Abstract
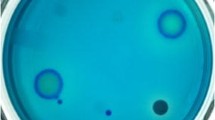
ε-poly-l-lysine (ε-PL) is a homo-poly-amino acid of l-lysine which is used as a safe food preservative. The productivity of ε-PL in currently reported wild type strains is low. This study was aimed at finding novel ε-PL producing strains with higher productivity and new fermentative characters. An improved detection method was employed using methylene blue as an ε-PL secretion indicator. 137 strains forming transparent circles were isolated. The best one was identified as Streptomyces griseofuscus according to the morphological characteristics and the comparison of internal transcribed spacer (ITS) ribosomal DNA (rDNA) gene sequences. The fermentative behavior of S. griseofuscus was investigated, and the ε-PL production was enhanced to 2.3 g/L in 5-L bioreactor by a pH control strategy. The yield of ε-PL reached 7.5 g/L in the fed-batch process. Compared with the reported wild type strains, S. griseofuscus produced relatively higher amounts of ε-PL, and might be a promising Streptomyces for ε-PL production.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hiraki J, Ichikawa T, Ninomiya S (2003) Use of ADME studies to confirm the safety of polylysine as a preservative in food. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 37:328–340
Shih IL, Shen MH (2006) Microbial synthesis of poly (ε-lysine) and its various applications. Bioresour Technol 97:1148–1159
Shima S, Sakai H (1977) Polylysine produced by Streptomyces. Agric Biol Chem 41:1807–1809
Nishikawa M, Ogawa K (2002) Distribution of microbes producing antimicrobial ε-Poly-l-Lysine polymers in soil microflora determined by a novel method. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:3575–3581
Holt JG, Krieg NR, Sneath PHA, Staley JT, Williams ST (1994) Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology, 9th edn. The Williams and Wilkins Company, Baltimore
Hirohara H, Takehara M, Saimura M, Masayuki A, Miyamoto M (2006) Biosynthesis of poly(ɛ-l-lysine)s in two newly isolated strains of Streptomyces sp. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 73:321–331
Shima S, Sakai H (1981) Poly-l-lysine Produced by Streptomyces. Part III. Chemical studies. Agric Biol Chem 45:2497–2502
Itzhaki RF (1972) Colorimetric method for estimating poly-lysine and polyarginine. Anal Biochem 50:569–574
Shima S, Sakai H (1981) Poly-l-lysine Produced by Streptomyces. Part II. Taxonomy and fermentation studies. Agric Biol Chem 45:2503–2508
Duan S, Zhu WS (2007) Isolating of a ε-Polylysine-producing strain. Food Ferment Ind 33:14–17
Zhu HY, Xu H, Wu Q (2005) Screening and identification of ε-PL producing strain. Microbiol 32:127–130
Zhang C, Zhang DR (2006) A Simple and sensitive method for screening ε-PL producing strains from soils. J Shandong Univ 44:1104–1107
Kahar P, lwata T, Hiraki J (2001) Enhancement of ε-poly-l-lysine production by Streptomyces albulus strain 410 using pH control. J Biosci Bioeng 91:190–194
Kito M, Takimoto R, Yoshida T, Nagasawa T (2002) Purification and characterization of ε-poly-l-lysine-degrading enzyme from an ε-poly-l-lysine-producing strain Streptomyces albulus. Arch Microbiol 178:325–330
Zhang Y et al (2010) ε-Poly-l-Lysine production by immobilized cells of Kitasatospora sp. MY 5-36 in repeated fed-batch cultures. Bioresour Technol. doi:10,1016/j.biortech,2010.02.021
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Tang, L., Chen, X. et al. Isolation and characterization of a novel ε-poly-l-lysine producing strain: Streptomyces griseofuscus . J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 38, 557–563 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-010-0803-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-010-0803-9