Abstract
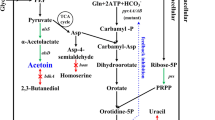
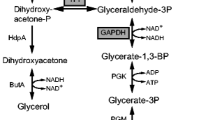
In this study, the effects of citrate addition on d-ribose production were investigated in batch culture of a transketolase-deficient strain, Bacillus subtilis EC2, in shake flasks and bioreactors. Batch cultures in shake flasks and a 5-l reactor indicated that supplementation with 0.2–0.5 g l−1 of citrate enhanced d-ribose production. When B. subtilis EC2 was cultivated in a 15-l reactor in a complex medium, the d-ribose concentration was 70.9 g l−1 with a ribose yield of 0.497 mol mol−1. When this strain was grown in the same medium supplemented with 0.3 g l−1 of citrate, 83.4 g l−1 of d-ribose were obtained, and the ribose yield was increased to 0.587 mol mol−1. Addition of citrate reduced the activities of pyruvate kinase and phosphofructokinase, while it increased those of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase. Metabolic flux distribution in the stationary phase indicated that citrate addition resulted in increased fluxes in the pentose phosphate pathway and TCA cycle, and decreased fluxes in the glycolysis and acetate pathways.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babul J (1978) Phosphofructokinases from Escherichia coli. Purification and characterization of the nonallosteric isozyme. J Biol Chem 253:4350–4355
Bergmeyer HU (1983) Methods of enzymatic analysis, vol 3. Verlag Chemie, Berlin
Blangy D, Buc H, Monod J (1968) Kinetics of the allosteric interactions of phosphofructokinase from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol 31:13–35. doi:10.1016/0022-2836(68)90051-X
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Chen SX, Chu J, Zhuang YP, Zhang SL (2005) Enhancement of inosine production by Bacillus subtilis through suppression of carbon overflow by sodium citrate. Biotechnol Lett 27:689–692. doi:10.1007/s10529-005-4686-1
Dauner M, Sauer U (2001) Stoichiometric growth model for riboflavin-producing Bacillus subtilis. Biotechnol Bioeng 76:132–143. doi:10.1002/bit.1153
De Wulf P, Soetaert W, Schwengers D, Vandamme EJ (1996) d-glucose does not catabolite repress a transketolase-deficient d-ribose-producing Bacillus subtilis mutant strain. J Ind Microbiol 17:104–109. doi:10.1007/BF01570052
De Wulf P, Soetaert W, Schwengers D, Vandamme EJ (1996) Screening and mutational improvement of a d-ribose secreting Candida pelliculosa strain. J Ferment Bioeng 82:1–7. doi:10.1016/0922-338X(96)89446-3
De Wulf P, Vandamme EJ (1997) Production of d-ribose by fermentation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 48:141–148. doi:10.1007/s002530051029
De Wulf P, Soetaert W, Schwengers D, Vandamme EJ (1997) Optimization of d-ribose production with a transketolase-affected Bacillus subtilis mutant strain in glucose and gluconic acid-based media. J Appl Microbiol 83:25–30. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2672.1997.00161.x
Diesterhaft MD, Freese E (1973) Role of pyruvate carboxylase, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, and malic enzyme during growth and sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem 248:6062–6070
Dittrich CR, Bennett GN, San KY (2005) Characterization of the acetate-producing pathways in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Prog 21:1062–1067. doi:10.1021/bp050073s
Evans PR, Hudson PJ (1979) Structure and control of phosphofructokinase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Nature 279:500–504. doi:10.1038/279500a0
Evans PR, Farrants GW, Hudson PJ (1981) Phosphofructokinase: structure and control. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 293:53–62. doi:10.1098/rstb.1981.0059
Goel A, Lee J, Domach MM, Ataai MM (1995) Suppressed acid formation by cofeeding of glucose and citrate in Bacillus culture: emergence of pyruvate kinase as a potential metabolic engineering site. Biotechnol Prog 11:380–385. doi:10.1021/bp00034a003
Goel A, Lee J, Domach MM, Ataai MM (1999) Metabolic fluxes, pools and enzyme measurements suggest a tighter coupling of energetics and biosynthetic reactions associated with reduced pyruvate kinase flux. Biotechnol Bioeng 64:129–134. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0290(19990720)64:2<129::AIDBIT1>3.0.CO;2-I
