Abstract
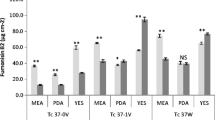
Tolypocladium inflatum is known primarily for its production of the cyclosporines that are used as an immunosuppressive drug. However, we report here the production of the carcinogenic fumonisins B2 and B4 by this biotechnologically relevant fungal genus. These mycotoxins were detected in 11 strains tested from three species: Tolypocladium inflatum, T. cylindrosporum, and T. geodes. Production of fumonisins by Fusarium spp. and Aspergillus niger is highly medium- and temperature-dependent, so the effect of these parameters on fumonisin production by three T. inflatum strains was studied. Maximum production was achieved on media with high sugar content incubated at 25–30°C. Since these results demonstrate that fumonisin production could be widespread within the genus Tolypocladium, the potential contamination of commercial cyclosporine preparations with fumonisins needs to be investigated.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker SE (2006) Aspergillus niger genomics: past, present and into the future. Med Mycol 44:S17–S21
Balakrishnan K, Pandey A (1996) Influence of amino acids on the biosynthesis of cyclosporin A by Tolypocladium inflatum. Appl Microbiol Biotech 45:800–803
Balaraman K, Mathew N (2006) Optimization of media composition for the production of cyclosporin A by Tolypocladium species. Indian J Med Res 123:525–530
Bandani AR, Khambay BPS, Faull JL, Newton R, Deadman M, Butt TM (2000) Production of efrapeptins by Tolypocladium species and evaluation of their insecticidal and antimicrobial properties. Mycol Res 104:537–544
Bezuidenhout SC, Gelderblom WCA, Gorst-Allman CP, Horak RM, Marasas WFO, Spiteller G, Vleggaar R (1988) Structure elucidation of the fumonisins, mycotoxins from Fusarium moniliforme. J Chem Soc Chem Commun 11:743–745
Bissett J (1983) Notes on Tolypocladium and related genera. Can J Bot 61:1311–1329
Branham BE, Plattner RD (1993) Isolation and characterization of a new fumonisin from liquid cultures of Fusarium moniliforme. J Nat Prod 56:1630–1633
Caldas ED, Jones AD, Ward B, Winter CK, Gilchrist DG (1994) Structural characterization of 3 new AAL toxins produced by Alternaria alternata f. sp. lycopersici. J Agric Food Chem 42:327–333
Chen JP, Mirocha CJ, Xie WP, Hogge L, Olson D (1992) Production of the mycotoxin fumonisin B1 by Alternaria alternata f. sp. lycopersici. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:3928–3931
EEC (2007) Setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs as regards Fusarium toxins in maize and maize products. Comm Eur Communities 1126:14–16
Frisvad JC (1983) A selective and indicative medium for groups of Penicillium viridicatum producing different mycotoxins in cereals. J Appl Bacteriol 54:409–416
Frisvad JC, Samson RA (2004) Polyphasic taxonomy of Penicillium subgenus Penicillium—A guide to identification of food and air-borne terverticillate Penicillia and their mycotoxins. Stud Mycol 49:1–173
Frisvad JC, Smedsgaard J, Samson RA, Larsen TO, Thrane U (2007) Fumonisin B2 production by Aspergillus niger. J Agric Food Chem 55:9727–9732
Gelderblom WCA, Jaskiewicz K, Marasas WFO, Thiel PG, Horak RM, Vleggaar R, Kriek NPJ (1988) Fumonisins-Novel mycotoxins with cancer-promoting activity produced by Fusarium moniliforme. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:1806–1811
Hocking AD, Pitt JI (1980) Dichloran glycerol medium for enumeration of xerophilic fungi from low moisture foods. Appl Environ Microbiol 39:488–492
Hodge KT, Krasnoff SB, Humber RA (1996) Tolypocladium inflatum is the anamorph of Cordyceps subsessilis. Mycologia 88:715–719
