intestinal bacteria. Anaerobe 18:445–453
Paoletti L, Lu YJ, Schujman GE, de Mendoza D, Rock CO (2007) Coupling of fatty acid and phospholipid synthesis in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 189:5816–5824
Perera IC, Grove A (2010) Molecular mechanisms of ligand-mediated attenuation of DNA binding by MarR family transcriptional regulators. J Mol Cell Biol 2:243–254
Phugare SS, Kalyani DC, Patil AV, Jadhav JP (2011) Textile dye degradation by bacterial consortium and subsequent toxicological analysis of dye and dye metabolites using cytotoxicity, genotoxicity and oxidative stress studies. J Hazard Mater 186:713–723
Pinho MG, de Lencastre H, Tomasz A (2000) Cloning, characterization, and inactivation of the gene pbpC, encoding penicillin-binding protein 3 of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol 182:1074–1079
Qiu R, Pei W, Zhang L, Lin J, Ji G (2005) Identification of the putative staphylococcal AgrB catalytic residues involving the proteolytic cleavage of AgrD to generate autoinducing peptide. J Biol Chem 280:16695–16704
Rafii F, Hall JD, Cerniglia CE (1997) Mutagenicity of azo dyes used in foods, drugs and cosmetics before and after reduction by Clostridium species from the human intestinal tract. Food Chem Toxicol 35:897–901
Rau J, Stolz A (2003) Oxygen-insensitive nitroreductases NfsA and NfsB of Escherichia coli function under anaerobic conditions as lawsone-dependent azo reductases. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:3448–3455
Saavedra L, Sesma F (2005) Atypical genetic locus associated with the zwf gene encoding the glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase from Enterococcus mundtii CRL35. Curr Microbiol 51:148–152
Sakoulas G, Eliopoulos GM, Moellering RC, Wennersten C, Venkataraman L, Novick RP, Gold HS (2002) Accessory gene regulator (agr) locus in geographically diverse Staphylococcus aureus isolates with reduced susceptibility to vancomycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 46:1492–1502
Sasindran SJ, Saikolappan S, Dhandayuthapani S (2007) Methionine sulfoxide reductases and virulence of bacterial pathogens. Future Microbiol 2:619–630
Schreier HJ, Brown SW, Hirschi KD, Nomellini JF, Sonenshein AL (1989) Regulation of Bacillus subtilis glutamine synthetase gene expression by the product of the glnR gene. J Mol Biol 210:51–63
Schreier HJ, Caruso SM, Maier KC (2000) Control of Bacillus subtilis glutamine synthetase expression by glnR from Staphylococcus aureus. Curr Microbiol 41:425–429
Scovill WH, Schreier HJ, Bayles KW (1996) Identification and characterization of the pckA gene from Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol 178:3362–3364
Singh VK, Moskovitz J (2003) Multiple methionine sulfoxide reductase genes in Staphylococcus aureus: expression of activity and roles in tolerance of oxidative stress. Microbiology 149:2739–2747
Stingley RL, Zou W, Heinze TM, Chen HZ, Cerniglia CE (2010) Metabolism of azo dyes by human skin microbiota. J Med Microbiol 59:108–114
Stolz A (2001) Basic and applied aspects in the microbial degradation of azo dyes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 56:69–80
Streker K, Freiberg C, Labischinski H, Hacker J, Ohlsen K (2005) Staphylococcus aureus NfrA (SA0367) is a flavin mononucleotide-dependent NADPH oxidase involved in oxidative stress response. J Bacteriol 187:2249–2256
Tolner B, Poolman B, Konings WN (1992) Characterization and functional expression in Escherichia coli of the sodium/proton/glutamate symport proteins of Bacillus stearothermophilus and Bacillus caldotenax. Mol Microbiol 6:2845–2856
Tong W, Cao X, Harris S, Sun H, Fang H, Fuscoe J, Harris A, Hong H, Xie Q, Perkins R (2003) Arraytrack–supporting toxicogenomic research at the US Food and Drug Administration National Center for Toxicological Research. Environ Health Perspect 111:1819–1826
Wang QM, Peery RB, Johnson RB, Alborn WE, Yeh W-K, Skatrud PL (2001) Identification and characterization of a monofunctional glycosyltransferase from Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol 183:4779–4785
Wang RF, Chen H, Paine DD, Cerniglia CE (2004) Microarray method to monitor 40 intestinal bacterial species in the study of azo dye reduction. Biosens Bioelectron 20:699–705
Wray LV, Ferson AE, Rohrer K, Fisher SH (1996) TnrA, a transcription factor required for global nitrogen regulation in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci 93:8841–8845
Xu H, Heinze TM, Paine DD, Cerniglia CE, Chen H (2010) Sudan azo dyes and Para Red degradation by prevalent bacteria of the human gastrointestinal tract. Anaerobe 16:114–119
Yang YH, Dudoit S, Luu P, Lin DM, Peng V, Ngai J, Speed TP (2002) Normalization for cDNA microarray data: a robust composite method addressing single and multiple slide systematic variation. Nucleic Acids Res 30:e15–e15
Yernool D, Boudker O, Folta-Stogniew E, Gouaux E (2003) Trimeric subunit stoichiometry of the glutamate transporters from Bacillus caldotenax and Bacillus stearothermophilus. Biochemistry 42:12981–12988
Yoshida H, Yamada M, Kuramitsu S, Kamitori S (2008) Structure of a putative molybdenum-cofactor biosynthesis protein C (MoaC) from Sulfolobus tokodaii (ST0472). Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 64:589–592
Yu NY, Wagner JR, Laird MR, Melli G, Rey S, Lo R, Dao P, Sahinalp SC, Ester M, Foster LJ (2010) PSORTb 3.0: improved protein subcellular localization prediction with refined localization subcategories and predictive capabilities for all prokaryotes. Bioinformatics 26:1608–1615
Zaprasis A, Hoffmann T, Stannek L, Gunka K, Commichau FM, Bremer E (2014) The γ-aminobutyrate permease GabP serves as the third proline transporter of bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 196:515–526
Zhang Y, An Y, Jiang L, Geng C, Cao J, Jiang L, Zhong L (2011) The role of oxidative stress in Sudan IV-induced DNA damage in human liver-derived HepG2 cells. Environ Toxicol 26:292–299
Zhang Y, Meng D, Wang Z, Guo H, Wang Y, Wang X, Dong X (2012) Oxidative stress response in atrazine-degrading bacteria exposed to atrazine. J Hazard Mater 229:434–438
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. Steven L. Foley and Kidon Sung for their critical review of this manuscript. This study was funded by National Center for Toxicological Research, United States Food and Drug Administration, and supported in part by appointments (HP and JF) to the Postgraduate Research Fellowship Program by the Oak Ridge Institute for Science and Education through an interagency agreement between the US Department of Energy and the US Food and Drug Administration. The views presented in this article do not necessarily reflect those of the Food and Drug Administration.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, H., Xu, J., Kweon, OG. et al. Differential gene expression in Staphylococcus aureus exposed to Orange II and Sudan III azo dyes. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 42, 745–757 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-015-1599-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-015-1599-4