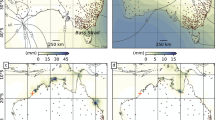
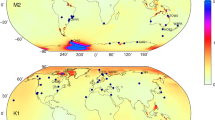
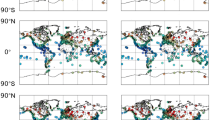
Abstract
The Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) can monitor earth deformation at different frequencies, including sub-diurnal, fortnightly and seasonal bands. In standard 24-h GNSS data processing, we correct ocean tide loading (OTL) displacements by conventional models. Errors in the OTL modeling may lead to incorrect geophysical interpretation of observed displacements due to residual sub-daily OTL signals propagated to longer periods. OTL models and propagated signals have been studied mainly using GPS data, which introduce systematic errors at K1 and K2 tidal periods. We analyze the OTL residual displacements of eight major diurnal and semidiurnal tides derived from the FES2014b ocean tide atlas, using GPS, Galileo and GLONASS observations, and comparing both kinematic and static estimation approaches. The static method appears to be the most reliable way to retrieve the OTL residuals from other error sources with lower formal uncertainty. For the K1, K2 and S2 tides, the agreement improves by up to 55% when using Galileo and/or GLONASS, compared to GPS. We implemented an optimal weighting strategy with downweighted GPS contribution to the observation of K1/K2 for improving the estimation of the residual OTL errors. Several spurious signals appear for GPS, Galileo and GLONASS at the fortnightly band resulting from the propagation of mismodeled OTL. Estimating residual tidal coefficients alongside the 24-h static station positions mitigates the spectral power of these signals. Additional spurious signals appear at harmonics of the Galileo and GLONASS constellation repeat periods of 10 and 8 sidereal days, respectively. These signals cannot be attributed to mismodeled OTL.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
RINEX were obtained through the online archives of the Crustal Dynamics Data Information System (CDDIS) https://cddis.nasa.gov/archive/gnss/data/daily/. The orbit and clock products were provided by the GRGS Analysis Center.
References
Abbaszadeh M, Clarke PJ, Penna NT (2020) Benefits of combining GPS and GLONASS for measuring ocean tide loading displacement. J Geodesy 94(7):63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-020-01393-5
Abraha KE, Teferle FN, Hunegnaw A, Dach R (2018) Effects of unmodelled tidal displacements in GPS and GLONASS coordinate time-series. Geophy J Int 214(3):2195–2206. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggy254
Blewitt G (2003) Self-consistency in reference frames, geocenter definition, and surface loading of the solid Earth. J Geophys Res Solid Earth. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002JB002082
Bos MS, Penna NT, Baker TF, Clarke PJ (2015) Ocean tide loading displacements in western Europe: 2. GPS-observed anelastic dispersion in the asthenosphere. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 120(9):6540–6557. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015JB011884
Choi K, Bilich A, Larson KM, Axelrad P (2004) Modified sidereal filtering: implications for high-rate GPS positioning. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004GL021621
Collilieux X, Altamimi Z, Coulot D, Ray J, Sillard P (2007) Comparison of very long baseline interferometry, GPS, and satellite laser ranging height residuals from ITRF2005 using spectral and correlation methods. J Geophys Res Solid Earth. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007JB004933
Dong D, Fang P, Bock Y, Cheng MK, Miyazaki S (2002) Anatomy of apparent seasonal variations from GPS-derived site position time series. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 107(B4):ETG9-1-ETG9-16. https://doi.org/10.1029/2001JB000573
Fu Y, Freymueller JT, van Dam T (2012) The effect of using inconsistent ocean tidal loading models on GPS coordinate solutions. J Geodesy 86(6):409–421. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-011-0528-1
Haigh ID et al (2020) The tides they are A-Changin’: a comprehensive review of past and future nonastronomical changes in tides, their driving mechanisms, and future implications. Rev Geophys 58(1):e2018RG000636. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018RG000636
Katsigianni G, Loyer S, Perosanz F (2019a) PPP and PPP-AR kinematic post-processed performance of GPS-only, Galileo-only and multi-GNSS. Remote Sens 11(21):2477. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11212477
