Abstract
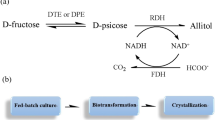
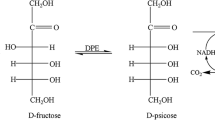
An engineered strain for the conversion of d-fructose to allitol was developed by constructing a multi-enzyme coupling pathway and cofactor recycling system in Escherichia coli. d-Psicose-3-epimerase from Ruminococcus sp. and ribitol dehydrogenase from Klebsiella oxytoca were coexpressed to form the multi-enzyme coupling pathway for allitol production. The cofactor recycling system was constructed using the formate dehydrogenase gene from Candida methylica for continuous NADH supply. The recombinant strain produced 10.62 g/l allitol from 100 mM d-fructose. To increase the intracellular concentration of the substrate, the glucose/fructose facilitator gene from Zymomonas mobilis was incorporated into the engineered strain. The results showed that the allitol yield was enhanced significantly to 16.53 g/l with a conversion rate of 92 %. Through optimizing conversion conditions, allitol was produced effectively on a large scale by the whole-cell biotransformation system; the yield reached 48.62 g/l when 500 mM d-fructose was used as the substrate.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bäumchen C, Bringer-Meyer S (2007) Expression of glf Z.m . increases d-mannitol formation in whole cell biotransformation with resting cells of Corynebacterium glutamicum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76:545–552. doi:10.1007/s00253-007-0987-8
Chan HC, Zhu Y, Hu Y, Ko TP, Huang CH, Ren F, Chen CC, Ma Y, Guo RT, Sun Y (2012) Crystal structures of d-psicose 3-epimerase from Clostridium cellulolyticum H10 and its complex with ketohexose sugars. Protein Cell 3:123–131. doi:10.1007/s13238-012-2026-5
Chandrasekhar B (2010) Synthesis of some monocyclic and bicyclic polyhydroxy nitrogen heterocyclic compounds (Azasugars). PhD Thesis, Indian Institute of Chemical Technology, Hyderabad
Han W, Zhu Y, Men Y, Yang J, Liu C, Sun Y (2014) Production of allitol from d-psicose by a novel isolated strain of Klebsiella oxytoca G4A4. J Basic Microbiol 53:1–7. doi:10.1002/jobm.201300647
Ishida Y, Kamiya T, Itoh H, Kimura Y, Izumori K (1997) Cloning and characterization of the d-tagatose 3-epimerase gene from Pseudomonas cichorii ST-24. J Ferment Bioeng 83:529–534. doi:10.1016/S0922-338X(97)81132-4
Itoh H, Sato T, Izumori K (1995) Preparation of d-psicose from d-fructose by immobilized d-tagatose 3-epimerase. J Ferment Bioeng 80:101–103. doi:10.1016/0922-338X(95)98186-O
Izumori K (2006) Izumoring: a strategy for bioproduction of all hexoses. J Biotechnol 124:717–722. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2006.04.016
Kataoka M, Yamamoto K, Kawabata H, Wada M, Kita K, Yanase H, Shimizu S (1999) Stereoselective reduction of ethyl 4-chloro-3-oxobutanoate by Escherichia coli transformant cells coexpressing the aldehyde reductase and glucose dehydrogenase genes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 51:486–490. doi:10.1007/s002530051421
Kaup B, Bringer-Meyer S, Sahm H (2004) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli: construction of an efficient biocatalyst for d-mannitol formation in a whole-cell biotransformation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64:333–339. doi:10.1007/s00253-003-1470-9
Kim HJ, Hyun EK, Kim YS, Lee YJ, Oh DK (2006) Characterization of an Agrobacterium tumefaciens d-psicose 3-epimerase that converts d-fructose to d-psicose. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:981–985. doi:10.1128/AEM.72.2.981-985.2006
Kizaki N, Yasohara Y, Hasegawa J, Wada M, Kataoka M, Shimizu S (2001) Synthesis of optically pure ethyl(S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutanoate by Escherichia coli transformant cells coexpressing the carbonyl reductase and glucose dehydrogenase genes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 55:590–595. doi:10.1007/s002530100599
Kornberg HL, Lambourne LTM, Sproul AA (2000) Facilitated diffusion of fructose via the phosphoenolpyruvate/glucose phosphotransferase system of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:1808–1812. doi:10.1073/pnas.97.4.1808
Mu W, Zhang W, Feng Y, Jiang B, Zhou L (2012) Recent advances on applications and biotechnological production of d-psicose. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 94:1461–1467. doi:10.1007/s00253-012-4093-1