Habison A, Kubicek CP, Röhr M (1983) Partial purification and regulatory properties of phosphofructokinase from Aspergillus niger. Biochem J 209:669–676. doi:0306-3275/83/030669-08$2.00
Han K, Lim HC, Hong J (1991) Acetate acid formation in Escherichia coli fermentation. Biotechnol Bioeng 39:663–671. doi:10.1002/bit.260390611
Han L, Doverskog M, Enfors SO, Häggström L (2002) Effect of glycine on the cell yield and growth rate of Escherichia coli: evidence for cell-density-dependent glycine degradation as determined by 13C NMR spectroscopy. J Biotechnol 92:237–249. doi:10.1016/S0168-1656(01)00373-X
Kachmar JF, Boyer PD (1953) Kinetic analysis of enzyme reactions II. The potassium activation and calcium inhibition of pyruvic phosphoferase. J Biol Chem 200:669–682
Kemp RG, Foe LG (1983) Allosteric regulatory properties of muscle phosphofructokinase. Mol Cell Biochem 57:147–154. doi:10.1007/BF00223529
Kishimoto K, Kintaka K, Uchiyama N (1990) Production of d-ribose. US patent 4904587
Krom BP, Warner JB, Konings WN, Lolkema JS (2000) Complementary metal ion specificity of the metal-citrate transporters CitM and CitH of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 182:6374–6381. doi:0021-9193/00/$04.00+0
Lee YN, Lessie TG (1974) Purification and characterization of the two 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase species from Psedomonas multivorans. J Bacteriol 120:1043–1057
Li H, Pajor AM (2002) Functional characterization of CitM, the Mg2+-citrate transporter. J Membr Biol 185:9–16. doi:10.1007/s00232-001-0106-1
Miyagawa K, Miyazaki J, Kanzaki N (1992) Method of producing d-ribose. European patent 0501765 A1
Newsholme EA, Sugden PH, Williams T (1977) Effect of citrate on the activities of 6-phosphofructokinase from nervous and muscle tissues from different animals and its relationship to the regulation of glycolysis. Biochem J 166:123–129
Park YC, Kim SG, Park K, Lee KH, Seo JH (2004) Fed-batch production of d-ribose from sugar mixtures by transketolase-deficient Bacillus subtilis SPK1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 66:297–302. doi:10.1007/s00253-004-1678-3
Park YC, Choi JH, Bennett GN, Seo JH (2006) Characterization of d-ribose biosynthesis in Bacillus subtilis JY200 deficient in transketolase gene. J Biotechnol 121:508–516. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2005.08.003
Peng L, Shimizu K (2003) Global metabolic regulation analysis for Escherichia coli K12 based on protein expression by 2-dimensional electrophoresis and enzyme activity measurement. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 61:163–178. doi:10.1007/s00253-002-1202-6
Peng Y, Wu Z, Li Y (2002) A method for the determination of d-ribose concentration in microbial fermented broth by spectrophotometry. Chin J Anal Chem 30:975-977. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3820.2002.08.020
Sasajima K, Yoneda M (1971) Carbohydrate metabolism-muntants of a Bacillus species. Part II. d-ribose accumulation by pentose phosphate pathway mutant. Agric Biol Chem 35:509–517
Sasajima K, Yoneda M (1989) Production of d-ribose by microorganism. In: Vandamme EJ (ed) Biotechnology of vitamin, pigments and growth factors. Elsevier Science Publishing Co., New York, pp 167–197
Srivastava RK, Wangikar PP (2008) Combined effects of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus substrates on d-ribose production via transketolase deficient strain of Bacillus pumilus. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 83:1110–1119. doi:10.1002/jctb.1936
Suárez DC, Liria CW, Kilikian BV (1998) Effect of yeast extract on Escherichia coli growth and acetic acid production. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 14:331–335. doi:10.1023/A:1008800908696
Wood WA (1982) Methods in enzymology. Academic Press, New York
Acknowledgment
This work was partly supported by the Project of Shanghai Leading Academic Disciplines, no. B505.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, L., Li, Z. & Ye, Q. Enhanced d-ribose biosynthesis in batch culture of a transketolase-deficient Bacillus subtilis strain by citrate. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 36, 1289–1296 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-009-0612-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-009-0612-1