Katsigianni G, Loyer S, Perosanz F, Mercier F, Zajdel R, Sośnica K (2019b) Improving Galileo orbit determination using zero-difference ambiguity fixing in a Multi-GNSS processing. Adv Space Res 63(9):2952–2963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2018.08.035
King M (2006) Kinematic and static GPS techniques for estimating tidal displacements with application to Antarctica. J Geodyn 41(1):77–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jog.2005.08.019
King MA, Penna NT, Clarke PJ, King EC (2005) Validation of ocean tide models around Antarctica using onshore GPS and gravity data. J Geophys Res Solid Earth. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004JB003390
King MA, Watson C (2010) Long GPS coordinate time series: multipath and geometry effects. J Geophys Res Solid Earth. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009jb006543
Koulali A, Clarke PJ (2020) Effect of antenna snow intrusion on vertical GPS position time series in Antarctica. J Geodesy 94(10):101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-020-01403-6
Li F, Lei J, Zhang S, Ma C, Hao W, E D, Zhang Q (2018) The impact of solid Earth-tide model error on tropospheric zenith delay estimates and GPS coordinate time series. Surv Rev 50(361): 355–363. https://doi.org/10.1080/00396265.2016.1277657
Loyer S, Perosanz F, Mercier F, Capdeville H, Marty J-C (2012) Zero-difference GPS ambiguity resolution at CNES–CLS IGS analysis center. J Geodesy 86(11):991–1003. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-012-0559-2
Lyard FH, Allain DJ, Cancet M, Carrère L, Picot N (2021) FES2014 global ocean tides atlas: design and performances. Ocean Sci. https://doi.org/10.5194/os-17-615-2021
Martens HR, Simons M, Owen S, Rivera L (2016) Observations of ocean tidal load response in South America from subdaily GPS positions. Geophy J Int 205(3):1637–1664. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggw087
Marty JC et al (2011) GINS: the CNES/GRGS GNSS scientific software. In: 3rd international colloquium scientific and fundamental aspects of the galileo programme, ESA proceedings WPP326, vol. 31, pp 8–10
Matviichuk B, King M, Watson C (2020) Estimating ocean tide loading displacements with GPS and GLONASS. Solid Earth 11(5):1849–1863. https://doi.org/10.5194/se-11-1849-2020
Melachroinos SA et al (2008) Ocean tide loading (OTL) displacements from global and local grids: comparisons to GPS estimates over the shelf of Brittany, France. J Geodesy 82(6):357–371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-007-0185-6
Niu Y, Li M, Wei N, Shi C, Chen G, Wang L (2021) The ocean pole tide loading and its effect on GPS position time-series. Geophy J Int 227(1):368–382. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggab231
Penna NT, Clarke PJ, Bos MS, Baker TF (2015) Ocean tide loading displacements in western Europe: 1. Validation of kinematic GPS estimates. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 120(9):6523–6539. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015JB011882
Penna NT, King MA, Stewart MP (2007) GPS height time series: short-period origins of spurious long-period signals. J Geophys Res Solid Earth. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005JB004047
Penna NT, Stewart MP (2003) Aliased tidal signatures in continuous GPS height time series. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003GL018828
Petit G, Luzum B (2010) IERS conventions. IERS Technical Note 36, Verlag des Bundesamts für Kartographie und Geodäsie, Germany
Pineau-Guillou L, Lazure P, Wöppelmann G (2021) Large-scale changes of the semidiurnal tide along North Atlantic coasts from 1846 to 2018. Ocean Sci 17(1):17–34. https://doi.org/10.5194/os-17-17-2021
Ragheb AE, Clarke PJ, Edwards SJ (2007) GPS sidereal filtering: coordinate- and carrier-phase-level strategies. J Geodesy 81(5):325–335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-006-0113-1
Ray J, Altamimi Z, Collilieux X, van Dam T (2008) Anomalous harmonics in the spectra of GPS position estimates. GPS Solut 12(1):55–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-007-0067-7
Rebischung P, Collilieux X, Metivier L, Altamimi Z, Chanard K (2021) Analysis of IGS REPRO3 station position time series. In: AGU 2021 Fall Meeting https://doi.org/10.1002/essoar.10509008.1
Sahin M, Cross PA, Sellers PC (1992) Variance component estimation applied to satellite laser ranging. Bull Géodésique 66(3):284–295. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02033189
