Abstract
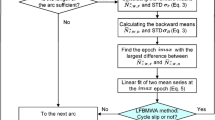
Since 2020, the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) has launched new precise point positioning service which provides precise correction of GPS and BDS-3 satellites to help users realize real-time precise point positioning, known as PPP-B2b service. After being fully operational for more than one year, this contribution comprehensively analyzes the performance of PPP-B2b in terms of correction availability, clock and orbit quality and positioning accuracy with PPP-B2b messages of nearly 48 weeks from 2021 to 2022. The results show that in the PPP-B2b service, the orbit radial differences of BDS-3 MEO, GPS, and BDS-3 IGSO satellites are 0.056 m, 0.069 m, and 0.172 m, respectively, compared to the GFZ final orbit, while the difference of along-track and cross-track is more than three times the radial. For BDS-3 MEO satellites from different manufacturers, the RMS of Satellite Laser Ranging (SLR) residuals is different, with a maximum of 0.11 m. Restricted by the regional tracking network, the correction series of PPP-B2b service are discontinuous, and there are constant satellite-specific clock biases in different arcs of the satellite. Thus, the STD and RMS of satellite clock offset and signal-in-space ranging error (SISRE) are calculated using the method of weighting by arcs. The STD of SISRE for BDS-3 MEO, GPS and BDS-3 IGSO are 0.059 m, 0.092 m and 0.174 m, respectively. A total of 108 days of observation data from 12 MGEX stations of the East Asia region are selected to analyze the positioning performance of PPP-B2b. The results of day-by-day static PPP are stable at the centimeter level, while the average convergence time of GPS-only (61.65 min) is longer than BDS-3-only (45.12 min), which the constant bias in clock offset may cause. To analyze the effect of this bias, the bias is calculated and used as a correction to the PPP-B2b clocks. The convergence time of BDS-3 and GPS positioning is reduced by 48.7% and 65.9%, respectively, after correcting this bias, which confirms the influence of clock constant bias on positioning convergence.





















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The BDS-3 CNAV1 broadcast ephemeris files are downloaded from the website of Test and Assessment Research Center of China Satellite Navigation Office (ftp://ftp2.csno-tarc.cn/cnav). And the LNAV ephemeris for GPS and the GFZ final product are downloaded from the Wuhan University Data Centre of IGS (ftp://igs.gnsswhu.cn/). All the MGEX observation data can be accessed from ftp://igs.gnsswhu.cn//pub/gps/data/daily/.
References
Borio, D., T. Senni and I. Fernandez-Hernandez (2020). Experimental Analysis of a Candidate Galileo E6-B Data Dissemination Scheme.In: Proceedings of ION ITM 2020, Institute of Navigation, San Diego, California, Jan 21–24, pp 509–520.
Chen G, Wei N, Li M, Zhao Q, Zhang J (2022) BDS-3 and GPS/Galileo integrated PPP using broadcast ephemerides. GPS Solut. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-022-01311-6
CSNO (2020). BeiDou Navigation Satellite System Signal In Space Interface Control Document Precise Point Positioning Service Signal PPP-B2b (Version 1.0). http://www.beidou.gov.cn/xt/gfxz/202008/P020200803362062482940.pdf
CSNO (2021) BeiDou Navigation Satellite System Open Service Performance Standard (Version 3.0). http://www.beidou.gov.cn/xt/gfxz/202105/P020210526216231136238.pdf
Dai et al., 2016 Dai L, Chen Y, Lie A, Zeitzew M, Yuki Z (2016) StarFire™ SF3: worldwide centimeter-accurate real time GNSS positioning. In: Proceedings of ION GNSS 2016, Institute of Navigation, Portland, Oregon, USA, Sept 12–16, pp 3295–3320
Gong X, Lou Y, Zheng F, Gu S, Shi C, Liu J, Jing G (2018) Evaluation and calibration of BeiDou receiver-related pseudorange biases. GPS Solut 22(4):98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-018-0765-3
Guo W, Zuo H, Mao F, Chen J, Gong X, Gu S, Liu J (2022) On the satellite clock datum stability of RT-PPP product and its application in one-way timing and time synchronization. J Geod. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-022-01638-5
Hadas T, Bosy J (2014) IGS RTS precise orbits and clocks verification and quality degradation over time. GPS Solut 19(1):93–105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-014-0369-5
Hadas T, Kazmierski K, Sośnica K (2019) Performance of Galileo-only dual-frequency absolute positioning using the fully serviceable Galileo constellation. GPS Solut. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-019-0900-9
Kazmierski K, Zajdel R, Sośnica K (2020) Evolution of orbit and clock quality for real-time multi-GNSS solutions. GPS Solut. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-020-01026-6
Leandro R et al (2011) RTX positioning: the next generation of cm-accurate real-time GNSS positioning. In: Proceedings of ION GNSS 2011, Institute of Navigation, Portland, Oregon, USA, Sept 20–23