Muniruzzaman S, Kunihisa Y, Ichiraku K, Izumori K (1995) Purification and characterization of a ribitol dehydrogenase from Enterobacter agglomerans strain 221e. J Ferment Bioeng 79:496–498. doi:10.1016/0922-338X(95)91269-B
Muniruzzaman S, Tokunaga H, Izumori K (1995) Conversion of d-psicose to allitol by Enterobacter agglomerans strain 221e. J Ferment Bioeng 79:323–327. doi:10.1016/0922-338X(95)93989-W
Parker C, Barnell WO, Snoep JL, Ingram LO, Conway T (1995) Characterization of the Zymomonas mobilis glucose gacilitator gene product (glf) in recombinant Escherichia coli: examination of transport mechanism, kinetics and the role of glucokinase in glucose transport. Mol Microbiol 15:759–802. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.tb02350.x
Rath A, Glibowicka M, Nadeau VG, Chen G, Deber CM (2009) Detergent binding explains anomalous SDS-PAGE migration of membrane proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:1760–1765. doi:10.1073/pnas.0813167106
Takeshita K, Ishida Y, Takada G, Izumori K (2000) Direct production of allitol from d-fructose by a coupling reaction using d-tagatose 3-epimerase, ribitol dehydrogenase and formate dehydrogenase. J Biosci Bioeng 90:545–548. doi:10.1016/S1389-1723(01)80038-4
Walton AZ, Stewart JD (2004) Understanding and improving NADPH-dependent reactions by nongrowing Escherichia coli cells. Biotechnol Prog 20:403–411. doi:10.1021/bp030044m
Wang Q (2006) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for high yield of succinic acid. Ph.D. Dissertation, Tianjin University, Tianjin, China
Weisser P, Krämer R, Sahm H, Sprenger GA (1995) Functional expression of the glucose transporter of Zymomonas mobilis leads to restoration of glucose and fructose uptake in Escherichia coli mutants and provides evidence for its facilitator action. J Bacteriol 177:3351–3354
Wu J, Du G, Zhou J, Chen J (2013) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for (2S)-pinocembrin production from glucose by a modular metabolic strategy. Metab Eng 16:48–55. doi:10.1016/j.ymben.2012.11.009
Yamamoto H, Matsuyama A, Kobayashi Y (2003) Synthesis of ethyl (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutanoate using fabG-homologues. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 61:133–139. doi:10.1007/s00253-002-1188-0
Yang J, Zhu Y, Li J, Men Y, Sun Y, Ma Y (2014) Biosynthesis of rare ketoses through constructing a recombination pathway in an engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum. Biotechnol Bioeng. doi:10.1002/bit.25345
Zhang L, Mu W, Jiang B, Zhang T (2009) Characterization of d-tagatose-3-epimerase from Rhodobacter sphaeroides that converts d-fructose into d-psicose. Biotechnol Lett 31:857–862. doi:10.1007/s10529-009-9942-3
Zhao J, Li Q, Sun T, Zhu X, Xu H, Tang J, Zhang X, Ma Y (2013) Engineering central metabolic modules of Escherichia coli for improving β-carotene production. Metab Eng 17:42–50. doi:10.1016/j.ymben.2013.02.002
Zhou P, Li S, Xu H, Feng X, Ouyang P (2012) Construction and co-expression of plasmid encoding xylitol dehydrogenase and a cofactor regeneration enzyme for the production of xylitol from d-arabitol. Enzyme Microb Tech 51:119–124. doi:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2012.05.002
Zhu Y, Men Y, Bai W, Li X, Zhang L, Sun Y, Ma Y (2012) Overexpression of d-psicose 3-epimerase from Ruminococcus sp. in Escherichia coli and its potential application in d-psicose production. Biotechnol Lett 34:1901–1906. doi:10.1007/s10529-012-0986-4
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31101303), the High Technology and Research Development Program (2013AA102102), and the Key Programs of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (KSZD-EW-Z-019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Y. Zhu and H. Li have contributed equally to the work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Y., Li, H., Liu, P. et al. Construction of allitol synthesis pathway by multi-enzyme coexpression in Escherichia coli and its application in allitol production. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 42, 661–669 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-014-1578-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-014-1578-1