Sidorov D, Teferle FN (2015) Impact of antenna phase centre calibrations on position time series: preliminary results. In: international association of geodesy symposia, Springer International Publishing. pp 117–123 https://doi.org/10.1007/1345_2015_216
Stewart MP, Penna NT, Lichti DD (2005) Investigating the propagation mechanism of unmodelled systematic errors on coordinate time series estimated using least squares. J Geodesy 79(8):479–489. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-005-0478-6
Thomas ID, King MA, Clarke PJ (2007) A comparison of GPS, VLBI and model estimates of ocean tide loading displacements. J Geodesy 81(5):359–368. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-006-0118-9
Tregoning P, Watson C (2009) Atmospheric effects and spurious signals in GPS analyses. J Geophys Res Solid Earth. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JB006344
Vergnolle M, Bouin M-N, Morel L, Masson F, Durand S, Nicolas J, Melachroinos SA (2008) GPS estimates of ocean tide loading in NW-France: determination of ocean tide loading constituents and comparison with a recent ocean tide model. Geophy J Int 173(2):444–458. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2008.03734.x
Wang K, Chen H, Jiang W, Li Z, Ma Y, Deng L (2018) Improved vertical displacements induced by a refined thermal expansion model and its quantitative analysis in GPS height time series. J Geophys Eng 15(2):554–567. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-2140/aa93ae
Watson C, Tregoning P, Coleman R (2006) Impact of solid Earth tide models on GPS coordinate and tropospheric time series. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005GL025538
Wei G, Chen K, Ji R (2021) Improving estimates of ocean tide loading displacements with multi-GNSS: a case study of Hong Kong. GPS Solut 26(1):25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-021-01212-0
Yan H, Chen W, Zhu Y, Zhang W, Zhong M (2009) Contributions of thermal expansion of monuments and nearby bedrock to observed GPS height changes. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009GL038152
Yuan L, Chao BF, Ding X, Zhong P (2013) The tidal displacement field at Earth’s surface determined using global GPS observations. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 118(5):2618–2632. https://doi.org/10.1002/jgrb.50159
Zajdel R, Kazmierski K, Sośnica K (2022) Orbital artifacts in multi-GNSS precise point positioning time series. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 127(2):e2021JB022994. https://doi.org/10.1029/2021JB022994
Zhou M, Liu X, Yuan J, Jin X, Niu Y, Guo J, Gao H (2021) Seasonal variation of GPS-derived the principal ocean tidal constituents’ loading displacement parameters based on moving harmonic analysis in Hong Kong. Remote Sens 13(2):279. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13020279
Zumberge JF, Heflin MB, Jefferson DC, Watkins MM, Webb FH (1997) Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 102(B3):5005–5017. https://doi.org/10.1029/96JB03860
Acknowledgements
We thank comments by Dr. Nigel Penna, an anonymous reviewer, and the handling editor Dr. Alfred Leick that increased the quality and clarity of this manuscript. We are grateful to Prof. Jean-Paul Boy from Ecole et Observatoire des Sciences de la Terre (EOST), France, for providing the program to compute the ocean tide loading corrections. We also thank Jim Ray for helpful comments on an early version of the manuscript. This work was supported by Region Occitanie and the Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales (CNES).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HA-L, AS-G and FP contributed to the design of the study. HA undertook software modifications, GNSS data processing, and drafted the preliminary manuscript. HA-L, AS-G and FP participated in the analysis of the results and reviewed the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
F. Perosanz: Formerly at GET, Université Paul Sabatier, CNES, CNRS, IRD, UPS, Toulouse, France.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ait-Lakbir, H., Santamaría-Gómez, A. & Perosanz, F. Assessment of sub-daily ocean tide loading errors and mitigation of their propagation in multi-GNSS position time series. GPS Solut 27, 129 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-023-01467-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-023-01467-9