Isaac CE, Jones A, Pickard MA (1990) Production of cyclosporins by Tolypocladium niveum strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 34:121–127
Krasnoff SB, Gupta S, Stleger RJ, Renwick JAA, Roberts DW (1991) Antifungal and insecticidal properties of the efrapeptins—metabolites of the fungus Tolypocladium niveum. J Invertebr Pathol 58:180–188
Logrieco A, Doko B, Moretti A, Frisullo S, Visconti A (1998) Occurrence of fumonisin B1 and B2 in Fusarium proliferatum infected asparagus plants. J Agric Food Chem 46:5201–5204
Månsson M, Klejnstrup ML, Phipps RK, Nielsen KF, Frisvad JC, Gotfredsen CH, Larsen TO (2010) Isolation and NMR characterization of fumonisin B2 and a new fumonisin B6 from Aspergillus niger. J Agric Food Chem 58:949–953
Marasas WFO, Riley RT, Hendricks KA, Stevens VL, Sadler TW, Gelineau-van Waes J, Missmer SA, Cabrera J, Torres O, Gelderblom WCA, Allegood J, Martinez C, Maddox J, Miller JD, Starr L, Sullards MC, Roman AV, Voss KA, Wang E, Merrill Jr AH (2004) Fumonisins disrupt sphingolipid metabolism, folate transport, and neural tube development in embryo culture and in vivo: a potential risk factor for human neural tube defects among populations consuming fumonisin-contaminated maize. J Nutr 134:711–716
Marin S, Ramos AJ, Vazquez C, Sanchis V (2007) Contamination of pine nuts by fumonisin produced by strains of Fusarium proliferatum isolated from Pinus pinea. Lett Appl Microbiol 44:68–72
Martins ML, Martins HM, Bernardo F (2001) Fumonisins B1 and B2 in black tea and medicinal plants. J Food Prot 64:1268–1270
Mogensen JM, Frisvad JC, Thrane U, Nielsen KF (2010) Production of fumonisin B2 and B4 by Aspergillus niger on grapes and raisins. J Agric Food Chem 58:954–958
Mogensen JM, Larsen TO, Nielsen KF (2010) Widespread occurrence of the mycotoxin fumonisin B2 in wine. J Agric Food Chem 58:4853–4857
Mogensen JM, Nielsen KF, Samson RA, Frisvad JC, Thrane U (2009) Effect of temperature and water activity on the production of fumonisins by Aspergillus niger and different Fusarium species. BMC Microbiol 9:281
Musser SM, Gay ML, Mazzola EP, Plattner RD (1996) Identification of a new series of fumonisins containing 3-hydroxypyridine. J Nat Prod 59:970–972
Nielsen KF, Mogensen JM, Johansen M, Larsen TO, Frisvad JC (2009) Review of secondary metabolites and mycotoxins from the Aspergillus niger group. Anal Bioanal Chem 395:1225–1242
Nielsen KF, Smedsgaard J (2003) Fungal metabolite screening: database of 474 mycotoxins and fungal metabolites for dereplication by standardised liquid chromatography-UV-mass spectrometry methodology. J Chromatogr A 1002:111–136
Noonim P, Mahakarnchanakul W, Nielsen KF, Frisvad JC, Samson RA (2009) Fumonisin B2 production by Aspergillus niger from Thai coffee beans. Food Addit Contam 26:94–100
Park JW, Choi SY, Hwang HJ, Kim YB (2005) Fungal mycoflora and mycotoxins in Korean polished rice destined for humans. Int J Food Microbiol 103:305–314
Pel HJ, de Winde JH, Archer DB, Dyer PS, Hofmann G, Schaap PJ, Turner G, de Vries RP, Albang R, Albermann K, Andersen MR, Bendtsen JD, Benen JAE, van den Berg M, Breestraat S, Caddick MX, Contreras R, Cornell M, Coutinho PM, Danchin EGJ, Debets AJM, Dekker P, van Dijck PWM, Van Dijk A, Dijkhuizen L, Driessen AJM, d’Enfert C, Geysens S, Goosen C, Groot GSP, de Groot PWJ, Guillemette T, Henrissat B, Herweijer M, van den Hombergh JPTW, van den Hondel CAMJ, van der Heijden RTJM, van der Kaaij RM, Klis FM, Kools HJ, Kubicek CP, van Kuyk PA, Lauber J, LU X, van der Maarel MJEC, Meulenberg R, Menke H, Mortimer MA, Nielsen J, Oliver SG, Olsthoorn M, Pal K, van Peij NNME, Ram AFJ, Rinas U, Roubos JA, Sagt CMJ, Schmoll M, Sun JB, Ussery D, Varga J, Vervecken W, de Vondervoort PJJV, Wedler H, Wösten HAB, Zeng AP, van Ooyen AJJ, Visser J, Stam H (2007) Genome sequencing and analysis of the versatile cell factory Aspergillus niger CBS 513.88. Nat Biotechnol 25:221–231