Liu C et al (2020) Design and implementation of a BDS precise point positioning service. Navigation 67(4):875–891. https://doi.org/10.1002/navi.392
Liu Y, Yang C, Zhang M (2022) Comprehensive analyses of PPP-B2b performance in China and surrounding areas. Remote Sens. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030643
Lu X, Chen L, Shen N, Wang L, Jiao Z, Chen R (2021) Decoding PPP corrections from BDS B2b signals using a software-defined receiver: an initial performance evaluation. IEEE Sens J 21(6):7871–7883. https://doi.org/10.1109/jsen.2020.3041486
Malys S, Jensen PA (1990) Geodetic point positioning with gps carrier beat phase data from the CASA UNO experiment. Geophys Res Lett 17(5):651–654
Montenbruck O, Steigenberger P, Hauschild A (2014) Broadcast versus precise ephemerides: a multi-GNSS perspective. GPS Solut 19(2):321–333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-014-0390-8
Montenbruck O, Steigenberger P, Hauschild A (2018) Multi-GNSS signal-in-space range error assessment—Methodology and results. Adv Space Res 61(12):3020–3038. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2018.03.041
Montenbruck O et al (2017) The multi-GNSS experiment (MGEX) of the international GNSS Service (IGS)—achievements, prospects and challenges. Adv Space Res 59(7):1671–1697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2017.01.011
Nie Z, Liu F, Gao Y (2019) Real-time precise point positioning with a low-cost dual-frequency GNSS device. GPS Solut. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-019-0922-3
Nie Z, Wang B, Wang Z, He K (2020) An offshore real-time precise point positioning technique based on a single set of BeiDou short-message communication devices. J Geod. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-020-01411-6
Ren Z, Gong H, Peng J, Tang C, Huang X, Sun G (2021) Performance assessment of real-time precise point positioning using BDS PPP-B2b service signal. Adv Space Res 68(8):3242–3254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2021.06.006
Sośnica K, Zajdel R, Bury G, Bosy J, Moore M, Masoumi S (2020) Quality assessment of experimental IGS multi-GNSS combined orbits. GPS Solut. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-020-0965-5
Tang C, Hu X, Chen J, Liu L, Zhou S, Guo R, Li X, He F, Liu J, Yang J (2022) Orbit determination, clock estimation and performance evaluation of BDS-3 PPP-B2b service. J Geod. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-022-01642-9
Tang C et al (2018) Initial results of centralized autonomous orbit determination of the new-generation BDS satellites with inter-satellite link measurements. J Geod 92(10):1155–1169. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-018-1113-7
Tao J, Liu J, Hu Z, Zhao Q, Chen G, Ju B (2021) Initial Assessment of the BDS-3 PPP-B2b RTS compared with the CNES RTS. GPS Solut 25(4):131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-021-01168-1
Xu Y, Yang Y, Li J (2021) Performance evaluation of BDS-3 PPP-B2b precise point positioning service. GPS Solut 25(4):142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-021-01175-2
Yao Y, He Y, Yi W, Song W, Cao C, Chen M (2017) Method for evaluating real-time GNSS satellite clock offset products. GPS Solut 21(4):1417–1425. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-017-0619-4
Zajdel R, Steigenberger P, Montenbruck O (2022) On the potential contribution of BeiDou-3 to the realization of the terrestrial reference frame scale. GPS Solut. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-022-01298-0
Zhang L, Yang H, Gao Y, Yao Y, Xu C (2018) Evaluation and analysis of real-time precise orbits and clocks products from different IGS analysis centers. Adv Space Res 61(12):2942–2954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2018.03.029
Zhang W, Lou Y, Song W, Sun W, Zou X, Gong X (2022) Initial assessment of BDS-3 precise point positioning service on GEO B2b signal. Adv Space Res 69(1):690–700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2021.09.006
Zhang Y, Kubo N, Chen J, Wang A (2021) Calibration and analysis of BDS receiver-dependent code biases. J Geod 95(4):43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-021-01497-6
Zumberge JF, Heflin MB, Jefferson DC, Watkins MM, Webb FH (1997) Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 102(B3):5005–5017. https://doi.org/10.1029/96jb03860
Acknowledgements
The authors thank MGEX for offering observation data, precise satellite orbit and clock, and ILRS for providing SLR data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Author S.S and M.W designed the research; X.M provided the software; S.S and R.J analyzed the result; S.S, M.W and C.L wrote the main manuscript text; All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, S., Wang, M., Liu, C. et al. Long-term performance analysis of BDS-3 precise point positioning (PPP-B2b) service. GPS Solut 27, 69 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-023-01409-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-023-01409-5