Abstract
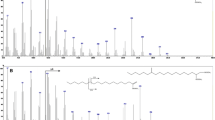
The polar lipid fatty acids, lipopolysaccharide hydroxy-fatty acids, and respiratory quinones of Geobacter metallireducens str. GS-15, Geobacter sulfurreducens str. PCA, and Geobacter bemidjiensis str. Bem are reported. Also, the lipids of G. metallireducens were compared when grown with Fe3+ or nitrate as electron acceptors and G. sulfurreducens with Fe3+ or fumarate. In all experiments, the most abundant polar lipid fatty acids were 14:0, i15:0, 16:1ω7c, 16:1ω5c, and 16:0; lipopolysaccharide hydroxy-fatty acids were dominated by 3oh16:0, 3oh14:0, 9oh16:0, and 10oh16:0; and menaquinone-8 was the most abundant respiratory quinone. Some variation in lipid profiles with strain were observed, but not with electron acceptor.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LPS ohFA:
-
Lipopolysaccharide hydroxy-fatty acids
- PLFA:
-
Polar lipid fatty acids
- MK:
-
Menaquinone
References
Balch WE, Fox GE, Magrum LJ, Woese CR, Wolfe RS (1979) Methanogens: reevaluation of a unique biological group. Microbiol Rev 43:260–296
Belyakova E, Rozanova E, Borzenkov I, Tourova T, Pusheva M, Lysenko A et al (2006) The new facultatively chemolithoautotrophic, moderately halophilic, sulfate-reducing bacterium Desulfovermiculus halophilus gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from an oil field. Microbiology 75:161–171. doi:10.1134/S0026261706020093
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol 37:911–917
Caccavo F, Lonergan DJ, Lovley DR, Davis M, Stolz JF, McInerney MJ (1994) Geobacter sulfurreducens sp. nov., a hydrogen- and acetate-oxidizing dissimilatory metal-reducing microorganism. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:3752–3759
Collins MD, Jones D (1981) Distribution of isoprenoid quinone structural types in bacteria and their taxonomic implications. Microbiol Rev 45:316–354
Dowling NJE, Widdel F, White DC (1986) Phospholipid ester-linked fatty acid biomarkers of acetate-oxidizing sulfate reducers and other sulfide forming bacteria. J Gen Microbiol 132:1815–1825
Edlund A, Nichols PD, Roffky R, White DC (1985) Extractable and lipopolysaccharide fatty acid and hydroxy acid profiles from Desulfovibrio species. J Lipid Res 26:982–988
Feio MJ, Beech IB, Carepo M, Lopes JM, Cheung CWS, Franco R et al (1998) Isolation and characterization of a novel sulphate-reducing bacterium of the Desulfovibrio genus. Anaerobe 4:117–130. doi:10.1006/anae.1997.0142
Geyer R, Peacock AD, White DC, Lytle C, Van Berkel GJ (2004) Atmospheric pressure chemical ionization and atmospheric pressure photoionization for simultaneous mass spectrometric analysis of microbial respiratory ubiquinones and menaquinones. J Mass Spectrom 39:922–929. doi:10.1002/jms.670
Guckert JB, Antworth CP, Nichols PD, White DC (1985) Phospholipid, ester-linked fatty acid profiles as reproducible assays for changes in prokaryotic community structure of estuarine sediments. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 31:147–158
Hatchikian EC (1974) On the role of menaquinone-6 in the electron transport of hydrogen: fumarate reductase system in the strict anaerobe Desulfovibrio gigas. J Gen Microbiol 81:261–266
Hedrick DB, Guckert JB, White DC (1991) Archaebacterial ether lipid diversity analyzed by supercritical fluid chromatography: integration with a bacterial lipid protocol. J Lipid Res 32:659–666
Lien T, Madsen M, Steen IH, Gjerdevik K (1998) Desulfobulbus rhabdoformis sp. nov., a sulfate reducer from a water–oil separation system. Int J Syst Bacteriol 48:469–474
Lin WC, Coppi MV, Lovley DR (2004) Geobacter sulfurreducens can grow with oxygen as a terminal electron acceptor. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:2525–2528. doi:10.1128/AEM.70.4.2525-2528.2004
Londry KL, Jahnke LL, Des Marais DJ (2004) Stable carbon isotope ratios of lipid biomarkers of sulfate-reducing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:745–751. doi:10.1128/AEM.70.2.745-751.2004
Louie TM, Mohn WW (1999) Evidence for a chemiosmotic model of dehalorespiration in Desulfomonile tiedjei DCB-1. J Bacteriol 181:40–46
Lovley DR, Fraga JL, Coates JD, Blunt-Harris EL (1999) Humics as an electron donor for anaerobic respiration. Environ Microbiol 1:89–98. doi:10.1046/j.1462-2920.1999.00009.x
Lovely DR, Giovannoni SJ, White DC, Champine JE, Phillips EJP, Gorby YA et al (1993) Geobacter metallireducens gen. nov. sp. nov., a microorganism capable of coupling the complete oxidation of organic compounds to the reduction of iron and other metals. Arch Microbiol 159:336–344
Lovley DR, Phillips EJP (1988) Novel mode of microbial energy metabolism: organic carbon oxidation coupled to dissimilatory reduction of iron or manganese. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:1472–1480