Rheeder JP, Marasas WFO, Vismer HF (2002) Production of fumonisin analogs by Fusarium species. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:2101–2105
Samson RA, Houbraken J, Thrane U, Frisvad JC, Andersen B (2010) Food and indoor fungi. CBS-KNAW Fungal Biodiversity Centre, Utrecht
Samson RA, Soares GG (1984) Entomopathogenic species of the hyphomycete genus Tolypocladium. J Invertebr Pathol 43:133–139
Scott PM, Lawrence GA (1995) Analysis of beer for fumonisins. J Food Prot 58:1379–1382
Simmons EG (2007) Alternaria. An identification manual. CBS-KNAW Fungal Biodiversity Centre, Utrecht
Solfrizzo M, de Girolamo A, Vitti C, Tylkowska K, Grabarkiewicz-Szczesna J, Szopinska D, Dorna H (2005) Toxigenic profile of Alternaria alternata and Alternaria radicina occurring on umbelliferous plants. Food Addit Contam 22:302–308
Stack ME (1998) Analysis of fumonisin B1 and its hydrolysis product in tortillas. J AOAC Int 81:737–740
Strasser H, Vey A, Butt TM (2000) Are there any risks in using entomopathogenic fungi for pest control, with particular reference to the bioactive metabolites of Metarhizium, Tolypocladium and Beauveria species? Biocontrol Sci Tech 10:717–735
Sung G-H, Hywel-Jones NL, Sung J-M, Luangsa-ard JJ, Shrestha B, Spatafora JW (2007) Phylogenetic classification of Cordyceps and the clavicipitaceous fungi. Stud Mycol 57:5–59
Sydenham EW, Shephard GS, Thiel PG, Marasas WFO, Stockenstrom S (1991) Fumonisin contamination of commercial corn-based human foodstuffs. J Agric Food Chem 39:2014–2018
US Food and Drug Administration (2001) Guidance for industry: fumonisin levels in human foods and animal feeds. United States Food and Drug Administration, Washington, DC
Vishwanath V, Sulyok M, Labuda R, Bicker W, Krska R (2009) Simultaneous determination of 186 fungal and bacterial metabolites in indoor matrices by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 395:1355–1372
Voss KA, Riley RT, Snook ME, Gelineau-van Waes J (2009) Reproductive and sphingolipid metabolic effects of fumonisin B1 and its alkaline hydrolysis product in LM/Bc mice: hydrolyzed fumonisin B1 did not cause neural tube defects. Toxicol Sci 112:459–467
Wild CP, Gong YY (2010) Mycotoxins and human disease: a largely ignored global health issue. Carcinogenesis 31:71–82
Zhu XC, Vogeler C, Du LC (2008) Functional complementation of fumonisin biosynthesis in FUM1-disrupted Fusarium verticillioides by the AAL-toxin polyketide synthase gene ALT1 from Alternaria alternata f. sp. lycopersici. J Nat Prod 71:957–960
Acknowledgments
J. M. M. and K. F. N. were funded by the Danish Food Industry Agency (grant 3304-FVEP-07-730-01). The Danish Research Council for Technology and Production Sciences (grant 274-08-0021) and EEC project MycoRed (KBBE-2007-222690-2) are acknowledged for financial support. A. K. was funded by MSM 0021620828. Dr. Techn. A. N. Neergaards & Hustrus Fond is acknowledged for its support of the LC–MS/MS instrument.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mogensen, J.M., Møller, K.A., von Freiesleben, P. et al. Production of fumonisins B2 and B4 in Tolypocladium species. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 38, 1329–1335 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-010-0916-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-010-0916-1