Maroc J, Azerad R, Kamen D, Gall JL (1970) Menaquinone (MK-6) in the sulfate- reducing obligate anaerobes, Desulfovibrio. Biochim Biophys Acta 197:87–89. doi:10.1016/0005-2728(70)90012-5
Mikoulinskaia O, Akimenko V, Galouchko A, Thauer RK, Hedderich R (1999) Cytochrome c-dependent methacrylate reductase from Geobacter sulfurreducens AM-1. Eur J Biochem 263:346–352. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1327.1999.00489.x
Mohanty SR, Kollah B, Hedrick DB, Peacock AD, Kukkadapu RK, Roden EE (2008) Biogeochemical processes in ethanol stimulated uranium-contaminated subsurface sediments. Environ Sci Technol 42:4384–4390. doi:10.1021/es703082v
Nevin KP, Holmes DE, Woodard TL, Hinlein ES, Ostendorf DW, Lovley DR (2005) Geobacter bemidjiensis sp. nov. and Geobacter psychrophilus sp. nov., two novel Fe(III)-reducing subsurface isolates. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1667–1674. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.63417-0
Nichols PD, Guckert JB, White DC (1986) Determination of monounsaturated fatty acid double-bond position and geometry for microbial monocultures and complex consortia by capillary GC-MS of their dimethyl disulphide adducts. J Microbiol Methods 5:49–55. doi:10.1016/0167-7012(86)90023-0
North NN, Dollhopf SL, Petrie L, Istok JD, Balkwill DL, Kostka JE (2004) Change in bacterial community structure during in situ biostimulation of subsurface sediment cocontaminated with uranium and nitrate. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:4911–4920. doi:10.1128/AEM.70.8.4911-4920.2004
Nottingham PM, Hungate RE (1969) Methanogenic fermentation of benzoate. J Bacteriol 98:1170–1172
Parker JH, Smith GA, Fredrickson HL, Vestal JR, White DC (1982) Sensitive assay, based on hydroxy fatty acids from lipopolysaccharide lipid A, for gram-negative bacteria in sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 44:1170–1177
Peacock AD, Chang Y-J, Istok JD, Krumholz L, Geyer R, Kinsall B et al (2004) Utilization of microbial biofilms as monitors of bioremediation. Microb Ecol 47:284–292. doi:10.1007/s00248-003-1024-9
Peacock AD, Mullen MD, Ringelberg DB, Tyler DD, Hedrick DB, Gale PM et al (2000) Soil microbial community responses to dairy manure or ammonium nitrate applications. Soil Biol Biochem 33:1011–1019. doi:10.1016/S0038-0717(01)00004-9
Reguera G, Nevin KP, Nicoll JS, Covalla SF, Woodard TL, Lovley DR (2006) Biofilm and nanowire production lead to increased current in microbial fuel cells. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:7345–7348. doi:10.1128/AEM.01444-06
Sakaguchi T, Arakaki A, Matsunaga T (2002) Desulfovibrio magneticus sp. nov., a novel sulfate-reducing bacterium that produces intracellular single-domain-sized magnetite particles. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:215–221
Sung Y, Fletcher KE, Ritalahti KM, Apkarian RP, Ramos-Hernández N, Sanford RA et al (2006) Geobacter lovleyi sp. nov. strain SZ, a novel metal-reducing and tetrachloroethene-dechlorinating bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:2775–2782. doi:10.1128/AEM.72.4.2775-2782.2006
Suzuki D, Ueki A, Amaishi A, Ueki K (2007) Desulfopila aestuarii gen. nov., sp. nov., a Gram-negative, rod-like, sulfate-reducing bacterium isolated from an estuarine sediment in Japan. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:520–526. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.64600-0
Taylor J, Parkes RJ (1983) The cellular fatty acids of the sulphate-reducing bacteria, Desulfobacter sp., Desulfobulbus sp. and Desulfovibrio desulfuricans. J Gen Microbiol 129:3303–3309
Weber MM, Matachiner JT, Peck HD (1970) Menaquinone-6 in the strict anaerobes Desulfovibrio vulgaris and Desulfovibrio gigas. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 38:197–204. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(70)90696-0
Zhang CL, Li Y, Ye Q, Fong J, Peacock AD, Blunt E et al (2003) Carbon isotope signatures of fatty acids in Geobacter metallireducens and Shewanella algae. Chem Geol 195:17–28. doi:10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00386-8
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Office of Science of the US Department of Energy, Biological and Environmental Research, grant DE-FG02-04ER63719.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
D. C. White: Deceased.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hedrick, D.B., Peacock, A.D., Lovley, D.R. et al. Polar lipid fatty acids, LPS-hydroxy fatty acids, and respiratory quinones of three Geobacter strains, and variation with electron acceptor. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 36, 205–209 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-008-0486-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-008-0486-7